Abstract
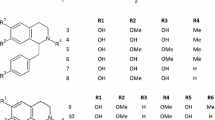
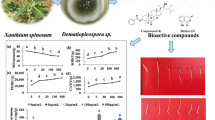
Plant latex is sequestered in laticiferous structures and exuded immediately from damaged plant tissues. The primary function of plant latex is related to defense responses to their natural enemies. Euphorbia jolkinii Boiss. is a perennial herbaceous plant that greatly threaten the biodiversity and ecological integrity of northwest Yunnan, China. Nine triterpenes (1–9), four non-protein amino acids (10–13) and three glycosides (14–16) including a new isopentenyl disaccharide (14), were isolated and identified from the latex of E. jolkinii. Their structures were established on the basis of comprehensive spectroscopic data analyses. Bioassay revealed that meta-tyrosine (10) showed significant phytotoxic activity, inhibiting root and shoot growth of Zea mays, Medicago sativa, Brassica campestris, and Arabidopsis thaliana, with EC50 values ranging from 4.41 ± 1.08 to 37.60 ± 3.59 µg/mL. Interestingly, meta-tyrosine inhibited the root growth of Oryza sativa, but promoted their shoot growth at the concentrations below 20 µg/mL. meta-Tyrosine was found to be the predominant constituent in polar part of the latex extract from both stems and roots of E. jolkinii, but undetectable in the rhizosphere soil. In addition, some triterpenes showed antibacterial and nematicidal effects. The results suggested that meta-tyrosine and triterpenes in the latex might function as defensive substances for E. jolkinii against other organisms.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal AA, Hastings AP (2019) Plant defense by latex: ecological genetics of inducibility in the milkweeds and a general review of mechanisms, evolution, and implications for agriculture. J Chem Ecol 45:1004–1018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-019-01119-8
Ahmad VU, Bano S, Mohammad FV (1985) Nepehinol-a new triterpene from Nepeta hindostana. Planta Med 51:521–523. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-969582
Akihisa T, Kimura Y, Kokke W, Takase SI, Yasukawa K, Tamura T (1996) Tirucalla-5,24-dien-3β-ol (13α,14β,17α,20S)-lanosta-5,24-dien-3β-ol and three other D5-unsaturated tirucallanes from the roots of Bryonia dioica Jacq: the first naturally occurring C-10 methylated tetracyclic triterpene alcohols with a D5-monounsaturated skeleton. J Chem Soc Perk T 1:2379–2384. https://doi.org/10.1039/p19960002379
Anyanga MO et al (2017) Segregation of hydroxycinnamic acid esters mediating sweetpotato weevil resistance in storage roots of sweetpotato. Front Plant Sci 8:1011. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01011
Bertin C, Weston LA, Huang T, Jander G, Owens T, Meinwald J, Schroeder FC (2007) Grass roots chemistry: meta-tyrosine, an herbicidal nonprotein amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:16964–16969. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0707198104
Bianchini JP, Gaydou EM, Rafaralahitsimba G, Waegell B, Zahra JP (1988) Dammarane derivatives in the fruit lipids of Olea madagascariensis. Phytochemistry 27:2301–2304. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(88)80147-X
Chen J, Zheng G, Zhang Y, Aisa HA, Hao XJ (2016) Phytotoxic terpenoids from Ligularia cymbulifera roots. Front Plant Sci 7:2033. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.02033
Chen X, Dang T-TT, Facchini PJ (2015) Noscapine comes of age. Phytochemistry 111:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.09.008
Cheng F, Cheng Z (2015) Research progress on the use of plant allelopathy in agriculture and the physiological and ecological mechanisms of allelopathy. Front Plant Sci 6:1020. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01020
Chow JK, Akhtar Y, Isman MB (2005) The effects of larval experience with a complex plant latex on subsequent feeding and oviposition by the cabbage looper moth: Trichoplusia ni (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Chemoecology 15:129–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00049-005-0304-x
Czarnota MA, Paul RN, Weston LA, Duke SO (2003) Anatomy of sorgoleone-secreting root hairs of Sorghum species. Int J Plant Sci 164:861–866. https://doi.org/10.1086/378661
Dussourd DE, Eisner T (1987) Vein-cutting behavior: insect counterploy to the latex defense of plants. Science 237:898–901. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3616620
Dussourd DE, Hoyle AM (2000) Poisoned plusiines: toxicity of milkweed latex and cardenolides to some generalist caterpillars. Chemoecology 10:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/pl00001810
Gunawardana M et al (2015) Euphorbia plant latex is inhabited by diverse microbial communities. Am J Bot 102:1966–1977. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1500223
Hagel JM, Yeung EC, Facchini PJ (2008) Got milk? The secret life of laticifers. Trends Plant Sci 13:631–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2008.09.005
He F et al (2008) Eight new diterpenoids from the roots of Euphorbia nematoopha. Helv Chim Acta 91:2139–2147. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.200890230
Hua J, Liu Y, Xiao CJ, Jing SX, Luo SH, Li SH (2017) Chemical profile and defensive function of the latex of Euphorbia peplus. Phytochemistry 136:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.12.021
Hua J, Liu YC, Jing SX, Luo SH, Li SH (2015) Macrocyclic diterpenoids from the latex of Euphorbia helioscopia. Nat Prod Commun 10:2037–2039
Huang CS et al (2014) Antifeedant and antiviral diterpenoids from the fresh roots of Euphorbia jolkinii. Nat Prod Bioprospect 4:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13659-014-0009-3
Isono F, Sakaida Y, Takahashi S, Kinoshita T, Nakamura T, Inukai M (1993) Mureidomycins E and F, minor components of mureidomycins. J Antibiot 46:1203–1207. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.46.1203
Jadranin M et al (2013) Jatrophane diterpenoids from the latex of Euphorbia dendroides and their anti-P-glycoprotein activity in human multi-drug resistant cancer cell lines. Phytochemistry 86:208–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2012.09.003
Joubert E, de Beer D, Malherbe CJ, Muller N, Bonnet SL, van der Westhuizen JH, Ferreira D (2013) Occurrence and sensory perception of Z-2-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-3-phenylpropenoic acid in rooibos (Aspalathus linearis). Food Chem 136:1078–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.014
Kamara BI, Brandt EV, Ferreira D, Joubert E (2003) Polyphenols from honeybush tea (Cyclopia intermedia). J Agric Food Chem 51:3874–3879. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0210730
Khan F, Kumari M, Cameotra SS (2013) Biodegradation of the allelopathic chemical m-tyrosine by Bacillus aquimaris SSC5 involves the homogentisate central pathway. PLoS ONE 8:e75928. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075928
Knight SA (1974) Carbon-13 NMR spectra of some tetra- and pentacyclic triterpenoids. Magn Reson Chem 6:603–611. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrc.1270061112
Konno K (2011) Plant latex and other exudates as plant defense systems: roles of various defense chemicals and proteins contained therein. Phytochemistry 72:1510–1530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.02.016
Konno K et al (2006) Mulberry latex rich in antidiabetic sugar-mimic alkaloids forces dieting on caterpillars. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:1337–1341. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506944103
Kushiro T, Shibuya M, Masuda K, Ebizuka Y (2000) Mutational studies on triterpene syntheses: engineering lupeol synthase into beta-amyrin synthase. J Am Chem Soc 122:6816–6824. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0010709
Lee SH, Tanaka T, Nonaka G, Nishioka I (2004) Structure and biogenesis of jolkinin, a highly oxygenated ellagitannin from Euphorbia jolkinii. J Nat Prod 67:1018–1022. https://doi.org/10.1021/np0400297
Lee SY, Choi SU, Lee JH, Lee DU, Lee KR (2010) A new phenylpropane glycoside from the rhizome of Sparganium stoloniferum. Arch Pharm Res 33:515–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0404-1
Liu Q et al (2014) Allelochemicals in the rhizosphere soil of Euphorbia himalayensis J Agric Food Chem 62:8555–8561. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf502020v
Liu Y, Feng Z, Deng F (2014) Vegetation indices of Euphorbia jolkinii as an indicator plant of grassland degradation. Acta Agrestia Sin 22:455–460
Macías FA, Marín D, Oliverosbastidas A, Molinillo JM (2009) Rediscovering the bioactivity and ecological role of 1,4-benzoxazinones. Nat Prod Rep 26:478–489. https://doi.org/10.1039/b700682a
Macías FA, Oliveros-Bastidas A, Marín D, Carrera C, Chinchilla N, Molinillo JMG (2008) Plant biocommunicators: their phytotoxicity, degradation studies and potential use as herbicide models. Phytochem Rev 7:179–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-007-9062-4
Matayatsuk C, Poljak A, Bustamante S, Smythe GA, Kalpravidh RW, Sirankapracha P, Fucharoen S, Wilairat P (2007) Quantitative determination of ortho- and meta-tyrosine as biomarkers of protein oxidative damage in beta-thalassemia. Redox Rep 12:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1179/135100007x200272
Mithoefer A, Boland W (2012) Plant defense against herbivores: chemical aspects. Annu Rev Plant Biol 63:431–450. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103854
Mothes K, Schutte HR, Muller P, Vonarden M, Tummler R (1964) m-Tyrosin, eine neue Aminosäure aus dem Milchsaft von Euphorbia Myrsinites L. Z Naturforsch B 19b:1161–1162. https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-1964-1219
Müller P, Schütte HR (1968) 1-Methyl-6-hydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid in the milky juice of Euphorbia myrsinites L. Z Naturforsch B 23:491–493
Ono M, Yoshida A, Ito Y, Nohara T (1999) Phenethyl alcohol glycosides and isopentenol glycoside from fruit of Bupleurum falcatum. Phytochemistry 51:819–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(99)00073-4
Ornstein PL, Arnold MB, Augenstein NK, Paschal JW (1991) Syntheses of 6-oxodecahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylates. Useful intermediates for the preparation of conformationally defined excitatory amino acid antagonists. J Org Chem 56:4388–4392. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo00014a012
Reynolds WF, McLean S, Poplawski J, Enriquez RG, Escobar LI, Leon I (1986) Total assignment of 13C and 1H spectra of three isomeric triterpenol derivatives by 2D NMR: an investigation of the potential utility of 1H chemical shifts in structural investigations of complex natural products. Tetrahedron 42:3419–3428. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-4020(01)87309-9
Sajid M, Azim MK (2012) Characterization of the nematicidal activity of natural honey. J Agric Food Chem 60:7428–7434. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf301653n
Sessa RA, Bennett MH, Lewis MJ, Mansfield JW, Beale MH (2000) Metabolite profiling of sesquiterpene lactones from Lactuca species. J Biol Chem 275:26877–26884. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M000244200
Shi QW, Su XH, Kiyota H (2008) Chemical and pharmacological research of the plants in genus Euphorbia. Chem Rev 108:4295–4327. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr078350s
Tanveer A, Khaliq A, Javaid MM, Chaudhry MN, Awan I (2013) Implications of weeds of genus Euphorbia for crop production: a review. Planta Daninha 31:723–731. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-83582013000300024
Teresa JD, Urones JG, Marcos IS, Basabe P, Cuadrado MJS, Moro RF (1987) Triterpenes from Euphorbia broteri. Phytochemistry 26:1767–1776. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(00)82286-4
Vasas A, Hohmann J (2014) Euphorbia diterpenes: isolation, structure, biological activity, and synthesis (2008–2012). Chem Rev 114:8579–8612. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400541j
Vasas A, Rédei D, Csupor D, Molnár J, Hohmann J (2012) Diterpenes from european Euphorbia species serving as prototypes for natural-product-based drug discovery. Eur J Org Chem 2012:5115–5130. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201200733
Wang SY et al (2016) New triterpenoids from the latex of Euphorbia resinifera Berg. Fitoterapia 108:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2015.11.009
Wang Y, Luo SH, Hua J, Liu Y, Jing SX, Li XN, Li SH (2015) Capitate glandular trichomes of Paragutzlaffia henryi harbor new phytotoxic labdane diterpenoids. J Agric Food Chem 63:10004–10012. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b04113
Wu DG, Sorg B, Adolf W, Seip EH, Hecker E (1992) Oligo- and macrocyclic diterpenes in Thymelaeaceae and Euphorbiaceae occurring and utilized in Yunnan (southwest China). 2. Ingenane type diterpene esters from Euphorbia nematocypha Hand.-Mazz. Phytother Res 6:237–240. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.2650060503
Yildirim A, Mavi A, Oktay M, Kara AA, Algur OF, Bilaloglu V (2000) Comparison of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of tilia (Tilia argentea desf ex DC), sage (Salvia triloba L.), and black tea (Camellia sinensis) extracts. J Agric Food Chem 48:5030–5034. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf000590k
Zer H, Mizrahi H, Malchenko N, Avin-Wittenberg T, Klipcan L, Ostersetzer-Biran O (2020) The phytotoxicity of meta-tyrosine is associated with altered phenylalanine metabolism and misincorporation of this non-proteinogenic phe-analog to the plant’s proteome. Front Plant Sci 11:140. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00140
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of the analytical center of Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, for measurements of the NMR, MS, IR, UV, and CD spectral data.
Funding
This research was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31900299 and 32000273).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors made contributions to the experiment and manuscript. SLi, SLuo and YL conceived the research and designed the experiments. SLuo, CH, JH, SJ, LT and TT performed the experiments. SLuo wrote the main manuscript and prepared figures and tables. SLi and YL revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
NMR data of compounds 1–13, 15, and 16. 1D and 2D NMR spectra of compound 14. CD spectra of compounds 10–13. The effects of shoots growth of Oryza sativa on the treatment with meta-tyrosine (10). (DOCX 20.0 MB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, S., Huang, C., Hua, J. et al. Defensive Specialized Metabolites from the Latex of Euphorbia jolkinii. J Chem Ecol 49, 287–298 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-023-01413-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-023-01413-6