Abstract
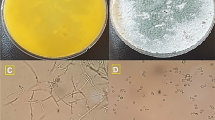
Green nanotechnology provides tools for the transformation of biological systems toward safe and cost-effective approaches of nanomaterial synthesis for biomedical applications. The aim of the current investigation was to mycosynthesis of functional platinum nanoparticles (PtNPs) by Penicillium pinophilum cell-free filtrate using hydrogen hexachloroplatinate (IV) hexahydrate (H2PtCl6) as substrate. The UV–Visible spectroscopy, TEM, XRD, DLS, FTIR, TGA–DSC and GC–MS were used to characterize the mycosynthesized PtNPs. UV–visible spectrum of mycosynthesized PtNPs showed maximum absorption peak at 263 nm. The band gap energy of the PtNPs was estimated as 3.78 eV. TEM showed the PtNPs in different shapes with the size ranged from 2 to 25 nm. DLS demonstrated the size range of 2–30 nm for synthesized PtNPs. A zeta potential of − 43.0 ± 1.0 mV with a single peak was recorded for PtNPs. The XRD peaks 40.3, 46.8 and 68.2 with the plane of platinum crystals (111), (200), and (220) were identified indicating that the PtNPs were face-centered, cubic, and crystalline in nature. Mycosynthesized PtNPs were analyzed by simultaneous TGA–DSC showed thermal stability for PtNPs. The FTIR results showed the presence of some bio-molecules in fungal cell-free filtrate as possible bio-reducing and capping agent of PtNPs. GC–MS analysis of fungal cell-free filtrate showed 10 peaks representative of related compounds. The mycosynthesized PtNPs displayed antimicrobial activity (8.1 ± 0.8 to 24.3 ± 0.8 mm) against various important fungal and bacteria pathogens. They were toxic for cancer cell-line HepG-2 at IC50 value of 184.07 μg/ml. Microscopy images showed morphological changes and reduction of cancer cells populations in PtNPs-treated cell-line. Altogether, our results demonstrated for the first time the green synthesis of PtNPs using Penicillium pinophilum. Synthesized PtNPs were not only active against fungal and bacteria pathogens, but also they showed strong cytotoxic effects against human cancer cell-line HepG-2. Thus, they may be considered as promising chemotherapeutics to combat malignancies and overcome life-threatening infections arisen from multidrug resistant fungi and bacteria in practice.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
R. K. Kubayashi and G. Nakazato (2020). Front. Microbiol. 11, 1421. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01421.
M. Gholami-Shabani, F. Sotoodehnejadnematalahi, M. Shams-Ghahfarokhi, A. Eslamifar, and M. Razzaghi-Abyaneh (2021). J. Nanomat. 2021, Article ID 7532660. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/7532660.
P. Khandel and S. K. Shahi (2018). J. Nanostruct. Chem. 8, 369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-018-0285-2.
M. Adnan (2021). Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 51, 280. https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2020.1784231.
M. Rai, S. Bonde, P. Golinska, J. Trzcińska-Wencel, A. Gade, K. Abd-Elsalam, S. Shende, S. Gaikwad, and A. Ingle (2021). J. Fungi 7, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7020139.
J. Huang, L. Lin, D. Sun, H. Chen, D. Yang, and Q. Li (2015). Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 6330. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CS00133A.
N. Naimi-Shamel, P. Pourali, and S. Dolatabadi (2019). J. Mycol. Med. 29, 7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycmed.2019.01.005.
M. Gholami-Shabani, A. Akbarzadeh, D. Norouzian, A. Amini, Z. Gholami-Shabani, A. Imani, M. Chiani, G. Riazi, M. Shams-Ghahfarokhi, and M. Razzaghi-Abyaneh (2014). Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 172, 4084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0809-2.
M. Jeyaraj, S. Gurunathan, M. Qasim, M. H. Kang, and J. H. Kim (2019). Nanomaterials 9, 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121719.
V. R. Yenumula and P. K. Nagadesi (2018). Biogenic synthesis of engineered platinum nanomaterial: a review. Int. J. Sci. Dev. Res. 3, 216.
E. Castro-Longoria, S. D. Moreno-Velasquez, A. R. Vilchis-Nestor, E. Arenas-Berumen, and M. Avalos-Borja (2012). J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 22, 1000. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1110.10085.
K. Gupta and T. S. Chundawat (2019). Mater. Res. Exp. 6, 1050d6. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab4219.
C. X. Li, S. Zhao, T. Zhang, L. Xian, L. S. Liao, J. L. Liu, and J. X. Feng (2017). Sci. Rep. 7, 490. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00567-0.
R. Dobrucka (2019). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 26, 31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.11.012.
M. Gholami-Shabani, Z. Gholami-Shabani, M. Shams-Ghahfarokhi, A. Akbarzadeh, G. Riazi, and M. Razzaghi-Abyaneh (2016). Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 12, 199.
P. Soltani-Horand, H. Vaghari, J. Soltani-Horand, M. Adibpour, and H. Jafarizadeh-Malmiri (2020). Int. J. Nanosci. 19, 1950009. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219581X19500091.
H. G. Nada, H. E. Ali, R. R. El-Behery, S. M. Shanab, and E. H. Elshatoury (2021). J. Clust. Sci. 17, 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02122-4.
R. Surega, B. Anita, S. Ramakrishnan, K. Gunasekaran, and S. Nakkeran (2020). Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 9, 1939. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2020.902.221.
S. Mourdikoudis, R. M. Pallares, and N. T. Thanh (2018). Nanoscale 10, 12871. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR02278J.
N. Farkas and J. A. Kramar (2012). J. Nanopart. Res. 2, 120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05220-6.
M. M. Mollick, B. Bhowmick, D. Mondal, D. Maity, D. Rana, S. K. Dash, and D. Chattopadhyay (2014). RSC Adv. 4, 37838. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA07285E.
S. Sampaio and J. C. Viana (2018). Adv. Nat. Sci.: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9, 045002. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6254/aae987.
F. Anum, K. Jabeen, S. Javad, S. Iqbal, A. Tahir, Z. Javed, N. Cruz-Martins, S. A. Ayatollahi, J. Sharifi-Rad, M. M. Alshehri, and W. C. Cho (2021). J. Nanomater. 2021, 2992335. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2992335.
A. W. Bayer, W. M. Kirby, J. C. Sherris, and M. Turck (1966). Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 45, 493.
A. Nanda and S. Majeed (2014). Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 6, 609.
J. L. Rios, M. C. Recio, and A. Villar (1988). J. Ethnopharmacol. 23, 127. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-8741(88)90001-3.
A. A. Kajani, A. K. Bordbar, S. H. Esfahani, and A. Razmjou (2016). RSC Adv. 6, 63973. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA09050H.
H. Mohammadi, A. Abedi, A. Akbarzadeh, M. J. Mokhtari, H. E. Shahmabadi, M. R. Mehrabi, and M. Chiani (2013). Int. Nano Lett. 3, 28. https://doi.org/10.1186/2228-5326-3-28.
G. Prasannaraj and P. Venkatachalam (2017). Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8, 025001. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6254/aa6d2c.
S. N. Syed Abdul Rahman, N. Abdul Wahab, and S. N. Abd Malek (2013). Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 257108. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/257108.
K. Liu, P. C. Liu, R. Liu, and X. Wu (2015). Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 21, 15. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSMBR.893327.
S. Burattini and E. Falcieri (2013). Methods Mol. Biol. 1004, 77. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-383-1_7.
C. Sakthivel, L. Keerthana, and L. Prabha (2019). Johnson Matthey Technol. Rev. 63, 122. https://doi.org/10.1595/205651319X15498900266305.
L. Ma, W. Su, J. X. Liu, X. X. Zeng, Z. Huang, W. Li, Z. C. Liu, and J. X. Tang (2017). Mater. Sci. Eng. 77, 963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.294.
K. S. Siddiqi and A. Husen (2016). Nanoscale Res. Lett. 11, 98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1311-2.
N. S. Al-Radadi (2018). Arab. J. Chem. 12, 330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2018.05.008.
G. V. Lowry, R. J. Hill, S. Harper, A. F. Rawle, C. O. Hendren, F. Klaessig, U. Nobbmann, P. Sayre, and J. Rumble (2016). Environ. Sci. Nano 3, 953. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EN00136J.
P. Suryavanshi, R. Pandit, A. Gade, M. Derita, S. Zachino, and M. Rai (2017). Lebenson Wiss Technol. 81, 188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.03.038.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding
Research reported in this publication was supported by Elite Researcher Grant Committee under award numbers 958634 and 963646 from the National Institute for Medical Research Development (NIMAD), Tehran, Iran to M.R-A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.G-S and M.R-A analyzed and interpreted the data and wrote the original manuscript. M.G-S, M.S-G, F.S, A.E and M.R-A conducted the experiments, performed the data curation, and reviewed the manuscript. M.R-A and F.S supervised the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gholami-Shabani, M., Sotoodehnejadnematalahi, F., Shams-Ghahfarokhi, M. et al. Platinum Nanoparticles as Potent Anticancer and Antimicrobial Agent: Green Synthesis, Physical Characterization, and In-Vitro Biological Activity. J Clust Sci 34, 501–516 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-022-02225-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-022-02225-6