Abstract
In recent years, small-scale studies have suggested that we may be able to substantially strengthen children's general cognitive abilities and intelligence quotient (IQ) scores using a relational operant skills training program (SMART). Only one of these studies to date has included an active Control Condition, and that study reported the smallest mean IQ rise. The present study is a larger stratified active-controlled trial to independently test the utility of SMART training for raising Non-verbal IQ (NVIQ) and processing speed. We measured personality traits, NVIQs, and processing speeds of a cohort of school pupils (aged 12–15). Participants were allocated to either a SMART intervention group or a Scratch computer coding control group, for a period of 3 months. We reassessed pupils’ NVIQs and processing speeds after the 3-month intervention. We observed a significant mean increase in the SMART training group’s (final nexp = 43) NVIQs of 5.98 points, while there was a nonsignificant increase of 1.85 points in the Scratch active-control group (final ncont = 27). We also observed an increase in processing speed across both conditions (final nexp = 70; ncont = 55) over Time. Our results suggest that relational skills training may be useful for improving performance on matrices tasks, and perhaps in future, accelerating children’s progression toward developmental milestones.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Scores on tests of disparate aspects of cognitive performance positively co-vary. Based on that common variance, it is also possible to extract a common latent factor from these tests (known as g; cf., Haier 2016). Once corrected for age, this common factor is typically known as an intelligence quotient (IQ), and is used to rank individuals intellectually, relative to their peers. Not only is IQ a reflection of the common variance across tests, but IQ scores in turn predict scores across tests (Conway and Kovacs 2015; Van Der Maas et al. 2006). “Tests”, in this case, includes not only paper-and-pencil tests, but any enterprise in which success depends upon the capacity for relatively complex symbolic manipulation, including education, occupation, health behaviors, and social success (cf., Strenze 2007, for a full review). Furthermore, IQ appears to be the most powerful predictor of success in cognitively complex domains. For example, O’Boyle and colleagues’ (2011) meta-analysis found that IQ is a much better predictor of job performance than “emotional intelligence” and The Big Five personality traits. IQ also predicts educational attainment more so than personality (Bergold and Steinmayr 2018), with Conscientiousness positively associated and Neuroticism negatively associated with attainment. The predictive validity of IQ is arguably among the best-established findings in psychology (Gottfredson and Deary 2004; Haier 2016; Ritchie 2015), along with behavioral selection by consequences (Skinner 1957).
The acid test of whether one has enhanced g, or IQ, is that any improvement will manifest across multiple tests. Psychologists have not managed to develop cognitive training exercises such that reliably produce cross-domain effects. That is, training participants in one, or even several cognitive skills, will not generally result in improvements in tests of other cognitive skills. For example, training working memory will typically not increase performance on tests of general knowledge, and subsequently, real-world outcomes predicted by performance on tests of general knowledge (Haier 2016; Peijnenborgh et al. 2016; Ritchie 2015; Sala and Gobet 2017b). Indeed, there is mounting evidence that a large portion of the variation in intellectual abilities is attributable to variation in a relatively small number of genes (Davies et al. 2018; Hill et al. 2018a, b; Plomin and Von Stumm 2018; Savage et al. 2018; Smith-Woolley et al. 2018; Zabaneh et al. 2017). However, it is not yet clear how much of cognitive ability is malleable, how much of it is fixed, and how much is attributable to random environmental variation. Some variance in cognitive ability may yet be manipulable from outside of the organism.
Cognitive training is a resource-intensive enterprise (Mohammed et al. 2017), so we must pay close attention to strategies that have not yielded positive results in the past. For example, perhaps the most recent and largely unsuccessful attempt to raise general cognitive ability (albeit the most successful to date) to gain mainstream traction was a working memory training known as N-Back training. Despite several reported successful N-Back training studies (Buschkuehl et al. 2014; Jaeggi et al. 2010, 2011; Ramani et al. 2017; Stepankova et al. 2014), other researchers have failed to independently replicate these training effects (Chooi and Thompson 2012; Clark et al. 2017; Colom and Román 2018; Colom et al. 2013; Melby-Lervåg and Hulme 2013, 2016; Melby-Lervåg et al. 2016; Park and Brannon 2016; Rabipour and Raz 2012; Redick et al. 2013; Salminen et al. 2012; Schwaighofer et al. 2015; Shipstead et al. 2012; Soveri et al. 2017; Stephenson and Halpern 2013; Strobach and Huestegge 2017; Thompson et al. 2013). A meta-analysis conducted by the research group by whom N-Back training was originally advocated reported a 2–3-point mean increase in IQ across all available studies at that time (Au et al. 2015), and many believe there is no effect of working memory training at all (cf., Peijnenborgh et al. 2016; Sala and Gobet 2017a, b). Our interpretation of the available data is that there is an overwhelming weight of evidence on the side of the null hypothesis that working memory training is not an effective way to improve general cognitive ability. The same can be said of music (Sala and Gobet 2017a), chess (Sala et al. 2017), video game training (Simons et al. 2016), and compensatory education (McKey 1985), all of which are arguably theoretically quite imprecise approaches. On the other hand, converging evidence from education (Alexander 2019), cognitive science (Goldwater and Schalk 2016; Halford et al. 1998), linguistics (Everaert et al. 2015), neuroscience (Davis et al. 2017), and especially behavior analysis suggest that successful cognition involves the ability to relate symbols for functional purposes.
According to one track of behavior-analytic research known as Relational Frame Theory (RFT; Hayes et al. 2001), human language and cognition both, at their core, involve the adaptive ability to respond symbolically to environmental contingencies. RFT purports that the key skill underlying the complexity and generativity in language and cognition is arbitrarily applicable relational responding (AARR). AARR, writ large, is the behavior of responding to one event in terms of another based on their symbolic properties. For example, “left” is only understood relative to “right” (spatial responding; May et al. 2017), “more” relative to “less” (comparative responding; Dymond and Barnes 1995), “before” relative to “after” (temporal responding; O’Hora et al. 2008), “part” relative to “whole” (hierarchical responding; Slattery and Stewart 2014), or “opposite/different” relative to “same” (equivalence; Steele and Hayes 1991).
These patterns of relational framing of behavioral events (AARR) develop as a person recognizes physical relational regularities in the presence of a particular contextual cue (non-arbitrarily applicable relational responding; NAARR). Recognition of physical similarity between stimuli appears to be a natural concept that does not require learning (cf., Zentall et al. 2018). It is also possible to learn more complex patterns of relational (as opposed to physical) responding from that starting point. For example, one can condition either a human or a non-human to choose a picture of an apple in the presence of a picture of a different apple. After multiple exemplars of responding based on the common physical properties of stimuli wherein (1) a relational pattern of behavior has been consistently reinforced by the verbal community (e.g., a parent or teacher saying ‘correct’ or ‘yes, well done’), (2) in a particular context, then (3) (only) humans can abstract the pattern of behavior and apply it to novel stimuli based on the contextual cue alone, independent of whether a physical relation exists (cf., Barnes-Holmes and Barnes-Holmes 2000). In experimental terms, what would this look like? If several instances of matching behavior (e.g., matching apples to apples, matching people to people) are reinforced across multiple trials in which the word “same” is spoken, then matching behavior will come under stimulus control of the contextual cue “same” such that it becomes a generalized operant. Subsequently, an experimenter can use the word “same” to indicate that physically dissimilar stimuli (e.g., an apple and the word “úl”—the Irish word for apple) should be treated as being functionally the same. The critical test of this is whether the participant responds to the word “úl” as if it had the functional properties of an apple (round, sweet, nutritious, etc.). Based on this simple pattern of relational framing, experimenters can then train more complex operants, such as distinction and opposition (cf., Steele and Hayes 1991).
There are three core properties of AARR. The first is mutual entailment: Given the relation “A is to B” (or A:B), it is possible to symbolically derive B:A without the need for explicit training of B:A. For simpler relations such as “same”, “different”, and “opposite”, the A:B relation is the same as the derived symmetrical relation, B:A (e.g., if A = B, then B = A; if A is the opposite of B, then B is the opposite of A). For other relations such as “more than/less than”, the generalized operant follows an asymmetrical pattern of behavior (e.g., if A is more than B, B is less than A). In this example, more than and less than are separate contextual cues that bring about different patterns of behavior on a set of stimuli (cf., Pennie and Kelly 2018). The second property of AARR is combinatorial entailment. Here, having learnt an A:B relation and a B:C relation, it becomes possible to syllogistically derive relations between previously unrelated stimuli (i.e., A:C and C:A). For instance, if one British pound (A) is greater than one US dollar (B), and one dollar (B) is more than one Japanese Yen (C), then I can derive that one Yen (C) is less than one pound (A). The third property of AARR is transformation of stimulus functions, wherein stimulus functions change in accordance with their relations with other stimuli. Given the A:C and C:A derivations in the previous example, I will treat the Yen as less valuable than the pound by choosing the pound, if given the choice. However, AARR is also a necessarily contextually controlled set of behaviors. For example, if you found yourself in Japan with US dollars and have no means of trading currency, in that context, one dollar is no longer more than one Yen. The relation brought to bear on stimuli depends on both (1) the context, and (2) the needs/values of the person. Training generalized operants allows the person to adapt and function effectively across multiple environments/contexts across time, nonetheless.
“Strengthening Mental Abilities with Relational Training” (SMART) is an online program that trains relational framing operants via multiple exemplar training in a gamified format (Cassidy et al. 2016). Across 70 stages of incrementing complexity, SMART trains both symmetrical (same/opposite) and asymmetrical (more/less) patterns of relational framing between arbitrary nonsense syllables. For example, given the relations “WUG is more than JUP” and “JUP is more than PEK” in a set of training trials, participants will derive that PEK is less than WUG in a test trial despite WUG and PEK never before appearing on screen together during training trials. The use of nonsense syllables allows the experimenter to train the pattern of AARR independent of the nature of the stimuli involved. In other words, as participants have no prior pre-experimental history with the nonsense syllables, greater experimental control and internal validity is established. The SMART program includes a 55-item test of relational operant skills known as the Relational Abilities Index (RAI; Colbert et al. 2017) that correlates strongly with both full-scale and component measures of IQ.
A key feature of operant skills is that they are patterns of behavior that can be trained (cf., Kishita et al. 2013; Moran et al. 2015). SMART has previously been proposed as one way of training the generally adaptive operant repertoires that manifest as g. In an initial pilot study, Cassidy et al. (2011) assessed the IQs of four children (aged 10–12) at baseline, following stimulus equivalence training (the most basic form of relational framing; cf., Sidman 1971), and finally, after SMART training. Experimental participants showed large rises in IQ (> 1 SD on the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children; WISC-III) following both stimulus equivalence and especially after SMART training, while four inactive controls (aged 8–12) did not. In a second experiment, children with educational difficulties were exposed to the SMART intervention, finding another large increase in IQ such that participants with educational difficulties were intellectually indistinguishable from their typically developing peers (Cassidy et al. 2011). The sample size and experimental design of this study lacked power and rigour. Nonetheless, the magnitude of the observed IQ gains merited attention, as the items on the IQ test were not structurally related to one another, nor to the training, in any obvious way, suggesting that the researchers had demonstrated the elusive cross-domain transfer effects.
These initial results have since been corroborated with larger samples. For example, Cassidy et al. 2016 reported that fifteen 11–12-year-olds who completed SMART training gained 23 IQ points on the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-IV (WISC-IV), rising from a mean of 97 to a mean of 120. The magnitude of this average IQ score increase needs to be acknowledged here as it is an increase of one-and-a-half standard deviations (i.e., a standard deviation on a Wechsler IQ test is 15 points). To put this finding in context, these results far-exceed the 2–3 point average increase found using N-Back training (Au et al. 2015) and therefore demand replication in a larger controlled experiment. In their second experiment, 30 15–17-year-old children completed SMART training. Cassidy et al. (2016) observed substantial improvements on both the verbal and numerical subscales of the differential aptitude test, indicating yet further transfer of the training effects toward developmentally and educationally relevant tests.
Other small-scale relational skills training intervention studies have also reported to enhance scores on various tests of specific cognitive abilities such as analogical responding (Ruiz and Luciano 2011), hierarchical responding (Mulhern et al. 2017, 2018), statistical learning (Sandoz and Hebert 2017), and, overall general cognitive ability (Parra and Ruiz 2016; Thirus et al. 2016; Vizcaíno-Torres et al. 2015), though they are typically underpowered. Taken together, however, these studies show some evidence for the utility of relational skills training and that operant abilities are skills through which we adapt to our environments (cf., also O’Hora et al. 2008; O’Hora et al. 2005; O’Toole et al. 2009; also cf., Cassidy et al. 2010, for a discussion of how relational skills are related to IQ test items).
Hayes and Stewart (2016) attempted to independently replicate and extend previous findings on the utility of SMART training. They tested the differential effects of SMART training (n = 14) and an active Control Condition (computer programming, which also involves symbolic manipulation; n = 14) for improving performance on memory, literacy, and numeracy in children aged 10–11 years. Those who completed SMART training improved their scores on the digit span letter/number sequencing task, spelling, reading, and numerical operations. This remains the only active-controlled RCT testing the far-transfer of SMART training effects to date. We sought to extend this research in a much larger sample.
The training effects of SMART also appear to manifest in non-Western samples. For example, Amd and Roche (2018) provided SMART training to a sample of 35 socially disadvantaged children in Bangladesh and observed rises in fluid intelligence (as measured using Raven’s Matrices). Furthermore, those who completed more training stages showed the greatest improvements in fluid intelligence. This raises the question of whether there was a common factor (e.g., motivation) responsible for both the number of training stages completed and for the observed improvement in fluid intelligence. We attempted to address this question in the current study.
It is now more important than ever to provide large-scale, well-controlled tests of the utility of SMART training. The main aim of this study was to provide a larger-scale, independent, stratified (by ability) active-controlled trial to test the effects of SMART training on one indicator of Non-verbal IQ (NVIQ), the domain-general ability to manipulate abstractions for functional purposes, and processing speed. However, as previously mentioned, there are also non-cognitive factors such as Conscientiousness and Neuroticism which may affect test performance (Bergold and Steinmayr 2018). Personality, in particular may be a useful “catch all” way of measuring non-cognitive factors, as previous research has found that it may account for factors such as test anxiety (Chamorro-Premuzic et al. 2008), emotional intelligence (Schulte et al. 2004), and grit (Ivcevic and Brackett 2014). Therefore, a secondary aim of the present study was to assess whether cognitive and non-cognitive factors (i.e., personality traits) are differentially associated with the amount of SMART training students complete.
Method
Participants
We recruited from a cohort of 183 school pupils aged 12–15 years and then assigned them to one of two conditions (cf., Design for details). Participants were in the first year of a new post-primary curriculum at an Irish secondary school (i.e., high school). Before the study began, parents and school management were provided with information on the aims of the study and what it would involve, after which electronic assent for pupils to participate was recorded. At the beginning of the study, participants were presented with an electronic study information page during class and given the opportunity to ask questions. Those who wished to participate subsequently provided informed consent, which was recorded electronically.
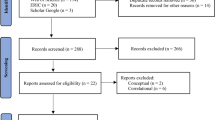
Exclusion criteria To ensure equal opportunity to participate, those who were allocated to the Control Condition were given access to SMART training after the study. In each of our two main analyses (DV = NVIQ/DV = processing speed), we excluded those who: (1) did not complete both a Time 1 and Time 2 assessment, (2) did not provide their age so that we could compute standard scores, (3) those who appeared to under-perform at Time 1 (Time 1 NVIQ < 70 or ΔNVIQ > 30), (4) those whose Time 1 and Time 2 data could not be linked (i.e., no ID provided).
Inclusion criteria To be included in this study, participants needed to be students at the school in question, participating in the standard curriculum, in their first year of the Irish secondary school curriculum.
Final numbers Out of the 183-student cohort, eight students were excluded from the study at the request of the school. The remaining 175 were stratified (by ability, based on a prior entrance examination) to mixed-ability classes; four of these classes were in the Experimental Condition (SMART; n = 93) and three were in the Control Condition (Scratch; n = 82), with a Control:Experimental ratio of 88.17:100.00. Another 57 students chose not to complete the NVIQ test at any time point. Twenty NVIQ scores were completed at Time 2 (M = 104.50) but could not be linked to a corresponding IQ test at Time 1. Similarly, 45 NVIQ scores completed at Time 1 (M = 99.80) could not be linked to the corresponding test at Time 2. Nineteen participants who only provided NVIQ data at Time 1 did not include their participant IDs, so we do not know precisely how many cases with missing data at one time point have corresponding data at the other time point that simply cannot be linked and how many were absent/withdrew at one time point or the other. Overall, 70 participants completed both NVIQ tests and included IDs at both times such that their data could be linked for final analyses (overall, MTime 1 = 106.83; MTime 2 = 111.07), 43 of whom completed SMART training, and 27 of whom completed Scratch training (a Control: Experimental ratio of 62.79:100.00).
Fourteen students did not complete the Digit Symbol test at any time point. Twenty-four Digit Symbol scores were completed at Time 1 (MTime 1 = 35.96) but could not be linked to the corresponding test at Time 2. 21 Digit Symbol scores were obtained at Time 2 (MTime 2 = 36.76) but could not be linked to the corresponding test at Time 1. We analyzed data from 125 participants in our final analysis of the effects of SMART training on processing speed, 70 of whom completed SMART training, and 55 of whom completed Scratch training (a Control/Experimental ratio of 78.57:100.00). More details concerning specific demographic information can be found in Table 1.
Measures
We chose NVIQ and Processing Speed as our two main outcome variables, as they both differed substantially from the experimental and control training tasks. As such, our two outcome variables, NVIQ and Processing Speed, functioned as tests of differential cross-domain transfer of training effects.
Non-Verbal IQ We measured NVIQ using the Non-Verbal subscale of the Kaufman Brief Intelligence Test (KBIT-2; Kaufman and Kaufman 2004). This is a 46-item standardized test of abstract matrix reasoning ability. Across these 46 trials, participants were presented with a series of abstract geometric/colored shapes and were required to complete the pattern by selecting the appropriate image from an array of possible alternatives. As such, this is a test of abstract symbolic manipulation. The test–retest reliability of the KBIT-2 Non-Verbal subscale was higher in our Control Condition (r[25] = .84, p < .001) than in the Experimental Condition (r[41] = .64, p < .001).
Processing Speed As an indicator of psychomotor performance, we measured processing speed using an automated version of the Digit Symbol Substitution Test, which is a timed (2-min) task-switching exercise, commonly employed in intelligence testing (cf., McLeod et al. 1982). In this test, participants were presented with a “key” for pairing digits (1–9) with respective arbitrary symbols. Their task was then to progress through a random list of these arbitrary symbols, entering the corresponding number in a box under each, referring back to the “key” as necessary. Therefore, within the 2-min time limit, the number of trials correctly completed was used as an indicator of each participant’s net processing speed. The test–retest reliability of the Digit Symbol Substitution Test was similar in our Control Condition (r[53] = .77, p < .001) and in the Experimental Condition (r[68] = .73, p < .001).
Personality We also measured personality factors using the Big Five Aspects Scale (BFAS; DeYoung et al. 2007), as we wanted to include exploratory analyses of the effects of non-cognitive individual differences and behavioral preferences on study participation. The BFAS is a 100-item self-report scale on non-cognitive behavioral preferences/temperaments that provides fifteen different scores: each of the Big Five traits, and two “aspects” comprising each. These are Neuroticism (aspects: Volatility and Withdrawal), Agreeableness (Compassion/Politeness), Conscientiousness (Industriousness/Orderliness), Extraversion (Assertiveness/Enthusiasm), and Openness (Intellectual/Aesthetic Openness). Aspects of the Big Five have been found to differentially predict behavior. For example, the two aspects of Openness differentially predict success in the arts and sciences (Kaufman et al. 2016). The two aspects of each Big Five domain are, therefore, likely to provide important differentiations for assessing discriminant validity within each domain. Scores on each of the Big Five are derived based on the average score on each of its two aspect sub-scales. The BFAS is answered one a seven-point Likert scale (Disagree Strongly–Agree Strongly). Table 2 presents baseline Cronbach’s α values for each of the 10 personality aspects. The BFAS is a well-validated measure, converging strongly with other measures of the Big Five (DeYoung et al. 2007). However, as can be seen in Table 2, the Cronbach’s α values we produced with younger participants were not as strong as those originally reported in the sample in which this scale was validated (αrange = .75–.85; De Young et al. 2007), so results reported below in relation to personality factors must be interpreted with caution.
Design
Allocation to Conditions
Participants were allocated to one of two conditions, the Experimental and Control Conditions (see below). All students applying to the school in question completed a literacy and numeracy test prior to entry. Subsequently, those who had specific learning difficulties were not eligible to participate in the present study. All other students were stratified to mixed-ability classes by school administrators to pursue the standard curriculum prior to the beginning of this study by the first-year coordinator. At the beginning of this study, the IT coordinator supervising the training selected which of the mixed-ability classes would be in each condition based on timetabling convenience. We tested for differences in median scores in Age, NVIQ, Processing Speed, and Personality across the Experimental and Control Conditions at Time 1. Those in the Experimental Condition scored higher in Trait Agreeableness than those in the Control Condition (U = − 3.50, p < .05). Importantly, though, there were no differences in Age, NVIQ, Processing Speed, Trait Neuroticism, Aspect Volatility, Aspect Withdrawal, Trait Conscientiousness, Aspect Industriousness, Aspect Orderliness, Trait Extraversion, Aspect Enthusiasm, Aspect Assertiveness, Trait Openness, Aspect Intellect, nor Aspect Aesthetic Openness across conditions at Time 1. There were also no differences in the components of Trait Agreeableness (Aspect Compassion and Aspect Politeness) across conditions at Time 1. Therefore, it appears that our method of allocating participants to Condition did not distribute participant traits unevenly across conditions.
Experimental Conditions
Those in the Experimental Condition were given access to SMART training for a period of three months, in which they received 240 min of supervised SMART training during their Information Communications Technology class under their teacher’s supervision. During this period, participants were also encouraged to practice SMART training at home. To encourage extra participation, we held a monthly prize draw for which participants were given tickets commensurate with the number of training points earned that month. At the same time, those in the Control Condition (hereinafter, Group 2) were given 240 min of Scratch computer coding training in their Information Communications Technology classes over the same period. Participants in this condition were assigned mandatory computer coding homework and were not eligible for the monthly prize draw. We measured participants’ NVIQs and processing speeds before and after SMART / Scratch training. We also measured personality traits at baseline.
SMART Experimental Condition
Participants received training in the general ability to derive relations between arbitrary nonsense syllables based on English language contextual cues. This program trained the receptive ability to derive relations of sameness/opposition and more than/less than. The training consisted of 70 stages of incrementing complexity (see Fig. 1).
Participants unlocked new stages of increased complexity upon mastery of the previous stage. For example, the early stages involve simply deriving relations based on A-B networks (e.g., JUM is the same as GUP. Is GUP opposite JUM?), while a more complex network might involve A-C networks (e.g., LEP is the same as FOP. TEK is opposite FOP. Is TEK the same as LEP?). More advanced stages involved more/less relations, which are more complex because they are asymmetrical. For example, if A is “the same as” B, then B is simply “the same as” A, while on the other hand, if A is “more than” B, B is not simply “more than” A. Users were limited to progressing through a maximum of five new stages per day by the software. During blocks of training trials, participants received corrective feedback provided after each response (see Fig. 2, top). To proceed from a training block to testing, participants were required to answer 16 trials consecutively correct. During testing, participants received the same array of trial types, but without corrective feedback (see Fig. 2, bottom). Each nonsense syllable stimulus was only used once across all training and testing stages, ensuring that each trial was unique. Participants were given a maximum of 30 s to respond to each trial before the software recorded an incorrect response and presented a new trial. Participants had the option to adjust the time limit for each trial if they wished to challenge themselves further, however, we did not control for the use of this feature.
Scratch Active Control
Scratch training is a computer coding training program for children which aims to teach them how to program their own computer game (for a detailed overview, cf., Hayes and Stewart 2016). In early lessons, participants were introduced to the Scratch interface and learned how to create and manipulate a character in their virtual environment. Participants used computer code that relied on developing an understanding of coordinate geometry and integers to assign movement functions to computer keys so that participants could manipulate their character with the keyboard. Subsequent lessons involved using code to develop their character and create a game-like environment in which it would operate. This activity was led by their classroom teacher on a weekly basis. In accordance with RFT, computer coding involves the manipulation of symbols for pragmatic purposes, but with less precision than SMART training.
In the case of Scratch, behavioral reinforcement came in the form of the “completed” program successfully running, rather than by reinforcing individual behaviors that led to the program running. In SMART, rewarding individual correct responses (thereby reinforcing them) was a core and deliberate feature of the training. There was no way of directly yoking progress with Scratch training to that of SMART, as Scratch was not set out in stages, per se, meaning that Scratch progress was not easily measurable. Nonetheless, both interventions were given equal classroom time, making any overall differences in engagement likely to be due to either (i) differences in the degree to which schedules of reinforcement were built into each intervention or (ii) individual differences across groups, which we have tried to account for with baseline measures of cognitive ability and personality.
Results
Preliminary Analyses
Preliminary descriptive statistics (including means, standard deviations, and confidence intervals) for our main variables of interest can be found in Tables 3 and 4.
We then explored the intercorrelations between our main variables of interest, using a Bonferroni correction to control for multiple comparisons (see Table 5).
Test Completion
Due to high rates of absence and attrition, we decided to explore the characteristics of those who were not eligible for the final analysis further. We particularly wanted to know whether those who completed a Time 1 NVIQ test but did not complete it at Time 2 were of lower baseline ability, as this could affect our results. Using a single-sample t-test, we compared the overall Time 1 NVIQ scores (M = 104.83) to the known mean score for those who only completed the Time 1 NVIQ test and not the Time 2 test (M = 99.80). These scores were significantly different from one another (t[116] = 3.34, p = .001). Therefore, if the predicted training effects are found in the Experimental Condition (SMART) only, they might be (1) deflated if those with lower baseline ability benefit from the training most, or (2) over-inflated if those with higher baseline ability appear to benefit most.
Training Completion
Training completion was quite low (M = 15.77, SD = 8.19), perhaps indicating that the schedules of reinforcement included did not motivate those in the Experimental Condition. We examined the relationship between the number of SMART stages those in the training group completed and all our other baseline measures (see Tables 3, 4, and 5) to understand who, in our sample, was likely to engage in training. There was a moderate negative relationship between the Volatility aspect of the Neuroticism trait and the number of training stages completed (r[89] = − .35, p = .016). We also observed a stronger relationship between training completion and the Politeness aspect of Agreeableness (r[87] = .40, p = .002). We found no other relationships between personality traits, nor their aspects, nor baseline NVIQ and processing speed, and training completion.
Non-Verbal IQ
In the Experimental Condition, the mean number of training stages completed was 16.45 (SD = 8.40, Mdn = 16) out of the 70 stages available. We removed two cases (one in each condition) who improved by 49 NVIQ points from Time 1 to Time 2, assuming this to be a result of test error at Time 1. We used a mixed-design analysis of variance to assess the effects of one between-subjects factor (Condition: SMART and Scratch) and one repeated measures factor (Time: Time 1 and Time 2) on NVIQ (see Fig. 3).
We observed no significant main effect of Condition on NVIQ (F[1, 68] = .48, MSE = 251.41, p = .493). However, we did observe an overall effect of Time on NVIQ (F[1, 68] = 16.44, MSE = 29.75, p < .001, ƞp2 = .20/d = .53, 1 − β = .98). There was also an interaction effect between Condition and Time on NVIQ (F[1, 68] = 5.01, MSE = 29.75, p = .027, ƞp2 = .07/d = .34; 1 − β = .60). This interaction was such that, when observing the simple effects in the Experimental Condition, we found significant increases in NVIQ from Time 1 (M = 106.65, SD = 12.03) to Time 2 (M = 112.63, SD = 10.19) indicating that the training was successful in this condition (ΔNVIQ = 5.98; F[1, 68] = 25.81, p < .001, CI = 3.53–8.32, ƞp2 = .28/d = .38, dppc2 = .341). However, in the Control Condition, there was no significant change (ΔNVIQ = 1.70; F[1, 68] = 1.32, p = .255, CI = − 4.66–1.26, ƞp2 = .02) in NVIQ from Time 1 (M = 106.89, SD = 12.99) to Time 2 (M = 108.58, SD = 12.85).
Which Participants Improved with Training? Previously, we provided information on who, in the Experimental Condition, completed more SMART training. Now, we will provide information on who, in the Experimental Condition benefited most from the training. There was a strong negative relationship between baseline NVIQ and the degree to which participants in the SMART training group’s NVIQ scores changed from Time 1 to Time 2 (r[42] = − .57, p < .001; see Fig. 4).
We conducted a simple linear regression to explore this further. Baseline NVIQ explained 30.5% of the variance in the NVIQ Change. This model was a significantly better predictor of NVIQ Change than the mean (F[1. 42] = 17.96, p < .001). Baseline NVIQ (b = − .39. β = − .55) significantly predicted changes in NVIQ (t = − 4.24, p < .001). The beta value indicates that for every additional NVIQ point at Time 1, those who complete 16 stages of SMART training will gain .39 fewer NVIQ points at Time 2.
Interestingly, visual inspection of the relationship between the Scratch control participants’ baseline NVIQ and their Time 1 to Time 2 NVIQ change (r[26] = − .37, p = .058) shows an almost identical pattern as in the Experimental Condition, save for there being no increases in those with baseline NVIQ below the median of 107 (see Fig. 5), which was the median NVIQ at baseline for both conditions. There were no relationships between personality factors, nor their aspects, and the SMART training group’s changes in NVIQ. We also examined the relationship between the number of SMART training stages completed in the Experimental Condition and NVIQ changes and observed no linear relationship between the two (r[42] = .21, p = .172). However, after controlling for baseline NVIQ, there was a clear positive linear relationship between the number of training stages completed and the observed NVIQ gain (r[39] = .43, p = .005).
Processing Speed
We used a mixed-design analysis of variance to assess the effects of one between-subjects factor (Condition: SMART and Scratch) and one repeated measures factor (Time: Time 1 and Time 2) on processing speed (see Fig. 6).
We observed no significant main effect of Condition on processing speed (F[1, 123] = .23, MSE = 217.74, p = .561). We observed an overall effect of Time on processing speed (F[1, 123] = 23.10, MSE = 33.93, p < .001, ƞp2 = .16/d = .48, 1 – β = .99). There was no interaction effect of Condition and Time on processing speed (F[1, 123] = .03, MSE = 33.93, p = .868). That is, both those in the Experimental and Control Conditions demonstrated improved processing speed with time (dppc2 = − .024).
Discussion
The results revealed that SMART training improved NVIQ, while Scratch computer coding, our active Control Condition, did not. Previous studies report a pre and post training RAI score (cf., Colbert et al. 2017), implying that every participant completed 55 stages of SMART training, compared to an average of 16 stages in the current study. Therefore, while the magnitude of the increase in NVIQ was not as high as was typically reported in previous SMART studies (e.g., change in full-scale IQ = 23.27 in Cassidy et al. (2016), in a similar demographic), it is notable that this low dosage yielded a NVIQ increase that was twice as large as the most popular working memory training (cf., Au et al. 2015), with a large effect size. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest study of the effects of SMART training to date and therefore represents a significant stepping stone on the way to conducting critical large-scale, double-blind randomized controlled trials. Intensive supervision and one-to-one or one-to-few teaching is typical of other applied behavior-analytic interventions (in both research and practice) and so it is possible that, in the previous smaller studies, the training was supervised more intensively. This study was one of the first to implement a larger-scale test of the utility of behavior change techniques based on advances in operant conditioning (cf., Dymond and Roche 2013), a cogent theory of adaptive language and cognition that has been in development since the mid-twentieth century. In contrast, previous attempts at training cognitive ability have been either (1) developed for commercial purposes (e.g., Lumosity) or (2) aimed at training a single cognitive process (e.g., working memory), rather than being based on a carefully developed theory of general language and cognition (cf., Hayes et al. 2001) that aspires to be consistent with modern evolution science (Wilson and Hayes 2018).
These results show no evidence that SMART training is any more effective than computer coding for improving processing speed. Participants in both conditions improved to a similar degree across time. There are two possible reasons for this. First, it is possible that neither SMART nor Scratch were effective for improving processing speed, but rather, both improved as a function of time. Second, it is possible that both SMART and Scratch helped to improve processing speed equally. We did not have an inactive control group to help to answer this question in the current study. One recent pilot study by McLoughlin et al. (2018) found that a small dosage of SMART training helped to improve the speed at which participants completed the KBIT-2, while there was no such improvement in the inactive control participants. For this reason, it is arguably more probable that both SMART and Scratch were effective interventions for increasing processing speed. It, therefore, suggests that the differential effects of SMART compared to Scratch on NVIQ reported previously targeted the non-shared variance between NVIQ and processing speed. However, as baseline NVIQ and processing speed were not correlated, this is will require further research to elucidate.
Here, we observed that training relational skills, a form of advanced syllogistic reasoning, helped to improve performance on a conventional matrices test, while computer coding did not. Each trial in the matrices test involved a series of geometrical shapes in a sequence, and the participants were required to complete the sequence. Conversely, the training involved deriving arbitrary relations between nonsense syllables. Initially, it appears that these are two quite different types of task, thus providing evidence for the far-transfer effects of the training. Previous cognitive training programs have observed some short-term transfer of training effects (e.g., at one week and at one month in Blieszner et al. 1981) in older adults, but these effects disappeared by six months. This is also analogous to the effects of early compensatory education programs such as Head Start (cf., Haier 2016), as those children who were given extra educational opportunities excelled initially, but after a few years these advantages “washed out”. A critical future test of the efficacy of SMART training will be to test whether training effects transfer even further towards school grades, and whether transfer effects last over time.
On the other hand, SMART was no more effective than computer coding for improving processing speed. One potential (ad-hoc) explanation for this finding is that the Digit Symbol test of processing speed involves simple task switching behaviors, as opposed to active manipulation of abstract symbols. As such, performance on the Digit Symbol test may be a more direct reflection of one’s neural efficiency, while the matrices test requires additional acquired operant repertoires because each trial involves more active problem-solving behaviors.
According to the theory of general intelligence, we may expect that observing transfer of training effects from one domain to another would mean that the training effects would transfer to all other domains. However, our results present mixed evidence for the far-transfer effects of SMART training. To explore this further in the future, we may turn to neuroscience. Perhaps the most popular neurobiological account of intelligence, the parieto-frontal integration theory (P-FIT; Jung and Haier 2007), suggests that intelligence involves an interaction between the frontal and parietal lobes in the brain. According to Jung and Haier (2007), more intelligent people are more neuronally efficient, as evidenced by lower activity in the parieto-frontal regions. However, this is not to say that simple processing speed should necessarily improve. Alternatively, it is possible that parieto-frontal efficiency reflects more efficient and less-labored responding in accordance with contextual cues, which is what relational operant skills training explicitly aims to improve. It appears from these data that we trained the general ability to manipulate abstractions and should expect SMART training to improve performance on tests that require symbolic manipulation rather than simple switching behaviors, as in the Digit Symbol test. Therefore, one plausible hypothesis for future research is that relative mastery of SMART training will decrease activity in the parieto-frontal regions of the brain when engaging in complex cognitive tasks, thus providing further evidence of the far-transfer effects of the training.
We also found that those who were less Volatile and more Polite completed more SMART training. This seems to imply that those who can calmly engage with challenging scenarios (low Volatility) and who follow teachers’ instructions (high Politeness) will complete more training, all things being equal. These results may merit following-up in future research but must be treated with caution as we did not observe adequate internal reliability coefficients using the BFAS in this age group. At the same time, those who had higher baseline NVIQ scores did not complete more training. Therefore, these results do not support the hypothesis that those who are smarter at Time 1 find training easier and therefore enter a positive feedback loop during the earlier stages that allows them to progress more overall in terms of training completed (i.e., The Matthew Effect). This is a counterintuitive finding, as it is incongruent with a recent finding by Redick et al. (2018), who recently reported a positive relationship between baseline cognitive ability and working memory training progress. Taken together, these findings highlight the importance of accounting for the role of individual differences in behavior modification. For example, if a child in the classroom is known to exhibit temperamental behavior, a teacher might know in advance that they will require more support with the SMART programme and can plan accordingly. However, this might also mean providing targeted relational training to address particular skill deficits, or to develop interventions to be accessible and acceptable to people of different temperaments.
Our data may suggest compensation effects similar to those observed when training executive functions (cf., Titz and Karbach 2014). There was a strong negative relationship between baseline ability and change in NVIQ in the training group, but no such relationship in the control group. It appears that those who were lower in relational skills and/or intellectual ability at baseline benefited more from lower-complexity training, while those with higher baseline ability did not reach the stages that would push their intellectual limits toward improvement. This finding is also apparent in the narrowing of the standard deviation of the SMART group’s NVIQ from Time 1 to Time 2. Previous studies in this area have not found this negative relationship between baseline ability and IQ change. This may be due to the fact that it was more difficult to detect effects in previous SMART studies with comparatively small sample sizes, which highlights the need for larger trials in the future. It may also be due to the differences in training completion across studies; perhaps after Stage 20 (for example) everyone is challenged to improve, thereby reducing the baseline ability-IQ change correlation coefficient with each subsequent stage completed beyond that. In the bigger picture, this finding suggests that SMART may be a means of reducing cognitive inequality, which is especially important given that jobs of lower complexity are rapidly being automated out of existence.
Future research should, of course, aim to have better retention. Nonetheless, a negative relationship between baseline ability and NVIQ change was only observed in the Experimental (i.e., SMART) Condition. While this will remain an open limitation of the present study, we hope that it will provide better justification for larger, better-controlled trials than the smaller-scale research studies published in this area to date.
We were only able to analyze data from a relatively small portion of the original sample. There were several reasons for this. First, a large proportion of students completed only one of the tests (i.e., pre- or post-training NVIQ/processing speed only), making them ineligible for a pairwise repeated measures analysis. Second, other students failed to provide their age, making it impossible to compute their standardized test score for NVIQ. Finally, we removed two cases (one in each condition) who improved by 49 NVIQ points from Time 1 to Time 2, assuming this apparent increase to be a result of test error at Time 1. This highlights the logistical difficulty in implementing such a study in schools with children of this age, against which any potential benefit of the training must be weighed.
Participants were not blind to their study condition, and so it is possible that the changes in NVIQ observed herein were partially attributable to a placebo effect. Participants were incentivized to take part in SMART training and not Scratch coding, meaning that there might have been motivational differences across groups. We did not measure motivational differences in this study, but we consider it to be important for future studies to explore this possibility. Interestingly, the magnitude of the increase in the SMART group (5.98 NVIQ points; > .5 SD) is considerable. Furthermore, when we analyzed the relationship between the number of training stages completed and NVIQ change in the Experimental Condition while controlling for baseline NVIQ, there was a moderate positive relationship (r = .43), providing further support for the hypothesis that the training intervention itself was largely responsible for the observed NVIQ gain. This is nonetheless an area that merits future study. To be confident that this is not a placebo effect, it would be useful to conduct a double-blind randomized experiment in which participants systematically receive different dosages of training across several groups.
The present study is only the second test of the efficacy of SMART training to employ an active control condition, and it is also by far the largest. While the allocation to each condition was not random, technically, the even distribution of 17/18 traits across conditions at Time 1 indicates that the outcome of our allocation process was as if random allocation had occurred. Therefore, this study design can be considered to be comparable to a randomized controlled trial, which is often considered to be a gold-standard in the hierarchy of evidence for the effectiveness of any given intervention (Kaptchuk 2001). This study also provided some evidence to suggest that different personalities will complete different amounts of SMART training, all things being equal, and that baseline NVIQ is unrelated to training completion. As such, future studies of this size must consider how to ensure that all students complete the training. It also raises several questions about the efficacy of SMART training that have yet to be answered, and we have outlined studies that would allow us to address these in the future. Despite some limitations, this study is by far the largest controlled test of the efficacy of SMART training to date. With a relatively low training dosage, we yielded an increase in NVIQ that is at least twice that of the next most effective cognitive training published in mainstream psychological literature to date. Therefore, relational operant skills training is a promising behavioral training intervention for the future.
References
Alexander, P. A. (2019). Individual differences in college-age learners: The importance of relational reasoning for learning and assessment in higher education. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 89(3), 416–428. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12264.
Amd, M., & Roche, B. (2018). Assessing the effects of a relational training intervention on fluid intelligence among a sample of socially disadvantaged children in Bangladesh. The Psychological Record, 68(2), 141–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40732-018-0273-4.
Au, J., Sheehan, E., Tsai, N., Duncan, G. J., Buschkuehl, M., & Jaeggi, S. M. (2015). Improving fluid intelligence with training on working memory: A meta-analysis. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 22(2), 366–377. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-014-0699-x.
Bergold, S., & Steinmayr, R. (2018). Personality and intelligence interact in the prediction of academic achievement. Journal of Intelligence, 6(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence6020027.
Blieszner, R., Willis, S. L., & Baltes, P. B. (1981). Training research in aging on the fluid ability of inductive reasoning. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 2(3), 247–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/0193-3973(81)90005-8.
Buschkuehl, M., Hernandez-Garcia, L., Jaeggi, S. M., Bernard, J. A., & Jonides, J. (2014). Neural effects of short-term training on working memory. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 14(1), 147–160. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-013-0244-9.
Cassidy, S., Roche, B., Colbert, D., Stewart, I., & Grey, I. M. (2016). A relational frame skills training intervention to increase general intelligence and scholastic aptitude. Learning and Individual Differences, 47, 222–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2016.03.0011041-6080.
Cassidy, S., Roche, B., & Hayes, S. C. (2011). A relational frame training intervention to raise intelligence quotients: A pilot study. The Psychological Record, 61(2), 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395755.
Cassidy, S., Roche, B., & O’Hora, D. (2010). Relational frame theory and human intelligence. European Journal of Behavior Analysis, 11(1), 37–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/15021149.2010.11434333.
Chamorro-Premuzic, T., Ahmetoglu, G., & Furnham, A. (2008). Little more than personality: Dispositional determinants of test anxiety (the Big Five, core self-evaluations, and self-assessed intelligence). Learning and Individual Differences, 18(2), 258–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2007.09.002.
Chooi, W.-T., & Thompson, L. A. (2012). Working memory training does not improve intelligence in healthy young adults. Intelligence, 40(6), 531–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2012.07.004.
Clark, C. M., Lawlor-Savage, L., & Goghari, V. M. (2017). Working memory training in healthy young adults: Support for the null from a randomized comparison to active and passive control groups. PLoS ONE, 12(5), e0177707.
Colbert, D., Dobutowitsch, M., Roche, B., & Brophy, C. (2017). The proxy-measurement of intelligence quotients using a relational skills abilities index. Learning and Individual Differences, 57, 114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2017.03.010.
Colom, R., & Román, F. J. (2018). Enhancing Intelligence: From the Group to the Individual. Journal of Intelligence, 6(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence6010011.
Colom, R., Román, F. J., Abad, F. J., Shih, P. C., Privado, J., Froufe, M., et al. (2013). Adaptive n-back training does not improve fluid intelligence at the construct level: Gains on individual tests suggest that training may enhance visuospatial processing. Intelligence, 41(5), 712–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2013.09.002.
Conway, A. R. A., & Kovacs, K. (2015). New and emerging models of human intelligence. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science, 6(5), 419–426. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcs.1356.
Davies, G., Lam, M., Harris, S. E., Trampush, J. W., Luciano, M., …, Hill, W. D., et al. (2018). Study of 300,486 individuals identifies 148 independent genetic loci influencing general cognitive function. Nature Communications, 9(1), 2098. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04362-x.
Davis, T., Goldwater, M., & Giron, J. (2017). From concrete examples to abstract relations: The rostrolateral prefrontal cortex integrates novel examples into relational categories. Cerebral Cortex, 27(4), 2652–2670. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw099.
DeYoung, C. G., Quilty, L. C., & Peterson, J. B. (2007). Between facets and domains: 10 aspects of the Big Five. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 93(5), 880–896. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.93.5.880.
Dymond, S., & Roche, B. (2013). Advances in relational frame theory: Research and application. Oakland, CA: Context Press.
Everaert, M. B. H., Huybregts, M. A. C., Chomsky, N., Berwick, R. C., & Bolhuis, J. J. (2015). Structures, not strings: Linguistics as part of the cognitive sciences. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 19(12), 729–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2015.09.008.
Goldwater, M. B., & Schalk, L. (2016). Relational categories as a bridge between cognitive and educational research. Psychological Bulletin, 142(7), 729–757. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000043.
Gottfredson, L. S., & Deary, I. J. (2004). Intelligence predicts health and longevity, but why? Current Directions in Psychological Science, 13(1), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0963-7214.2004.01301001.x.
Haier, R. J. (2016). The neuroscience of intelligence. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Halford, G. S., Bain, J. D., Maybery, M. T., & Andrews, G. (1998). Induction of relational schemas: Common processes in reasoning and complex learning. Cognitive Psychology, 35(3), 201–245. https://doi.org/10.1006/cogp.1998.0679.
Hayes, J., & Stewart, I. (2016). Comparing the effects of derived relational training and computer coding on intellectual potential in school-age children. The British Journal of Educational Psychology, 86(3), 397–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12114.
Hayes, S. C., Barnes-Holmes, D., & Roche, B. (2001). Relational frame theory: A post-Skinnerian account of human language and cognition. New York, NY: Plenum Press.
Hill, W. D., Marioni, R. E., Maghzian, O., Ritchie, S. J., Hagenaars, S. P., …, McIntosh, A. M. (2018a). A combined analysis of genetically correlated traits identifies 187 loci and a role for neurogenesis and myelination in intelligence. Molecular Psychiatry, 24, 169–181. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-017-0001-5.
Hill, W. D., Arslan, R. C., Xia, C., Luciano, M., Amador, C.,Navarro, P., …,Penke, L. (2018b). Genomic analysis of family data reveals additional genetic effects on intelligence and personality. Molecular Psychiatry, 23, 2347–2362. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-017-0005-1.
Ivcevic, Z., & Brackett, M. (2014). Predicting school success: Comparing conscientiousness, grit, and emotion regulation ability. Journal of Research in Personality, 52(10), 29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2014.06.005.
Jaeggi, S. M., Buschkuehl, M., Jonides, J., & Shah, P. (2011). Short-and long-term benefits of cognitive training. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(25), 10081–10086. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1103228108.
Jaeggi, S. M., Studer-Luethi, B., Buschkuehl, M., Su, Y.-F., Jonides, J., & Perrig, W. J. (2010). The relationship between n-back performance and matrix reasoning—Implications for training and transfer. Intelligence, 38(6), 625–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2010.09.001.
Jung, R. E., & Haier, R. J. (2007). The Parieto-Frontal Integration Theory (P-FIT) of intelligence: Converging neuroimaging evidence. The Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 30(2), 135–187. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X07001185.
Kaptchuk, T. J. (2001). The double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial: Gold standard or golden calf? Journal of Clinical Epidemiology (Vol. 54). Retrieved from https://www.medschool.lsuhsc.edu/internal_medicine/residency/docs/JC 2015-03 Gold standard or golden calf_Nesh.PDF
Kaufman, A. S., & Kaufman, N. L. (2004). Kaufman brief intelligence test. Hoboken: Wiley Online Library.
Kaufman, S. B., Quilty, L. C., Grazioplene, R. G., Hirsh, J. B., Gray, J. R., Peterson, J. B., et al. (2016). Openness to experience and intellect differentially predict creative achievement in the arts and sciences. Journal of Personality, 84(2), 248–258. https://doi.org/10.1111/jopy.12156.
Kishita, N., Ohtsuki, T., & Stewart, I. (2013). The Training and Assessment of Relational Precursors and Abilities (TARPA): A follow-up study with typically developing children. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 2(1–2), 15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcbs.2013.01.001.
McKey, R. H. (1985). The impact of head start on children, families and communities. Final Report of the Head Start Evaluation, Synthesis and Utilization Project. Retrieved from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED263984.pdf
McLeod, D. R., Griffiths, R. R., Bigelow, G. E., & Yingling, J. (1982). An automated version of the digit symbol substitution test (DSST). Behavior Research Methods & Instrumentation, 14(5), 463–466. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03203313.
McLoughlin, S., Tyndall, I., & Pereira, A. (2018). Piloting a brief relational operant training program: Analyses of response latencies and intelligence test performance. European Journal of Behavior Analysis, 19(2), 228–246. https://doi.org/10.1080/15021149.2018.1507087.
Melby-Lervåg, M., & Hulme, C. (2013). Is working memory training effective? A meta-analytic review. Developmental Psychology, 49(2), 270. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0028228.
Melby-Lervåg, M., & Hulme, C. (2016). There is no convincing evidence that working memory training is effective: A reply to Au et al. (2014) and Karbach and Verhaeghen (2014). Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 23(1), 324–330. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-015-0862-z.
Melby-Lervåg, M., Redick, T. S., & Hulme, C. (2016). Working memory training does not improve performance on measures of intelligence or other measures of “far transfer” evidence from a meta-analytic review. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 11(4), 512–534. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691616635612.
Mohammed, S., Flores, L., Deveau, J., Hoffing, R. C., Phung, C., Parlett, C. M., …, Buschkuehl, M. (2017). The benefits and challenges of implementing motivational features to boost cognitive training outcome. Journal of Cognitive Enhancement, 1(4), 491–507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41465-017-0047-y.
Moran, L., Walsh, L., Stewart, I., McElwee, J., & Ming, S. (2015). Correlating derived relational responding with linguistic and cognitive ability in children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 19, 32–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2014.12.015.
Mulhern, T., Stewart, I., & Elwee, J. M. (2017). Investigating relational framing of categorization in young children. Psychological Record, 67(4), 519–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40732-017-0255-y.
Mulhern, T., Stewart, I., & McElwee, J. (2018). Facilitating relational framing of classification in young children. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 8, 55–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcbs.2018.04.001.
O’Hora, D., Pelaez, M., & Barnes-Holmes, D. (2005). Derived relational responding and performance in verbal subtests of the WAIS-III. The Psychological Record, 55, 155–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395504.
O’Hora, D., Peláez, M., Barnes-Holmes, D., Rae, G., Robinson, K., & Chaudhary, T. (2008). Temporal relations and intelligence : Correlating relational performance with performance on the WAIS-III. The Psychological Record, 58(1), 569–584. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395638.
O’Toole, C., Barnes-Holmes, D., Murphy, C., O’Connor, J., & Barnes-Holmes, Y. (2009). Relational flexibility and human intelligence: Extending the remit of skinner’s verbal behavior. International Journal of Psychology and Psychological Therapy, 9(1), 1–17.
Park, J., & Brannon, E. M. (2016). How to interpret cognitive training studies: A reply to Lindskog & Winman. Cognition, 150, 247–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2016.02.012.
Parra, I., & Ruiz, F. J. (2016). The effect on intelligence quotient of training fluency in relational frames of coordination. International Journal of Psychology and Psychological Therapy, 16(1), 1–12.
Peijnenborgh, J. C. A. W., Hurks, P. M., Aldenkamp, A. P., Vles, J. S. H., & Hendriksen, J. G. M. (2016). Efficacy of working memory training in children and adolescents with learning disabilities: A review study and meta-analysis. Neuropsychological Rehabilitation, 26(5–6), 645–672. https://doi.org/10.1080/09602011.2015.1026356.
Plomin, R., & Von Stumm, S. (2018). The new genetics of intelligence. Nature Reviews Genetics, 19(3), 148–159. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2017.104.
Rabipour, S., & Raz, A. (2012). Training the brain: Fact and fad in cognitive and behavioral remediation. Brain and Cognition, 79(2), 159–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2012.02.006.
Ramani, G. B., Jaeggi, S. M., Daubert, E. N., & Buschkuehl, M. (2017). Domain-specific and domain-general training to improve kindergarten children’s mathematics. Journal of Numerical Cognition, 3(2), 468–495. https://doi.org/10.5964/jnc.v3i2.31.
Redick, T. S., Shipstead, Z., Harrison, T. L., Hicks, K. L., Fried, D. E., Hambrick, D. Z., ..., Engle, R. W. (2013). No evidence of intelligence improvement after working memory training: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 142(2), 359-379. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0029082.
Ritchie, S. (2015). Intelligence: All that matters. London: Hodder & Stoughton.
Ruiz, F. J., & Luciano, C. (2011). Cross-domain analogies as relating derived relations among two separate relational networks. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 95(3), 369–385. https://doi.org/10.1901/jeab.2011.95-369.
Sala, G., Foley, J. P., & Gobet, F. (2017). The effects of chess instruction on pupils’ cognitive and academic skills: State of the art and theoretical challenges. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 1–4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00238.
Sala, G., & Gobet, F. (2017a). When the music’s over. Does music skill transfer to children’s and young adolescents’ cognitive and academic skills? A meta-analysis. Educational Research Review, 20, 55–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2016.11.005.
Sala, G., & Gobet, F. (2017b). Working memory training in typically developing children: A meta-analysis of the available evidence. Developmental Psychology, 53(4), 671–685. https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000265.
Salminen, T., Strobach, T., & Schubert, T. (2012). On the impacts of working memory training on executive functioning. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 6, 166. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2012.00166.
Sandoz, E. K., & Hebert, E. R. (2017). Using derived relational responding to model statistics learning across participants with varying degrees of statistics anxiety. European Journal of Behavior Analysis, 18(1), 113–131. https://doi.org/10.1080/15021149.2016.1146552.
Savage, J. E., Jansen, P. R., Stringer, S., Watanabe, K., Bryois, J., de Leeuw, C. A., …, Posthuma, D. (2018). Genome-wide association meta-analysis in 269,867 individuals identifies new genetic and functional links to intelligence. Nature Genetics, 50, 912–919. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0152-6.
Schulte, M. J., Ree, M. J., & Carretta, T. R. (2004). Emotional intelligence: Not much more than g and personality. Personality and Individual Differences, 37(5), 1059–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2003.11.014.
Schwaighofer, M., Fischer, F., & Bühner, M. (2015). Does working memory training transfer? A meta-analysis including training conditions as moderators. Educational Psychologist, 50(2), 138–166. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2015.1036274.
Shipstead, Z., Redick, T. S., & Engle, R. W. (2012). Is working memory training effective? Psychological Bulletin, 138(4), 628–654. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0027473.
Sidman, M. (1971). Reading and auditory-visual equivalences. Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, 14(1), 5–13. https://doi.org/10.1044/jshr.1401.05.
Simons, D. J., Boot, W. R., Charness, N., Gathercole, S. E., Chabris, C. F., Hambrick, D. Z., et al. (2016). Do “Brain-Training” programs work? Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 17(3), 103–186. https://doi.org/10.1177/1529100616661983.
Skinner, B. F. (1957). Verbal behavior. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Smith-Woolley, E., Pingault, J.-B., Selzam, S., Rimfeld, K., Krapohl, E., von Stumm, S., …, Plomin, R. (2018). Differences in exam performance between pupils attending selective and non-selective schools mirror the genetic differences between them. Npj Science of Learning, 3(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41539-018-0019-8.
Soveri, A., Karlsson, E., Waris, O., Grönholm-Nyman, P., & Laine, M. (2017). Pattern of near transfer effects following working memory training with a dual n-back task. Experimental Psychology, 64(4), 240–252. https://doi.org/10.1027/1618-3169/a000370.
Stepankova, H., Lukavsky, J., Buschkuehl, M., Kopecek, M., Ripova, D., & Jaeggi, S. M. (2014). The malleability of working memory and visuospatial skills: A randomized controlled study in older adults. Developmental Psychology, 50(4), 1049-1059. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0034913.
Stephenson, C. L., & Halpern, D. F. (2013). Improved matrix reasoning is limited to training on tasks with a visuospatial component. Intelligence, 41(5), 341–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2013.05.006.
Strenze, T. (2007). Intelligence and socioeconomic success: A meta-analytic review of longitudinal research. Intelligence, 35(5), 401–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2006.09.004.
Strobach, T., & Huestegge, L. (2017). Evaluating the effectiveness of commercial brain game training with working-memory tasks. Journal of Cognitive Enhancement, 1(4), 539–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41465-017-0053-0.
Thirus, J., Starbrink, M., & Jansson, B. (2016). Relational frame theory, mathematical and logical skills: A multiple exemplar training intervention to enhance intellectual performance. International Journal of Psychology and Psychological Therapy, 16(2), 141–155.
Thompson, T. W., Waskom, M. L., Garel, K.-L. A., Cardenas-Iniguez, C., Reynolds, G. O., Winter, R., …, Alvarez, G. A. (2013). Failure of working memory training to enhance cognition or intelligence. PLoS ONE, 8(5), e63614. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063614.
Titz, C., & Karbach, J. (2014). Working memory and executive functions: effects of training on academic achievement. Psychological Research, 78, 852–868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-013-0537-1.
Van Der Maas, H. L. J., Dolan, C. V., Grasman, R. P. P. P., Wicherts, J. M., Huizenga, H. M., & Raijmakers, M. E. J. (2006). A dynamical model of general intelligence: The positive manifold of intelligence by mutualism. Psychological Review, 113(4), 842–861. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.113.4.842
Vizcaíno-Torres, R. M., Ruiz, F. J., Luciano, C., López-López, J. C., Barbero-Rubio, A., & Gil, E. (2015). The effect of relational training on intelligence quotient: A case study. Psicothema, 27, 120–127. https://doi.org/10.7334/psicothema2014.149.
Wilson, D. S., & Hayes, S. C. (2018). Evolution and contextual behavioral science: An integrated framework for understanding, predicting, and influencing human behavior. New Harbinger: Context Press.
Zabaneh, D., Krapohl, E., Gaspar, H. A., Curtis, C., Lee, S. H., Patel, H., …, Breen, G. (2017). A genome-wide association study for extremely high intelligence. Molecular Psychiatry 23, 1226–1232. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2017.121.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr. Bryan Roche for allowing us access to his training software so we could test it independently.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval for this research was granted by the University of Chichester Research Ethics Committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
McLoughlin, S., Tyndall, I. & Pereira, A. Relational Operant Skills Training Increases Standardized Matrices Scores in Adolescents: A Stratified Active-Controlled Trial. J Behav Educ 31, 298–325 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-020-09399-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-020-09399-x