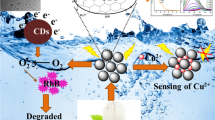
Abstract
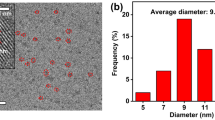
Freshwater contamination is a significant concern due to the increasing pollution by industrial activities. Dyes have a wide range of uses and are introduced at different stages of manufacture, raising the risk of unwanted human and environmental contact. Consequently, the demand for an effective method for removing dyes has become more important than before. In this context, carbon dots have been synthesized by the green synthesis method from coriander leaves (C-CDs) and used as a prospective adsorbent to remove (MB) methylene blue dye from aqueous solution. The as-synthesized C-CDs are characterized by HR-TEM, XRD, XPS, FTIR, Zeta potential, UV–visible, and photoluminescence (PL). Effects of different controlling parameters such as adsorbent dosage, pH, contact time, and initial MB dye concentration were investigated. The highest adsorption efficiency (82.6%) and maximum adsorption capacity (96.05 mg/g) of MB were obtained at optimum conditions (303 K). The adsorption isotherm data could be fitted well by Freundlich model, and the experimental data fitted to the Pseudo-Second-Order kinetic model. It is worth noting that C-CDs exhibited excellent sensitivity and high fluorescence quenching effect on Fe3+ ions.
Graphical Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.V. Chapman, T. Sullivan, The role of water quality monitoring in the sustainable use of ambient waters. One Earth 5, 132–137 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oneear.2022.01.008
E.F. Asamoah, M. Di Marco, J.E.M. Watson et al., Land-use and climate risk assessment for Earth’s remaining wilderness. Curr. Biol. 32, 4890-4899.e4 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2022.10.016
M. Adel, M.A. Ahmed, M.A. Elabiad, A.A. Mohamed, Removal of heavy metals and dyes from wastewater using graphene oxide-based nanomaterials: a critical review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 18, 100719 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2022.100719
P. Sharma, H.M.N. Iqbal, R. Chandra, Evaluation of pollution parameters and toxic elements in wastewater of pulp and paper industries in India: a case study. Chem. Environ. Eng. 5, 100163 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2021.100163
C. Wang, J. Li, L. Wang et al., Adsorption of dye from wastewater by zeolites synthesized from fly ash: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 17, 513–521 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1004-9541(08)60239-6
S.A. Ansari, F. Khan, A. Ahmad, Cauliflower leave, an agricultural waste biomass adsorbent, and its application for the removal of MB Dye from aqueous solution: equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Anal. Chem. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8252354
T.M. Eldeeb, U.O. Aigbe, K.E. Ukhurebor et al., Adsorption of methylene blue (MB) dye on ozone, purified and sonicated sawdust biochars. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03015-w
E.I. Unuabonah, G.U. Adie, L.O. Onah, O.G. Adeyemi, Multistage optimization of the adsorption of methylene blue dye onto defatted Carica papaya seeds. Chem. Eng. J. 155, 567–579 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.07.012
M.J. Uddin, R.E. Ampiaw, W. Lee, Adsorptive removal of dyes from wastewater using a metal-organic framework: a review. Chemosphere 284, 131314 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131314
S. Natarajan, H.C. Bajaj, R.J. Tayade, Recent advances based on the synergetic effect of adsorption for removal of dyes from waste water using photocatalytic process. J. Environ. Sci. 65, 201–222 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.03.011
H. Sadegh, G.A.M. Ali, Potential applications of nanomaterials in wastewater treatment, in Advanced Treatment Techniques for Industrial Wastewater (IGI Global, Pennsylvania, 2019), pp 51–61
A. Abu-Nada, A. Abdala, G. McKay, Removal of phenols and dyes from aqueous solutions using graphene and graphene composite adsorption: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 105858 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105858
O.A. Adeleke, A.A.A. Latiff, M.R. Saphira et al., Locally derived activated carbon from domestic, agricultural and industrial wastes for the treatment of palm oil mill effluent, in Nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019), pp. 35–62
M. Zhang, Q. Yao, C. Lu et al., Layered double hydroxide–carbon dot composite: high-performance adsorbent for removal of anionic organic dye. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 20225–20233 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am505765e
N. Jamaludin, S.A. Rashid, T. Tan, Natural biomass as carbon sources for the synthesis of photoluminescent carbon dots, in Synthesis, Technology and Applications of Carbon Nanomaterials (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019), pp. 109–134
K. Cheng, W. Shao, H. Li et al., Biomass derived carbon dots mediated exciton dissociation in rose flower-like carbon nitride for boosting photocatalytic performance. Ind. Crops Prod. 192, 116086 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.116086
C. Kang, Y. Huang, H. Yang et al., A review of carbon dots produced from biomass wastes. Nanomaterials 10, 2316 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112316
H. SalimiShahraki, Ahmad A. Qurtulen, Synthesis, characterization of carbon dots from onion peel and their application as absorbent and anticancer activity. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 150, 110514 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.110514
H.S. Shahraki, R. Bushra, N. Shakeel et al., Papaya peel waste carbon dots/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite: from photocatalytic decomposition of methylene blue to antimicrobial activity. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobab.2023.01.009
J. Hu, W. Jia, X. Yu et al., Carbon dots improve the nutritional quality of coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) by promoting photosynthesis and nutrient uptake. Environ. Sci. Nano 9, 1651–1661 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN01079D
W. Meng, X. Bai, B. Wang et al., Biomass-derived carbon dots and their applications. Energy Environ. Mater. 2, 172–192 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/eem2.12038
N. Tejwan, S.K. Saha, J. Das, Multifaceted applications of green carbon dots synthesized from renewable sources. Adv. Colloid Interfaces Sci. 275, 102046–48 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2019.102046
C. Sarkar, A.R. Chowdhuri, A. Kumar et al., One pot synthesis of carbon dots decorated carboxymethyl cellulose- hydroxyapatite nanocomposite for drug delivery, tissue engineering and Fe3+ ion sensing. Carbohydr. Polym. 181, 710–718 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.11.091
Y. Chen, X. Sun, W. Pan et al., Fe3+-sensitive carbon dots for detection of Fe3+ in aqueous solution and intracellular imaging of Fe3+ inside fungal cells. Front. Chem. 7, 1–9 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2019.00911
W. Liu, H. Diao, H. Chang et al., Green synthesis of carbon dots from rose-heart radish and application for Fe3+ detection and cell imaging. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 241, 190–198 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.10.068
M. Zulfajri, H.N. Abdelhamid, S. Sudewi et al., Plant part-derived carbon dots for biosensing. Biosensors 10, 68 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10060068
X. Sun, Y. Lei, Fluorescent carbon dots and their sensing applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 89, 163–180 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.02.001
J. Mondal, S.K. Srivastava, Green synthesis of carbon dot weak gel from pear juice: optical properties and sensing application. ChemistrySelect 3, 8444–8457 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201801383
A. Sachdev, P. Gopinath, Green synthesis of multifunctional carbon dots from coriander leaves and their potential application as antioxidants, sensors and bioimaging agents. Analyst 140, 4260–4269 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an00454c
U.A. Rani, L.Y. Ng, C.Y. Ng, E. Mahmoudi, A review of carbon quantum dots and their applications in wastewater treatment. Adv. Colloid Interfaces Sci. 278, 102124–26 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2020.102124
P.O. Bedolla, G. Feldbauer, M. Wolloch et al., Effects of van der Waals interactions in the adsorption of isooctane and ethanol on Fe(100) surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 17608–17615 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp503829c
A. Soltani, M. Faramarzi, S.A. Mousavi Parsa, A review on adsorbent parameters for removal of dye products from industrial wastewater. Water Qual. Res. J. 56, 181–193 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2166/wqrj.2021.023
S. Banerjee, M.C. Chattopadhyaya, Adsorption characteristics for the removal of a toxic dye, tartrazine from aqueous solutions by a low cost agricultural by-product. Arab. J. Chem. 10, S1629–S1638 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.06.005
T. Teymoorian, N. Hashemi, M.H. Mousazadeh, Z. Entezarian, N, S doped carbon quantum dots inside mesoporous silica for effective adsorption of methylene blue dye. SN Appl. Sci. 3, 1–14 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04287-z
M.A. Rahman, S.M.R. Amin, A.M.S. Alam, Removal of methylene blue from waste water using activated carbon prepared from rice husk. Dhaka Univ. J. Sci. 60, 185–189 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3329/dujs.v60i2.11491
N. Hasani, T. Selimi, A. Mele et al., Theoretical, equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamic investigations of methylene blue adsorption onto lignite coal. Molecules 27, 1856 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061856
J. Ederer, P. Ecorchard, M.Š Slušná et al., A study of methylene blue dye interaction and adsorption by monolayer graphene oxide. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 1–16 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7385541
F. Mohamed, M. Shaban, S.K. Zaki et al., Activated carbon derived from sugarcane and modified with natural zeolite for efficient adsorption of methylene blue dye: experimentally and theoretically approaches. Sci. Rep. 12, 18031 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-22421-8
M.S. Momina, I. Suzylawati, Study of the adsorption/desorption of MB dye solution using bentonite adsorbent coating. J. Water Process. Eng. 34, 101155–57 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101155
K. Bhattacharyya, A. Sharma, Kinetics and thermodynamics of methylene blue adsorption on neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf powder. Dye Pigment 65, 51–59 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2004.06.016
B.H. Hameed, D.K. Mahmoud, A.L. Ahmad, Equilibrium modeling and kinetic studies on the adsorption of basic dye by a low-cost adsorbent: coconut (Cocos nucifera) bunch waste. J. Hazard. Mater. 158, 65–72 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.034
V. Vadivelan, K.V. Kumar, Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. J. Colloid Interfaces Sci. 286, 90–100 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.01.007
I. Sierra, U. Iriarte-Velasco, E.A. Cepeda et al., Preparation of carbon-based adsorbents from the pyrolysis of sewage sludge with CO2. Investigation of the acid washing procedure. Desalin. Water Treat. 57, 16053–16065 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1075428
M. Zulfajri, Y.-T. Kao, G.G. Huang, Retrieve of residual waste of carbon dots derived from straw mushroom as a hydrochar for the removal of organic dyes from aqueous solutions. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 22, 100469 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2021.100469
H. Kumar, K. Bhardwaj, R. Sharma et al., Fruit and vegetable peels: utilization of high value horticultural waste in novel industrial applications. Molecules 25, 1–21 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25122812
Y. Zhou, Y. Liu, Y. Li et al., Multicolor carbon nanodots from food waste and their heavy metal ion detection application. RSC Adv. 8, 23657–23662 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra03272f
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge with thanks to the Department of Chemistry, AMU, Aligarh, for the financial support to carry out this work.
Funding
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HSS: Conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, investigation. Qurtulen: Data curation, reviewing. AA: Supervision, reviewing, and editing. SG: Editing. UM: Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shahraki, H.S., Ahmad, A., Qurtulen et al. Carbon Dots from Natural‐Product: Applications as Adsorbent and Sensing of Fe3+ Ions. J Inorg Organomet Polym 33, 3164–3177 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02707-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02707-8