Abstract
In this work, nanocellulose (NC), modified nanocellulose (pM-NC) and MOF composites (ZIF-8/pM-NC) were synthesized from Moringa olifera seed pod and were used for the dye adsorption. Samples were synthesized in aqueous media by one pot green methods. The prepared nanocellulose crystals were phosphorylated using orthophosphoric acid. Nano-sized cellulose ester derivatives having phosphoryl side groups were synthesized by the green phosphorylation of nanocrystalline cellulose, using water, then processed with phosphoric acid. Phosphorylated nanocellulose was added in the ZIF-8 precursor solution and sonicated to make MOF- nanocellulose composites. Structural investigation was performed using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR), which indicated the progressive removal of non-cellulosic constituents. Morphological study was conducted using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis revealed the increased crystallinity with successive treatments. Removal efficiency of Rhodamine-B dye by nanocellulose, phosphorylated nanocellulose and ZIF-8/pM-NC was studied. Influence of dosage of the adsorbent, pH, temperature and time were analyzed for the cationic dye removal. Increase in pH 6–12 was accompanied by an increase in the rhodamine dye adsorption. Taguchi L9 orthogonal array have been used for designing the experiments and the most influenced factors were selected and modeled by the RSM (BBD) method to obtain the highest percentage of rhodamine dye removal.
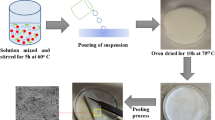
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All the data required for this article have been provided in the article itself and any information further required will be provided.
Code Availability
This article does not involve any software code.
References
M.T. Yagub, T.K. Sen, S. Afroze, H.M. Ang, Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Adv. Colloids Interface. Sci. 209, 172–184 (2014)
T.G. Ambaye, M. Vaccari, E.D. van Hullebusch, A. Amrane, S. Rtimi, Mechanisms and adsorption capacities of biochar for the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from industrial wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18, 3273–3294 (2021)
M. Harja, G. Buema, D. Bucur, Recent advances in removal of Congo Red dye by adsorption using an industrial waste. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 6087 (2022)
M. Dakiky, M. Khamis, A. Manassra, M. Mer’eb, Selective adsorption of chromium (VI) in industrial wastewater using low-cost abundantly available adsorbents. Adv. Environ. Res. 6(4), 533–540 (2002)
J. Hu, G. Chen, I.M. Lo, Selective removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewater using maghemite nanoparticle: performance and mechanisms. J. Environ. Eng. 132(7), 709–715 (2006)
Y. Liu, H. Liu, Z. Shen, Nanocellulose based filtration membrane in industrial waste water treatment: a review. Materials 14(18), 5398 (2021)
P. Phanthong, P. Reubroycharoen, S. Kongparakul, C. Samart, Z. Wang, X. Hao et al., Fabrication and evaluation of nanocellulose sponge for oil/water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 190, 184–189 (2018)
S. Mondal, Chemical modification of nanocellulose for water purification, in Nanocellulose and Its Composites for Water Treatment Application (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2021), pp. 51–61
O.M. Ama, U.O. Aigbe, W.W. Anku, O.A. Osibote, K. Pal, Degradation of methylene blue dye and bisphenol-a using expanded graphene–polypyrrole–magnetite nanocomposite. Top. Catal. 63, 1745 (2022)
S. Bhukal, A. Sharma, Rishi, Divya, S. Kumar, B. Deepak, et al., Spirulina based iron oxide nanoparticles for adsorptive removal of crystal violet dye. Top. Catal. 65(19–20), 1675–1685 (2022)
S. Bagyalakshmi, A. Sivakami, K. Pal, R. Sarankumar, C. Mahendran, Manufacturing of electrochemical sensors via carbon nanomaterials novel applications: a systematic review. J. Nanopart. Res. 24(10), 201 (2022)
N. Nath, A. Kumar, S. Chakroborty, S. Soren, A. Barik, K. Pal, F.G. de Souza Jr, Carbon nanostructure embedded novel sensor implementation for detection of aromatic volatile organic compounds: an organized review. ACS Omega 8(5), 4436–4452 (2023)
K. Pal, S. Chakroborty, P. Panda, N. Nath, S. Soren, Environmental assessment of wastewater management via hybrid nanocomposite matrix implications—an organized review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29(51), 76626–76643 (2022)
W. Xiao, Z.N. Garba, S. Sun, I. Lawan, L. Wang, M. Lin, Z. Yuan, Preparation and evaluation of an effective activated carbon from white sugar for the adsorption of rhodamine B dye. J. Clean. Prod. 253, 119989 (2020)
S. Khamparia, D. Jaspal, Investigation of adsorption of Rhodamine B onto a natural adsorbent Argemone mexicana. J. Environ. Manage. 183, 786–793 (2016)
P.P. Selvam, S. Preethi, P. Basakaralingam, N. Thinakaran, A. Sivasamy, S. Sivanesan, Removal of rhodamine B from aqueous solution by adsorption onto sodium montmorillonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 155(1–2), 39–44 (2008)
G. Vyavahare, P. Jadhav, J. Jadhav, R. Patil, C. Aware, D. Patil, R. Gurav, Strategies for crystal violet dye sorption on biochar derived from mango leaves and evaluation of residual dye toxicity. J. Clean. Prod. 207, 296–305 (2019)
C.V.T. Rigueto, I. Alessandretti, D.H. da Silva, M. Rosseto, R.A. Loss, C.A.Q. Geraldi, Agroindustrial wastes of banana pseudo-stem as adsorbent of textile dye: characterization, kinetic, and equilibrium studies. Chem. Afr. 4(4), 1069–1078 (2021)
S.A. Saad, K.M. Isa, R. Bahari, Chemically modified sugarcane bagasse as a potentially low-cost biosorbent for dye removal. Desalination 264(1–2), 123–128 (2010)
O.S. Bello, K.A. Adegoke, O.O. Akinyunni, Preparation and characterization of a novel adsorbent from Moringa oleifera leaf. Appl. Water Sci. 7(3), 1295–1305 (2017)
W.T. Wulandari, A. Rochliadi, I.M. Arcana, Nanocellulose prepared by acid hydrolysis of isolated cellulose from sugarcane bagasse, in IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 107, No. 1 (IOP Publishing, Bristol, 2016), p. 012045
F. Niu, M. Li, Q. Huang, X. Zhang, W. Pan, J. Yang, J. Li, The characteristic and dispersion stability of nanocellulose produced by mixed acid hydrolysis and ultrasonic assistance. Carbohydr. Polym. 165, 197–204 (2017)
Y. Peng, D.J. Gardner, Y. Han, A. Kiziltas, Z. Cai, M.A. Tshabalala, Influence of drying method on the material properties of nanocellulose I: thermostability and crystallinity. Cellulose 20(5), 2379–2392 (2013)
V. Kokol, M. Božič, R. Vogrinčič, A.P. Mathew, Characterisation and properties of homo- and heterogenously phosphorylated nanocellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 125, 301–313 (2015)
M. Hadid, H. Noukrati, A. Barroug, H. Sehaqui, Phosphorylated cellulose for water purification: a promising material with outstanding adsorption capacity towards methylene blue. Cellulose 28(12), 7893–7908 (2021)
A.G. Varghese, S.A. Paul, M.S. Latha, Remediation of heavy metals and dyes from wastewater using cellulose-based adsorbents. Environ. Chem. Lett. 17(2), 867–877 (2019)
A. Radhakrishnan, M. Jaabir, S. Jeyachandran, K. Thrini, A. Vijaya Anand, A. Murugesan, Nanocelluloses for removal of organic dyes from wastewater, in Handbook of Nanocelluloses: Classification, Properties, Fabrication, and Emerging Applications (Springer, Cham, 2022), pp. 1–28
A. Mautner, H.A. Maples, T. Kobkeatthawin, V. Kokol, Z. Karim, K. Li, A. Bismarck, Phosphorylated nanocellulose papers for copper adsorption from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 13(8), 1861–1872 (2016)
A.M. El-Shafei, A.M. Adel, A.A. Ibrahim, M.T. Al-Shemy, Dual functional jute fabric biocomposite with chitosan and phosphorylated nano-cellulose (antimicrobial and thermal stability). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 124, 733–741 (2019)
A. Mandal, D. Chakrabarty, Isolation of nanocellulose from waste sugarcane bagasse (SCB) and its characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 86(3), 1291–1299 (2011)
P. Phanthong, A. Abdula, Extraction of nanocellulose from raw apple stem. J. Jpn. Inst. Energy 94(8), 787–793 (2015)
E. Abraham, P.A. Elbi, B. Deepa, P. Jyotishkumar, L.A. Pothen, S.S. Narine, S. Thomas, X-ray diffraction and biodegradation analysis of green composites of natural rubber/nanocellulose. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 97(11), 2378–2387 (2012)
A. Kausar, R. Shahzad, S. Asim, S. BiBi, J. Iqbal, N. Muhammad, I.U. Din, Experimental and theoretical studies of Rhodamine B direct dye sorption onto clay-cellulose composite. J. Mol. Liq. 328, 115165 (2021)
P.M.M. da Silva, N.G. Camparotto, T.F. Neves, V.R. Mastelaro, B. Nunes, C.S.F. Picone, P. Prediger, Instantaneous adsorption and synergic effect in simultaneous removal of complex dyes through nanocellulose/graphene oxide nanocomposites: batch, fixed-bed experiments and mechanism. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 16, 100584 (2021)
A. Allwar, M.N. Fatima, B. Wiyantoko, Synthesis and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles doping on cellulose as adsorbent for removal of rhodamine B in aqueous solution. EKSAKTA J. Sci. Data Anal. 2(1), 45–54 (2021)
Funding
This work is independently funded. No outside organization has provided funding for it.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JGV contributed in the synthesis and applications, TNP (professor) contributed in the research plan and conceptualization. NA contributed in designing the experiments of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest for the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vijayan, J.G., Prabhu, T.N. & Asthana, N. Optimization of Rhodamine-B Dye Adsorption Using Moringa olifera Seed Pod Based NC, Phosphorylated NC and ZIF-8/pNC Composites. J Inorg Organomet Polym 33, 3716–3731 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02772-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02772-z