Abstract
Cu-MOFs are exciting materials with lots of unique characteristics which will be suitable for sensing applications. To date, there have not been any published review on the suitability and efficiency of Cu-MOFs on hydrogen peroxide sensing, despite its huge potential in this regard. This systematic review assessed published articles on the subject using the Web of Science. The included studies were assessed in terms of quality using the risk of bias assessment criteria. Out of the 101 screened articles, 50 studies were eligible and included in this review. Non-enzymatic detection of hydrogen peroxide using copper-based MOFs exhibited better performance in terms of limit of detection, sensitivity, and linear response than enzyme-assisted detection. Ligand type and Cu-MOF synthetic techniques demonstrated a great effect on the structural property of the synthesized MOF, which in turn improved its catalytic property. Based on the available data in the reviewed articles. Cu-MOFs has great potential for use as commercial hydrogen peroxide sensor. The successful design of a sensitive, accurate, and stable hydrogen peroxide sensor will be a significant breakthrough for industrial, medical, and environmental applications.





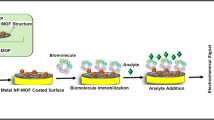
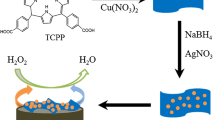
(Reproduced with permission from the publisher)


(Reproduced with permission from the publisher)

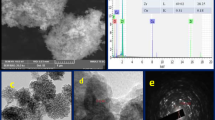
(Reproduced with permission from the publisher). b Amperometric response of CuCo–Cu@CoCH with various interferences [38] (Reproduced with permission from the publisher). c Current response of: of h-PtCu/C [27] d current response of PtCu@MOF-74/C [27] (Reproduced with permission from the publisher). e Current response of CuxO NPs@ZIF-8/GCE and f CuxO NPs/GCE to 50 μM H2O2, glucose, d-fructose, sucrose, α-lactose, l-cysteine, AA, UA and DA [41] (Reproduced with permission from the publisher).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Badoei-dalfard, N. Sohrabi, Z. Karami, G. Sargazi, Fabrication of an efficient and sensitive colorimetric biosensor based on Uricase/Th-MOF for uric acid sensing in biological samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 141, 111420 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111420
B. Halliwell, M.V. Clement, L.H. Long, Hydrogen peroxide in the human body. FEBS Lett. 486, 10–13 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(00)02197-9
M. Ghanei-Motlagh, M.A. Taher, M. Fayazi et al., Non-enzymatic amperometric sensing of hydrogen peroxide based on vanadium pentoxide nanostructures. J. Electrochem. Soc. 166, B367–B372 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0521906jes
J. Zhao, H. Yang, W. Wu et al., Flexible nickel–cobalt double hydroxides micro-nano arrays for cellular secreted hydrogen peroxide in-situ electrochemical detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 1143, 135–143 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.11.047
H. Sies, Role of metabolic H2O2 generation: redox signaling and oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 8735–8741 (2014)
F.J. Pérez, S. Rubio, An improved chemiluminescence method for hydrogen peroxide determination in plant tissues. Plant Growth Regul. 48, 89–95 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-005-5089-y
S.A. Hira, M. Nallal, K. Rajendran et al., Ultrasensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide and dopamine using copolymer-grafted metal–organic framework based electrochemical sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 1118, 26–35 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.04.043
T.P. Szatrowski, C.F. Nathan, Production of large amounts of hydrogen peroxide by human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 51, 794–798 (1991)
L. Zhang, F. Yuan, X. Zhang, L. Yang, Facile synthesis of flower like copper oxide and their application to hydrogen peroxide and nitrite sensing. Chem. Cent. J. 5, 75 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-5-75
K. Sankarasubramanian, K.J. Babu, P. Soundarrajan et al., A new catalyst Ti doped CdO thin film for non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor application. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 285, 164–172 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.161
S. Sardaremelli, H. Razmi, M. Hasanzadeh, N. Shadjou, A novel bioassay for the monitoring of hydrogen peroxide in human plasma samples based on binding of horseradish peroxidase-conjugated prostate specific antigen to poly (toluidine blue) as imprinted polymer receptor. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 145, 311–324 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.195
L. Jiang, Y. Zhao, P. Zhao et al., Electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide supported dumbbell-shaped CuCo2O4 for real-time monitoring of H2O2 released from cells. Microchem. J. 160, 105521 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105521
R. Zhang, W. Chen, Fe3C-functionalized 3D nitrogen-doped carbon structures for electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide. Sci. Bull. 60, 522–531 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-015-0740-0
H. Zhong, M. Ghorbani-Asl, K.H. Ly et al., Synergistic electroreduction of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide on bimetallic layered conjugated metal–organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 11, 1409 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15141-y
X. Li, Q.-L. Zhu, MOF-based materials for photo- and electrocatalytic CO2 reduction. EnergyChem 2, 100033 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enchem.2020.100033
W. Ling, Y. Hao, H. Wang et al., A novel Cu-metal–organic framework with two-dimensional layered topology for electrochemical detection using flexible sensors. Nanotechnology 30, 424002 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab30b6
S. Sun, J. Luo, Y. Qian et al., Metal–organic framework derived honeycomb Co9S8@C composites for high-performance supercapacitors. Adv. Energy Mater. 8, 1–9 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201801080
M.J. Page, J.E. McKenzie, P.M. Bossuyt et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (2021). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
S. Sornambikai, H. Amir, G. Bhuvaneshwari et al., Review—systematic review on electrochemical biosensing of breast cancer miRNAs to develop alternative DCIS diagnostic tool. ECS Sensors Plus 1, 021602 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1149/2754-2726/ac75c5
X. Guo, C. Lin, M. Zhang et al., 2D/3D copper-based metal–organic frameworks for electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide. Front. Chem. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2021.743637
D. He, F. Zhou, L. Sun et al., Gold/copper-based metal–organic framework/glassy carbon electrode as high efficient electrochemical sensor for determination of hydrogen peroxide. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 15, 11238–11249 (2020). https://doi.org/10.20964/2020.11.04
A.M. Golsheikh, G.-Y. Yeap, F.K. Yam, H.S. Lim, Facile fabrication and enhanced properties of copper-based metal organic framework incorporated with graphene for non-enzymatic detection of hydrogen peroxide. Synth. Met. 260, 116272 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2019.116272
H.-Y. Liu, J.-J. Wen, H.-X. Xu et al., Development of a copper-based metal organic electrode for nitrite sensing. J. AOAC Int. 104, 157–164 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoacint/qsaa089
Y. Zhou, C. Li, Y. Hao et al., Oriented growth of cross-linked metal–organic framework film on graphene surface for non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor of hydrogen peroxide in disinfectant. Talanta 188, 282–287 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.05.078
J. Li, Z.-X. Liu, Y.-X. Li et al., 2-Methylimidazole-assisted morphology modulation of a copper-based metal–organic framework transducer for enhanced electrochemical peroxidase-like activity. Electroanalysis (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202100423
J. Ma, G. Chen, W. Bai, J. Zheng, Amplified electrochemical hydrogen peroxide sensing based on Cu-porphyrin metal–organic framework nanofilm and G-quadruplex-hemin DNAzyme. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 58105–58112 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c09254
J. Yang, H. Ye, F. Zhao, B. Zeng, A novel CuxO nanoparticles@ZIF-8 composite derived from core-shell metal–organic frameworks for highly selective electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 20407–20414 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b06436
L. Wang, H. Yang, J. He et al., Cu-hemin metal–organic-frameworks/chitosan-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites with peroxidase-like bioactivity for electrochemical sensing. Electrochim. Acta 213, 691–697 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.07.162
H. Yao, W. Zhang, T. Yan et al., Electrochemical sensor for detection of hydrogen peroxide based on Cu-doped ZIF-8 material modified with chitosan and cytochrome C. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.20964/2022.06.68
D. Cheng, P. Li, X. Zhu et al., Enzyme-free electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide based on the three-dimensional flower-like Cu-based metal organic frameworks and MXene nanosheets(dagger). Chi. J. Chem. 39, 2181–2187 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.202100158
J. Ma, W. Bai, J. Zheng, Non-enzymatic electrochemical hydrogen peroxide sensing using a nanocomposite prepared from silver nanoparticles and copper (II)-porphyrin derived metal–organic framework nanosheets. Microchim. Acta (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3551-1
Y. Li, L. Hou, Z. Liu et al., A sensitive electrochemical MUC1 sensing platform based on electroactive Cu-MOFs decorated by AuPt nanoparticles. J. Electrochem. Soc. 167, 087502 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ab88b9
B. Li, D.-R. Kong, L.-H. Liu et al., Facile synthesis of copper and carbon co-doped peanut shell-like Mo2C/Mo3P electrocatalysts for ultra-sensitive amperometric detection of hydrogen peroxide. Microchem. J. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.107795
W. Ling, Y. Hao, H. Wang et al., A novel Cu–metal–organic framework with two-dimensional layered topology for electrochemical detection using flexible sensors. Nanotechnology (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab30b6
M. Hesari, R. Jia, M.V. Mirkin, Metal–organic-framework-based electrochemical nanosensor for hydrogen peroxide. ChemElectroChem (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.202200373
Y. Wang, W. Cao, L. Wang et al., Electrochemical determination of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol using a hybrid film composed of a copper-based metal organic framework and electroreduced graphene oxide. Microchim. Acta 185, 1–9 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2857-8
K. Karami, P. Bayat, H. Khosropour et al., Synthesis and characterization of a new Cu (BHB)(2)/Fe-MIL-101-NH2 composite: a novel hydrogen peroxide sensor based upon the bimetallic complex. J. Electrochem. Soc. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/abdb46
N. Han, S. Hu, L. Zhang et al., CuCo–Cu@CoCH stamen-like nanoarray prepared by co-reduction for electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151879
E. Zhou, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, X. He, Cu(II)-based MOF immobilized on multiwalled carbon nanotubes: synthesis and application for nonenzymatic detection of hydrogen peroxide with high sensitivity. Electroanalysis 26, 2526–2533 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201400341
W. Dang, Y. Sun, H. Jiao et al., AuNPs-NH2/Cu-MOF modified glassy carbon electrode as enzyme-free electrochemical sensor detecting H2O2. J. Electroanal. Chem. 856, 113592 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113592
L. Chen, T. Wang, Y. Xue et al., Rationally armoring PtCu alloy with metal–organic frameworks as highly selective nonenzyme electrochemical sensor. Adv. Mater. Interfaces (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201801168
H. Chen, T. Yang, F. Liu, W. Li, Electrodeposition of gold nanoparticles on Cu-based metal–organic framework for the electrochemical detection of nitrite. Sensors Actuators B-Chem. 286, 401–407 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.10.036
W. Meng, S. Xu, L. Dai et al., An enhanced sensitivity towards H2O2 reduction based on a novel Cu metal–organic framework and acetylene black modified electrode. Electrochim. Acta 230, 324–332 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.02.017
B. Wang, K. Kang, X. Ji et al., Multifunctional encapsulating gold nanoparticles into Cu-hemin/metal–organic frameworks for catechol electrochemical detection on graphene-based electrode. NANO (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793292020501556
S.E. Kim, A. Muthurasu, Highly oriented nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube integrated bimetallic cobalt copper organic framework for non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose and hydrogen peroxide sensor. Electroanalysis 33, 1333–1345 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202060566
B. Li, L.-H. Liu, X.-F. Zhang et al., Echinus-like Cu-Mo2C/C yolk-shell composites for ultrasensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide. Electrochim Acta (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2021.137908
M. Zhu, Y. Huang, Q. Deng et al., Highly flexible, freestanding supercapacitor electrode with enhanced performance obtained by hybridizing polypyrrole chains with MXene. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1600969 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.201600969
S. Zhou, L. Jiang, J. Zhang et al., Fabrication of Cu-hemin metal–organic-frameworks nanoflower supported on three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide for the amperometric detection of H2O2. Microchim. Acta (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04795-0
B. Li, L.-H. Liu, X.-F. Zhang et al., Novel neuron-network-like Cu-MoO2/C composite derived from bimetallic organic framework for highly efficient detection of hydrogen peroxide. Anal. Chim. Acta 1143, 73–83 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.11.038
J. Ma, J. Zheng, Voltammetric determination of hydrogen peroxide using AuCu nanoparticles attached on polypyrrole-modified 2D metal–organic framework nanosheets. Microchim. Acta (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04355-y
N.M. Umesh, K.K. Rani, R. Devasenathipathy et al., Preparation of Co-MOF derived Co(OH)2/multiwalled carbon nanotubes as an efficient bifunctional electro catalyst for hydrazine and hydrogen peroxide detections. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 93, 79–86 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2018.08.013
C. Li, T. Zhang, J. Zhao et al., Boosted Sensor performance by surface modification of bifunctional rht-type metal–organic framework with nanosized electrochemically reduced graphene oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 2984–2994 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b13788
X. Qiao, M. Arsalan, X. Ma et al., A hybrid of ultrathin metal–organic framework sheet and ultrasmall copper nanoparticles for detection of hydrogen peroxide with enhanced activity. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 413, 839–851 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-03038-0
L. Zhang, H. Liang, X. Ma et al., A vertically aligned CuO nanosheet film prepared by electrochemical conversion on Cu-based metal–organic framework for non-enzymatic glucose sensors. Microchem. J. 146, 479–485 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.01.042
L. Xu, Y. Xin, Y. Ma, P. Wang, Copper and molybdenum dioxide co-doped octahedral porous carbon framework for high sensitivity electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide. Ionics (Kiel) 28, 919–925 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04294-5
B. Li, L.-H.L.L. Liu, X.J.X.-F.X. Zhang et al., Smart nanocomposites of Cu-hemin metal–organic frameworks for electrochemical glucose biosensing. Microchim. Acta 9, 3766–3776 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202102855
M. Hassan, Y. Jiang, X. Bo, M. Zhou, Sensitive nonenzymatic detection of hydrogen peroxide at nitrogen-doped graphene supported-CoFe nanoparticles. Talanta 188, 339–348 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.06.003
D. Zhang, J. Zhang, R. Zhang et al., 3D porous metal–organic framework as an efficient electrocatalyst for nonenzymatic sensing application. Talanta 144, 1176–1181 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.07.091
H.T. Zhu, Y.Y. Ma, J. Du et al., Efficient electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide based on silver-centered preyssler-type polyoxometalate hybrids. Inorg. Chem. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c00244
Q. Wang, Y. Yang, F. Gao et al., Graphene oxide directed one-step synthesis of flowerlike graphene@HKUST-1 for enzyme-free detection of hydrogen peroxide in biological samples. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 32477–32487 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b11965
H. Cui, S. Cui, S. Zhang et al., Cu-MOF/hemin: a bionic enzyme with excellent dispersity for the determination of hydrogen peroxide released from living cells. Analyst 146, 5951–5961 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1an01323h
X. Liu, L. Ai, J. Jiang, Interconnected porous hollow CuS microspheres derived from metal–organic frameworks for efficient adsorption and electrochemical biosensing. Powder Technol. 283, 539–548 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2015.06.016
J. Li, K.-K. Lu, L.-H. Xu et al., Multi-tailoring of a modified MOF-derived CuxO electrochemical transducer for enhanced hydrogen peroxide sensing. Analyst 147, 72–79 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1an01864g
L. Wu, Z.-W. Lu, Y. Ma et al., Cu(II) metal–organic framework encapsulated in carbon paste electrode for high-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 48, e20038–e20046 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2040(20)60006-8
Z. Li, Y. Jiang, C. Liu et al., Emerging investigator series: dispersed transition metals on a nitrogen-doped carbon nanoframework for environmental hydrogen peroxide detection. Environ. Sci. 5, 1834–1843 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8en00498f
M. Naseri, L. Fotouhi, A. Ehsani, Nanostructured metal organic framework modified glassy carbon electrode as a high efficient non-enzymatic amperometric sensor for electrochemical detection of H2O2. J. Electrochem. Sci. Technol. 9, 28–36 (2018). https://doi.org/10.33961/JECST.2018.9.1.28
Z. Liang, D. Ou, D. Sun et al., Ultrasensitive biosensor for microRNA-155 using synergistically catalytic nanoprobe coupled with improved cascade strand displacement reaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111744
J. Zhu, W. Nie, Q. Wang et al., In situ growth of copper oxide-graphite carbon nitride nanocomposites with peroxidase-mimicking activity for electrocatalytic and colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide. Carbon 129, 29–37 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.11.096
D. Cheng, X. Xiao, X. Li et al., A non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing platform based on hemin@MOF composites for detecting hydrogen peroxide and DNA. J. Electrochem. Soc. 165, B885–B892 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0841816jes
D. Wu, Z. Xu, T. Zhang et al., Cu2O/CuO@rGO heterostructure derived from metal–organic-frameworks as an advanced electrocatalyst for non-enzymatic electrochemical H2O2 sensor. RSC Adv. 6, 103116–103123 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra23551d
C. Zhang, D. Zhang, Z. Ma, H. Han, Cascade catalysis-initiated radical polymerization amplified impedimetric immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of carbohydrate antigen 15–3. Biosens. Bioelectron. 137, 1–7 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.04.049
S. Dong, L. Peng, G. Suo et al., Metal complexes of 4,4′-bipyridine: characterization, electrochemical performance and application in high sensitivity detection of H2O2. J. Electrochem. Soc. 163, H775–H780 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0611609jes
C. Zhang, M. Wang, L. Liu et al., Electrochemical investigation of a new Cu-MOF and its electrocatalytic activity towards H2O2 oxidation in alkaline solution. Electrochem. Commun. 33, 131–134 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2013.04.026
W. Li, Y. Yang, C. Ma et al., A sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of CEA based on core–shell Cu2O@Cu-MOF@Au NPs nanostructure attached with HRP for triple signal amplification. J. Mater. Sci. 55, 13980–13994 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04904-z
C. Li, R. Wu, J. Zou et al., MNPs@anionic MOFs/ERGO with the size selectivity for the electrochemical determination of H2O2 released from living cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 116, 81–88 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.05.045
A.K. Singh, N. Jaiswal, R.K. Gautam, I. Tiwari, Development of g-C3N4/Cu-DTO MOF nanocomposite based electrochemical sensor towards sensitive determination of an endocrine disruptor BPSIP. J. Electroanal. Chem. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.115170
Y. Zhang, Y. Zhang, L. Li et al., One-step in situ growth of high-density POMOFs films on carbon cloth for the electrochemical detection of bromate. J. Electroanal. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.113939
C. Wei, X. Li, F. Xu et al., Metal organic framework-derived anthill-like Cu@carbon nanocomposites for nonenzymatic glucose sensor. Anal. Methods 6, 1550–1557 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ay41764f
J.J. Lu, J.J. Liang, H.Y. Lin et al., Four Anderson-type [TeMo6O24]6–-based metal–organic complexes with a new bis(pyrimidine)-bis(amide): multifunctional electrochemical and adsorption performances. CrystEngComm 24, 3921–3927 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ce00504b
S. Wang, Y. Yao, J. Zhao et al., A novel electrochemical sensor for glyphosate detection based on Ti3C2Tx/Cu-BTC nanocomposite. RSC Adv. 12, 5164–5172 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra08064d
L. Ding, F. Yan, Y. Zhang et al., Microflowers comprised of Cu/CuxO/NC nanosheets as electrocatalysts and horseradish peroxidase mimics. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3, 617–623 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b02156
W. Huang, Y. Xu, Z. Wang et al., Dual nanozyme based on ultrathin 2D conductive MOF nanosheets intergraded with gold nanoparticles for electrochemical biosensing of H2O2 in cancer cells. Talanta (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123612
K.C. Chen, H.L. Zhao, Z.X. Wang, M.B. Lan, Three-dimensional graphene-like homogeneous carbon architecture loaded with gold-platinum for the electrochemical detection of circulating tumor DNA. Mater. Today Chem. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2022.100892
L. Wang, T. Meng, H. Jia et al., Electrochemical study of hydrazine oxidation by leaf-shaped copper oxide loaded on highly ordered mesoporous carbon composite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 549, 98–104 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.04.063
Z. Chen, Z. Jing-Rui, H. Chao et al., Synthesis of porous CuO based on an etching strategy and application in electrochemical glucose sensing. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 37, 2249–2259 (2021). https://doi.org/10.11862/CJIC.2021.256
A. Tian, M. Yang, H. Ni et al., Use of symmetrical and pendant pyrazole derivatives for the construction of two polyoxometalate-based complexes as electrochemical sensors. Transit. Met. Chem. 43, 621–633 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-018-0250-4
S. Motoc, C. Cretu, O. Costisor et al., Cu(I) coordination complex precursor for randomized CuOx microarray loaded on carbon nanofiber with excellent electrocatalytic performance for electrochemical glucose detection. Sensors (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19245353
A.-X. Tian, M.-L. Yang, N. Sun et al., A series of pH-dependent POM-based compounds as photocatalysts and electrochemical sensors. Polyhedron 155, 337–350 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2018.08.065
L. Zhang, C. Ye, X. Li et al., A CuNi/C nanosheet array based on a metal–organic framework derivate as a supersensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Nano-Micro. Lett. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-017-0178-9
X. Chen, J. Dong, K. Chi et al., Electrically conductive metal–organic framework thin film-based on-chip micro-biosensor: a platform to unravel surface morphology-dependent biosensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202102855
Y. Ai, N. Gao, Q. Wang et al., Electrosynthesis of HKUST-1 on a carbon-nanotube-modified electrode and its application for detection of dihydroxybenzene isomers. J. Electroanal. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114161
H. Zhao, X. Du, H. Dong et al., Electrochemical immunosensor based on Au/Co-BDC/MoS2 and DPCN/MoS2 for the detection of cardiac troponin I. Biosens. Bioelectron. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112883
M.M. Habibi, M. Mousavi, Z. Shadman, J.B. Ghasemi, Preparation of a nonenzymatic electrochemical sensor based on a g-C3N4/MWO4 (M: Cu, Mn Co, Ni) composite for the determination of H2O2. New J. Chem. 46, 3766–3776 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1nj05711a
S. Hu, Y. Jiang, Y. Wu et al., Enzyme-free tandem reaction strategy for surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection of glucose by using the composite of Au nanoparticles and porphyrin-based metal–organic framework. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 55324–55330 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c12988
Y. Lu, D. Wu, Z. Li et al., MOFs-derived nano-CuO modified electrode as a sensor for determination of hydrazine hydrate in aqueous medium. Sensors (Switzerland) (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20010140
X. Ma, K. Tang, K. Lu et al., Programming a hollow core-shell CuS@CuSe heteromicrocubes synergizing superior multienzyme activity function as enhanced biosensing platforms. Sensors Actuators B-Chem. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2022.131592
Z. Qu, S. Li, W. Feng et al., Porous carbon substrate improving the sensing performance of copper nanoparticles toward glucose. Nanoscale Res. Lett. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-021-03579-y
D. Cheng, T. Wang, G. Zhang et al., A novel nonenzymatic electrochemical sensor based on double-shelled CuCo2O4 hollow microspheres for glucose and H2O2. J. Alloys Compd. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153014
C. Gong, Y. Shen, Y. Song, L. Wang, On–off ratiometric electrochemical biosensor for accurate detection of glucose. Electrochim. Acta 235, 488–494 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.03.144
L. Wang, C. Gong, Y. Shen et al., Conjugated schiff base polymer foam/macroporous carbon integrated electrode for electrochemical sensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 265, 227–233 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.03.041
S. Yang, M. Li, Z. Guo et al., Facile synthesis of Fe-MOF/rGO nanocomposite as an efficient electrocatalyst for nonenzymatic H2O2 sensing. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 14, 7703–7716 (2019). https://doi.org/10.20964/2019.08.42
X. Wang, J. Sun, H. Lin et al., A series of Anderson-type polyoxometalate-based metal–organic complexes: their pH-dependent electrochemical behaviour, and as electrocatalysts and photocatalysts. Dalt. Trans. 45, 12465–12478 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6dt02216b
Y. Yang, Q. Wang, W. Qiu et al., Covalent immobilization of Cu-3(btc)(2) at chitosan-electroreduced graphene oxide hybrid film and its application for simultaneous detection of dihydroxybenzene isomers. J. Phys. Chem. C 120, 9794–9803 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b01574
G. Liu, S. Liang, Q. Li et al., Metal/N-donor-induced versatile structures and properties of seven 0D → 3D complexes based on dpq/dppz and O-bridged tricarboxylate: fluorescence and electrochemical behaviors. CrystEngComm 22, 1209–1219 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ce01878f
Y. Jun, Z. Bao-Yue, T. Ai-Xiang, Four Keggin compounds modified by Tri- and tetra-nuclear metal–organic clusters: structures, selective photocatalytic and Hg2+ recognition characteristics. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 36, 1831–1844 (2020). https://doi.org/10.11862/CJIC.2020.218
S. Hu, Y. Lin, J. Teng et al., In situ deposition of MOF-74(Cu) nanosheet arrays onto carbon cloth to fabricate a sensitive and selective electrocatalytic biosensor and its application for the determination of glucose in human serum. Microchim. Acta (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04634-8
L. Li, X. Wang, N. Xu et al., Four octamolybdate complexes constructed from a quinoline-imidazole-monoamide ligand: structures and electrochemical, photocatalytic and magnetic properties. CrystEngComm 22, 8322–8329 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ce01239d
W. Pan, Z. Zheng, X. Wu et al., Facile synthesis of 2D/3D hierarchical NiCu bimetallic MOF for non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Microchem. J. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106652
X. Li, Y. Wang, K. Zhou et al., Isomeric organic ligand dominating polyoxometalate-based hybrid compounds: synthesis and as electrocatalysts and pH-sensitive probes. J. Coord. Chem. 71, 468–482 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2018.1443216
S.-J. Wang, F. Bigdeli, X.-W. Yan et al., Synthesis of a new binuclear Cu(II) complex: a precise sensor for H2O2 and a proper precursor for preparation of the CuO nanoparticles. J. Organomet. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jorganchem.2020.121507
J. Zhou, X. Li, L. Yang et al., The Cu-MOF-199/single-walled carbon nanotubes modified electrode for simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol with extended linear ranges and lower detection limits. Anal. Chim. Acta 899, 57–65 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.09.054
M.H. Mahnashi, A.M. Mahmoud, S.A. Alkahtani et al., Facile fabrication of a novel disposable pencil graphite electrode for simultaneous determination of promising immunosuppressant drugs mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus in human biological fluids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 412, 355–364 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02245-8
S. Yang, N. Xia, M. Li et al., Facile synthesis of a zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 with reduced graphene oxide hybrid material as an efficient electrocatalyst for nonenzymatic H2O2 sensing. RSC Adv. 9, 15217–15223 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra02096a
X. Wang, X. Bai, H. Lin et al., A series of new polyoxometalate-based metal–organic complexes with different rigid pyridyl-bis(triazole) ligands: assembly, structures and electrochemical properties. RSC Adv. 8, 22676–22686 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra03277g
L. Feng, J. Yang, S. Zhang et al., A capillary-based fluorimetric platform for the evaluation of glucose in blood using gold nanoclusters and glucose oxidase in the ZIF-8 matrix. Analyst 145, 5273–5279 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0an01090a
V. Mani, S. Selvaraj, T.K. Peng et al., ZnCo2O4 nanoflowers grown on Co3O4 nanowire-decorated Cu foams for in situ profiling of H2O2 in live cells and biological media. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2, 5049–5060 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.9b00969
S. Momeni, F. Sedaghati, CuO/Cu2O nanoparticles: a simple and green synthesis, characterization and their electrocatalytic performance toward formaldehyde oxidation. Microchem. J. 143, 64–71 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.07.035
H. Cunha-Silva, M. Julia Arcos-Martinez, Dual range lactate oxidase-based screen printed amperometric biosensor for analysis of lactate in diversified samples. Talanta 188, 779–787 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.06.054
P. Westbroek, E. Temmerman, Mechanism of hydrogen peroxide oxidation reaction at a glassy carbon electrode in alkaline solution. J. Electroanal. Chem. 482, 40–47 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(00)00009-7
X. Cai, E.E.L. Tanner, C. Lin et al., The mechanism of electrochemical reduction of hydrogen peroxide on silver nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 1608–1614 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP07492A
S.B. Hall, E.A. Khudaish, A.L. Hart, Electrochemical oxidation of hydrogen peroxide at platinum electrodes. Part V: inhibition by chloride. Electrochim. Acta 45, 3573–3579 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(00)00481-3
B. He, H. Liu, Electrochemical biosensor based on pyruvate oxidase immobilized AuNRs@Cu2O-NDs as electroactive probes loaded poly (diallyldimethylammonium chloride) functionalized graphene for the detection of phosphate. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 304, 127303 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127303
Y. Li, L. Hou, Z. Liu et al., A sensitive electrochemical MUC1 sensing platform based on electroactive Cu-MOFs decorated by AuPt nanoparticles. J. Electrochem. Soc. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ab88b9
J. Zeng, X. Ding, L. Chen et al., Ultra-small dispersed CuxO nanoparticles on graphene fibers for miniaturized electrochemical sensor applications. RSC Adv. 9, 28207–28212 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra03802g
Z. Li, Y. Jiang, C. Liu et al., Emerging investigator series: dispersed transition metals on a nitrogen-doped carbon nanoframework for environmental hydrogen peroxide detection. Environ. Sci. Nano 5, 1834–1843 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8en00498f
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Shaqra University, dwadami, Saudi Arabia for the provision of research facilities.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through the contributions of all authors. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript. The authors contributed equally.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alruwais, R.S., Adeosun, W.A. Electrochemical Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide Using Copper-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks: Nanoarchitectonics and Sensing Performance. J Inorg Organomet Polym 34, 14–37 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02787-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02787-6