Abstract
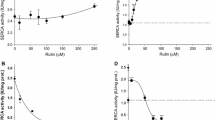
The use of a microsomal preparation from skeletal muscle revealed that both Ca2+ transport and Ca2+-dependent ATP hydrolysis linked to Sarco-Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+–ATPase are inhibited by epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). A half-maximal effect was achieved at approx. 12 μM. The presence of the galloyl group was essential for the inhibitory effect of the catechin. The relative inhibition of the Ca2+-ATPase activity decreased when the Ca2+ concentration was raised but not when the ATP concentration was elevated. Data on the catalytic cycle indicated inhibition of maximal Ca2+ binding and a decrease in Ca2+ binding affinity when measured in the absence of ATP. Moreover, the addition of ATP to samples in the presence of EGCG and Ca2+ led to an early increase in phosphoenzyme followed by a time-dependent decay that was faster when the drug concentration was raised. However, phosphorylation following the addition of ATP plus Ca2+ led to a slow rate of phosphoenzyme accumulation that was also dependent on EGCG concentration. The results are consistent with retention of the transporter conformation in the Ca2+-free state, thus impeding Ca2+ binding and therefore the subsequent steps when ATP is added to trigger the Ca2+ transport process. Furthermore, phosphorylation by inorganic phosphate in the absence of Ca2+ was partially inhibited by EGCG, suggesting alteration of the native Ca2+-free conformation at the catalytic site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blinks JR, Wier WG, Hess P, Prendergast F (1982) Measurement of Ca2+ concentrations in living cells. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 40:1–114
Campos-Toimil M, Orallo F (2007) Effects of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in Ca2+-permeable non-selective cation channels and voltage-operated Ca2+ channels in vascular smooth muscle cells. Life Sci 80:2147–2153
Champeil P, Guillain F (1986) Rapid filtration study of the phosphorylation-dependent dissociation of calcium from transport sites of purified sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase and ATP modulation of the catalytic cycle. Biochem 25:7623–7633
Chen ZY, Chan PT, Ho KY, Fung KP, Wang J (1996) Antioxidant activity of natural flavonoids is governed by number and location of their aromatic hydroxyl groups. Chem Phys Lipids 79:157–163
Chen R, Wang J-B, Zhang X-Q, Ren J, Zeng C-M (2011) Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) induced intermolecular cross-linking of membrane proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys 507:343–349
Chevallier J, Butow RA (1971) Calcium binding to the sarcoplasmic reticulum of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem 10:2733–2737
De Meis L, Vianna AL (1979) Energy interconversion by the Ca2+-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Ann Rev Biochem 48:275–292
Deye J, Elam C, Lape M, Ratliff R, Evans K, Paula S (2009) Structure-based virtual screening for novel inhibitors of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase and their experimental evaluation. Bioorg Med Chem 17:1353–1360
Eletr S, Inesi G (1972) Phospholipid orientation in sarcoplasmic membranes: spin-label ESR and proton MNR studies. Biochim Biophys Acta 282:174–179
Fabiato A (1988) Computer programs for calculating total from specified free or free from specified total ionic concentrations in aqueous solutions containing multiple metals and ligands. Meth Enzymol 157:378–417
Feng W, Cherednichenko G, Ward CW, Padilla IT, Cabrales E, Lopez JR, Eltit JM, Allen PD, Pessah IN (2010) Green tea catechins are potent sensitizers of ryanodine receptor type 1 (RyR1). Biochem Pharmacol 80:512–521
Froehlich JP, Taylor EW (1975) Transient state kinetic studies of sarcoplasmic reticulum adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem 250:2013–2021
Furukawa A, Oikawa S, Murata M, Hiraku Y, Kawanishi S (2003) (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate causes oxidative damage to isolated and cellular DNA. Biochem Pharmacol 66:1769–1778, http://www.healthymolecules.com/3d/epigallocatechin_gallate_3d.htm
Hayashi N, Ujihara T (2007) ‘Bitting effect’ stabilizing gallate-type catechin/quaternary ammonium ion complexes. Tetrahedron 63:9802–9809
Inesi G, Maring E, Murphy AJ, McFarland BH (1970) A study of the phosphorylated intermediate of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. Arch Biochem Biophys 138:285–294
Inesi G, Kurzmack M, Coan C, Lewis DE (1980) Cooperative calcium binding and ATPase activation in sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem 255:3025–3031
Inesi G, Kurzmack M, Kosk-Kosicka D, Lewis D, Scofano H, Guimaraes-Motta H (1982) Equilibrium and kinetic studies of calcium transport and ATPase activity in sarcoplasmic reticulum. Z Naturforsch 37c:685–691
Inesi G, Kurzmack M, Lewis D (1988) Kinetic and equilibrium characterization of an energy-transducing enzyme and its partial reactions. Meth Enzymol 157:154–190
Inoue T, Suzuki Y, Ra C (2011) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces cytokine production in mast cells by stimulating an extracellular superoxide-mediated calcium influx. Biochem Pharmacol 82:1930–1939
Jovanovic S, Simic MG (2000) Antioxidants in nutrition. Ann NY Acad Sci 899:326–334
Khan N, Mukhtar H (2007) Tea polyphenols for health promotion. Life Sci 81:519–533
Kim HJ, Yum KS, Sung J-H, Rhie D-J, Kim M-J, Min DS, Hahn SJ, Kim M-S, Jo Y-H, Yoon SH (2004) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate increases intracellular [Ca2+] in U87 cells mainly by influx of extracellular Ca2+ and partly by release of intracellular stores. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 369:260–267
Kolassa N, Punzengruber C, Suko J, Makinose M (1979) Mechanism of calcium-independent phosphorylation of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase by orthophosphate. FEBS Lett 108:495–500
Kurogi M, Miyashita M, Emoto Y, Kubo Y, Saitoh O (2012) Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin gallate activates TRPA1 in an intestinal enteroendocrine cell line, STC-1. Chem Senses 37:167–177
Kuzuhara T, Iwai Y, Takahashi H, Hatakeyama D, Echigo N (2009) Green tea catechins inhibit the endonuclease activity of influenza A virus RNA polymerase. PLoS Curr 1:RRN1052
Lambert JD, Elias RJ (2010) The antioxidant and pro-oxidant activities of green tea polyphenols: a role in cancer prevention. Arch Biochem Biophys 501:65–72
Lanzetta PA, Alvarez LJ, Reinach PS, Candia OA (1979) An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem 100:95–97
Lape M, Elam C, Versluis M, Kempton R, Paula S (2008) Molecular determinants of sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase inhibition by hydroquinone-based compounds. Proteins 70:639–649
Logan-Smith MJ, Lockyer PJ, East JM, Lee AG (2001) Curcumin, a molecule that inhibits the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum but increases the rate of accumulation of Ca2+. J Biol Chem 276:46905–46911
Lorenz M, Hellige N, Rieder P, Kinkel H-T, Trimpert C, Staudt A, Felix SB, Baumann G, Stangl K, Stangl V (2008) Possitive inotropic effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) involve activation of Na+/H+ and Na+/Ca2+ exchangers. Eur J Heart Fail 10:439–445
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mahmmoud YA (2008) Capsaicin stimulates uncoupled ATP hydrolysis by the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. J Biol Chem 283:21418–21426
Martonosi A, Feretos R (1964) The uptake of Ca2+ by sarcoplasmic reticulum fragments. J Biol Chem 239:648–658
Masuda H, de Meis L (1973) Phosphorylation of the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane by ortophosphate. Inhibition by calcium ions. Biochem 12:4581–4585
Nagle DG, Ferreira D, Zhou Y-D (2006) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): chemical and biomedical perspectives. Phytochemistry 67:1849–1855
Obara K, Miyashita N, Xu C, Toyoshima I, Sugita Y, Inesi G, Toyoshima C (2005) Structural role of countertransport revealed in Ca2+ pump crystal structure in the absence of Ca2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:14489–14496
Oneda H, Shiihara M, Inouye K (2003) Inhibitory effects of green tea catechins on the activity of human matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin). J Biochem 133:571–576
Sagara Y, Inesi G (1991) Inhibition of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transport ATPase by thapsigargin at subnanomolar concentrations. J Biol Chem 266:13503–13506
Sagara Y, Fernandez-Belda F, de Meis L, Inesi G (1992) Characterization of the inhibition of intracellular Ca2+ transport ATPases by thapsigargin. J Biol Chem 267:12606–12613
Sang S, Hou Z, Lambert JD, Yang CS (2005) Redox properties of tea polyphenols and related biological activities. Antioxid Redox Signal 7:1704–1714
Schwartzenbach G, Senn H, Anderegg G (1957) Komplexone.XXIX. Ein grosser Chelateffekt besonderer. Helv Chim Acta 40:1886–1900
Stangl V, Dreger H, Stangl K, Lorenz M (2007) Molecular targets of tea polyphenols in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc Res 73:348–358
Tadini-Buoninsegni F, Bartolommei G, Moncelli MR, Tal DM, Lewis D, Inesi G (2008) Effects of high-affinity inhibitors on partial reactions, charge movements, and conformational states of the Ca2+ transport ATPase (Sarco-endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase). Mol Pharmacol 73:1134–1140
Toyoshima C (2009) How Ca2+-ATPase pumps ions across the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793:941–946
Wang J-H, Cheng J, Li C-R, Ye M, Ma Z, Cai F (2011) Modulation of Ca2+ signals by epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Int J Mol Sci 12:742–754
Wictome M, Michelangeli F, Lee AG, East JM (1992) The inhibitors thapsigargin and 2,5-di(tert-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone favour the E2 form of the Ca2+, Mg2 + -ATPase. FEBS Lett 304:109–113
Wu P-P, Kuo S-C, Huang W-W, Yang J-S, Lai K-C, Chen H-J, Lin K-L, Chiu Y-J, Huang L-J, Chung J-G (2009) (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate induced apoptosis in human adrenal cancer NCI-H295 cells through caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathway. Anticancer Res 29:1435–1442
Yin S-T, Tang M-L, Deng H-M, Xing T-R, Chen J-T, Wang H-L, Ruan D-Y (2009) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induced primary cultures of rat hippocampal neurons death linked to calcium overload and oxidative stress. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 379:551–564
Yu X, Inesi G (1995) Variable stoichiometric efficiency of Ca2+ and Sr2+ transport by the sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem 270:4361–4367
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soler, F., Asensio, M.C. & Fernández-Belda, F. Inhibition of the intracellular Ca2+ transporter SERCA (Sarco-Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase) by the natural polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate. J Bioenerg Biomembr 44, 597–605 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-012-9462-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-012-9462-z