Abstract
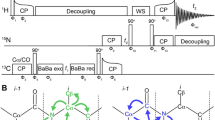
The use of small rotors capable of very fast magic-angle spinning (MAS) in conjunction with proton dilution by perdeuteration and partial reprotonation at exchangeable sites has enabled the acquisition of resolved, proton detected, solid-state NMR spectra on samples of biological macromolecules. The ability to detect the high-gamma protons, instead of carbons or nitrogens, increases sensitivity. In order to achieve sufficient resolution of the amide proton signals, rotors must be spun at the maximum rate possible given their size and the proton back-exchange percentage tuned. Here we investigate the optimal proton back-exchange ratio for triply labeled SH3 at 40 kHz MAS. We find that spectra acquired on 60 % back-exchanged samples in 1.9 mm rotors have similar resolution at 40 kHz MAS as spectra of 100 % back-exchanged samples in 1.3 mm rotors spinning at 60 kHz MAS, and for (H)NH 2D and (H)CNH 3D spectra, show 10–20 % higher sensitivity. For 100 % back-exchanged samples, the sensitivity in 1.9 mm rotors is superior by a factor of 1.9 in (H)NH and 1.8 in (H)CNH spectra but at lower resolution. For (H)C(C)NH experiments with a carbon–carbon mixing period, this sensitivity gain is lost due to shorter relaxation times and less efficient transfer steps. We present a detailed study on the sensitivity of these types of experiments for both types of rotors, which should enable experimentalists to make an informed decision about which type of rotor is best for specific applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal V et al (2014) De Novo 3D structure determination from sub-milligram protein samples by solid-state 100 kHz MAS NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. doi:10.1002/anie.201405730
Akbey U et al (2010) Optimum levels of exchangeable protons in perdeuterated proteins for proton detection in MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 46:67–73. doi:10.1007/S10858-009-9369-0
Akbey U et al (2014) Quadruple-resonance magic-angle spinning NMR spectroscopy of deuterated solid proteins. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53:2438–2442. doi:10.1002/anie.201308927
Asami S, Szekely K, Schanda P, Meier BH, Reif B (2012) Optimal degree of protonation for (1)H detection of aliphatic sites in randomly deuterated proteins as a function of the MAS frequency. J Biomol NMR 54:155–168. doi:10.1007/s10858-012-9659-9
Baldus M, Petkova AT, Herzfeld J, Griffin RG (1998) Cross polarization in the tilted frame: assignment and spectral simplification in heteronuclear spin systems. Mol Phys 95:1197–1207
Barbet-Massin E et al (2013) Out-and-back C–C scalar transfers in protein resonance assignment by proton-detected solid-state NMR under ultra-fast MAS. J Biomol NMR. doi:10.1007/s10858-013-9757-3
Barbet-Massin E et al (2014) Rapid proton-detected NMR assignment for proteins with fast magic angle spinning. J Am Chem Soc 136:12489–12497. doi:10.1021/ja507382j
Bockmann A et al (2009) Characterization of different water pools in solid-state NMR protein samples. J Biomol NMR 45:319–327. doi:10.1007/s10858-009-9374-3
Chevelkov V et al (2003) 1H detection in MAS solid-state NMR Spectroscopy of biomacromolecules employing pulsed field gradients for residual solvent suppression. J Am Chem Soc 125:7788–7789. doi:10.1021/ja029354b
Chevelkov V, Faelber K, Diehl A, Heinemann U, Oschkinat H, Reif B (2005) Detection of dynamic water molecules in a microcrystalline sample of the SH3 domain of a-spectrin by MAS solid-state NMR. J Biomol NMR 31:295–310. doi:10.1007/S10858-005-1718-Z
Chevelkov V, Rehbein K, Diehl A, Reif B (2006) Ultra-high resolution in proton solid-state NMR spectroscopy at high levels of deuteration. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:3878–3881. doi:10.1002/anie.200600328
Chevelkov V, Habenstein B, Loquet A, Giller K, Becker S, Lange A (2014) Proton-detected MAS NMR experiments based on dipolar transfers for backbone assignment of highly deuterated proteins. J Magn Reson 242:180–188. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2014.02.020
Hediger S, Meier BH, Ernst RR (1993) Cross-polarization under fast magic-angle sample-spinning using amplitude-modulated spin-lock sequences. Chem Phys Lett 213:627–635. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(93)89172-E
Huber M, Hiller S, Schanda P, Ernst M, Bockmann A, Verel R, Meier BH (2011) A proton-detected 4D solid-state NMR experiment for protein structure determination. ChemPhysChem 12:915–918. doi:10.1002/cphc.201100062
Huber M, With O, Schanda P, Verel R, Ernst M, Meier BH (2012) A supplementary coil for (2)H decoupling with commercial HCN MAS probes. J Magn Reson 214:76–80. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2011.10.010
Kay LE, Ikura M, Tschudin R, Bax A (1990) 3-Dimensional triple-resonance NMR-spectroscopy of isotopically enriched proteins. J Magn Reson 89:496–514. doi:10.1016/0022-2364(90)90333-5
Knight MJ et al (2011) Fast resonance assignment and fold determination of human superoxide dismutase by high-resolution proton-detected solid-state MAS NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:11697–11701. doi:10.1002/Anie.201106340
Knight MJ, Felli IC, Pierattelli R, Bertini I, Emsley L, Herrmann T, Pintacuda G (2012a) Rapid measurement of pseudocontact shifts in metalloproteins by proton-detected solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 134:14730–14733. doi:10.1021/ja306813j
Knight MJ et al (2012b) Structure and backbone dynamics of a microcrystalline metalloprotein by solid-state NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:11095–11100. doi:10.1073/pnas.1204515109
Laage S, Sachleben JR, Steuernagel S, Pierattelli R, Pintacuda G, Emsley L (2009) Fast acquisition of multi-dimensional spectra in solid-state NMR enabled by ultra-fast MAS. J Magn Reson 196(133–141):2008. doi:10.1016/J.Jmr.10.019
Lewandowski JR, Sein J, Sass HJ, Grzesiek S, Blackledge M, Emsley L (2010) Measurement of site-specific 13C spin-lattice relaxation in a crystalline protein. J Am Chem Soc 132:8252–8254. doi:10.1021/ja102744b
Lewandowski JR, Dumez JN, Akbey U, Lange S, Emsley L, Oschkinat H (2011) Enhanced resolution and coherence lifetimes in the solid-state NMR spectroscopy of perdeuterated proteins under ultrafast magic-angle spinning. J Phys Chem Lett 2:2205–2211. doi:10.1021/Jz200844n
Linser R, Fink U, Reif B (2008) Proton-detected scalar coupling based assignment strategies in MAS solid-state NMR spectroscopy applied to perdeuterated proteins. J Magn Reson 193(89–93):2008. doi:10.1016/J.Jmr.04.021
Linser R, Fink U, Reif B (2009) Probing surface accessibility of proteins using paramagnetic relaxation in solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 131:13703–13708. doi:10.1021/Ja903892j
Linser R, Fink U, Reif B (2010) Assignment of dynamic regions in biological solids enabled by spin-state selective NMR experiments. J Am Chem Soc 132:8891–8893. doi:10.1021/ja102612m
Linser R et al (2014) Solid-state NMR structure determination from diagonal-compensated, sparsely nonuniform-sampled 4D proton–proton restraints. J Am Chem Soc 136:11002–11010. doi:10.1021/Ja504603g
Marchetti A et al (2012) Backbone assignment of fully protonated solid proteins by 1H detection and ultrafast magic-angle-spinning NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:10756–10759. doi:10.1002/Anie.201203124
Nadaud PS, Helmus JJ, Sengupta I, Jaroniec CP (2010) Rapid acquisition of multidimensional solid-state NMR spectra of proteins facilitated by covalently bound paramagnetic tags. J Am Chem Soc 132:9561–9563. doi:10.1021/Ja103545e
Reif B, Jaroniec CP, Rienstra CM, Hohwy M, Griffin RG (2001) 1H–1H MAS correlation spectroscopy and distance measurements in a deuterated peptide. J Magn Reson 151:320–327. doi:10.1006/jmre.2001.2354
Shaka AJ, Keeler J, Frenkiel T, Freeman R (1983) An Improved sequence for broad-band decoupling—Waltz-16. J Magn Reson 52:335–338. doi:10.1016/0022-2364(83)90207-X
Stevens TJ et al (2011) A software framework for analysing solid-state MAS NMR data. J Biomol NMR 51:437–447. doi:10.1007/s10858-011-9569-2
van Rossum BJ, Castellani F, Rehbein K, Pauli J, Oschkinat H (2001) Assignment of the nonexchanging protons of the alpha-spectrin SH3 domain by two- and three-dimensional 1H–13C solid-state magic-angle spinning NMR and comparison of solution and solid-state proton chemical shifts. ChemBioChem 2:906–914. doi:10.1002/1439-7633(20011203)2:12<906:AID-CBIC906>3.0.CO;2-M
Verel R, Ernst M, Meier BH (2001) Adiabatic dipolar recoupling in solid-state NMR: the DREAM scheme. J Magn Reson 150:81–99. doi:10.1006/jmre.2001.2310
Ward ME, Shi L, Lake E, Krishnamurthy S, Hutchins H, Brown LS, Ladizhansky V (2011) Proton-detected solid-state NMR reveals intramembrane polar networks in a seven-helical transmembrane protein proteorhodopsin. J Am Chem Soc 133:17434–17443. doi:10.1021/ja207137h
Ward ME, Wang S, Krishnamurthy S, Hutchins H, Fey M, Brown LS, Ladizhansky V (2014) High-resolution paramagnetically enhanced solid-state NMR spectroscopy of membrane proteins at fast magic angle spinning. J Biomol NMR 58:37–47. doi:10.1007/s10858-013-9802-2
Wickramasinghe NP, Kotecha M, Samoson A, Past J, Ishii Y (2007) Sensitivity enhancement in 13C solid-state NMR of protein microcrystals by use of paramagnetic metal ions for optimizing 1H 1T relaxation. J Magn Reson 184:350–356. doi:10.1016/J.Jmr.2006.10.012
Wickramasinghe NP et al (2009) Nanomole-scale protein solid-state NMR by breaking intrinsic 1H 1T boundaries. Nat Methods 6:215–218. doi:10.1038/Nmeth.1300
Zhou DH, Rienstra CM (2008) High-performance solvent suppression for proton detected solid-state NMR. J Magn Reson 192:167–172. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2008.01.012
Zhou DH, Graesser DT, Franks WT, Rienstra CM (2006) Sensitivity and resolution in proton solid-state NMR at intermediate deuteration levels: quantitative linewidth characterization and applications to correlation spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 178:297–307. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2005.10.008
Zhou DH, Shah G, Cormos M, Mullen C, Sandoz D, Rienstra CM (2007a) Proton-detected solid-state NMR spectroscopy of fully protonated proteins at 40 kHz magic-angle spinning. J Am Chem Soc 129:11791–11801. doi:10.1021/ja073462m
Zhou DH et al (2007b) Solid-state protein-structure determination with proton-detected triple-resonance 3D magic-angle-spinning NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 46:8380–8383. doi:10.1002/anie.200702905
Zhou DH et al (2012) Solid-state NMR analysis of membrane proteins and protein aggregates by proton detected spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 54:291–305. doi:10.1007/s10858-012-9672-z
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Matthias Hiller and Sebastian Wegner for assistance installing and calibrating the probes in Berlin. A.J.N. was supported by fellowships from the Fulbright Program and the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. This work was also supported by the CNRS (TGIR-RMN-THC FR3050) and from a Joint Research Activity in the 7th Framework program of the EC (BioNMR No. 261863).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nieuwkoop, A.J., Franks, W.T., Rehbein, K. et al. Sensitivity and resolution of proton detected spectra of a deuterated protein at 40 and 60 kHz magic-angle-spinning. J Biomol NMR 61, 161–171 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-015-9904-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-015-9904-0