Abstract
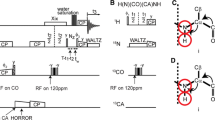
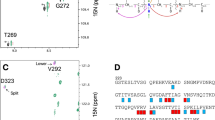
Heteronuclear direct-detection experiments, which utilize the slower relaxation properties of low γ nuclei, such as 13C have recently been proposed for sequence-specific assignment and structural analyses of large, unstructured, and/or paramagnetic proteins. Here we present two novel 15N direct-detection experiments. The CAN experiment sequentially connects amide 15N resonances using 13Cα chemical shift matching, and the CON experiment connects the preceding 13C′ nuclei. When starting from the same carbon polarization, the intensities of nitrogen signals detected in the CAN or CON experiments would be expected four times lower than those of carbon resonances observed in the corresponding 13C-detecting experiment, NCA-DIPAP or NCO-IPAP (Bermel et al. 2006b; Takeuchi et al. 2008). However, the disadvantage due to the lower γ is counteracted by the slower 15N transverse relaxation during detection, the possibility for more efficient decoupling in both dimensions, and relaxation optimized properties of the pulse sequences. As a result, the median S/N in the 15N observe CAN experiment is 16% higher than in the 13C observe NCA-DIPAP experiment. In addition, significantly higher sensitivity was observed for those residues that are hard to detect in the NCA-DIPAP experiment, such as Gly, Ser and residues with high-field Cα resonances. Both CAN and CON experiments are able to detect Pro resonances that would not be observed in conventional proton-detected experiments. In addition, those experiments are free from problems of incomplete deuterium-to-proton back exchange in amide positions of perdeuterated proteins expressed in D2O. Thus, these features and the superior resolution of 15N-detected experiments provide an attractive alternative for main chain assignments. The experiments are demonstrated with the small model protein GB1 at conditions simulating a 150 kDa protein, and the 52 kDa glutathione S-transferase dimer, GST.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnesano F, Banci L, Piccioli M (2005) NMR structures of paramagnetic metalloproteins. Q Rev Biophys 38:167–219
Balayssac S, Jimenez B, Piccioli M (2006) Assignment strategy for fast relaxing signals: complete aminoacid identification in thulium substituted calbindin D 9 K. J Biomol NMR 34:63–73
Bermel W, Bertini I, Felli IC, Kummerle R, Pierattelli R (2003) 13C Direct detection experiments on the paramagnetic oxidized monomeric copper, zinc superoxide dismutase. J Am Chem Soc 125:16423–16429
Bermel W, Bertini I, Felli IC, Lee YM, Luchinat C, Pierattelli R (2006a) Protonless NMR experiments for sequence-specific assignment of backbone nuclei in unfolded proteins. J Am Chem Soc 128:3918–3919
Bermel W, Bertini I, Felli IC, Piccioli M, Pierattelli R (2006b) 13C-detected protonless NMR spectroscopy of proteins in solution. Prog Nucl Magn Res Spec 48:25–45
Bermel W, Bertini I, Felli IC, Matzapetakis M, Pierattelli R, Theil EC, Turano P (2007) A method for Ca direct-detection in protonless NMR. J Magn Reson 188:301–310
Cai S, Seu C, Kovacs Z, Sherry AD, Chen Y (2006) Sensitivity enhancement of multidimensional NMR experiments by paramagnetic relaxation effects. J Am Chem Soc 128:13474–13478
Eletsky A, Moreira O, Kovacs H, Pervushin K (2003) A novel strategy for the assignment of side-chain resonances in completely deuterated large proteins using 13C spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 26:167–179
Emsley L, Bodenhausen G (1992) Optimization of shaped selective pulses for NMR using a quaternion description of their overall propagators. J Magn Reson 97:135–148
Enkhmandakh B, Makeyev AV, Bayarsaihan D (2006) The role of the proline-rich domain of Ssdp1 in the modular architecture of the vertebrate head organizer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:11631–11636
Ernst RR (1987) Principles of nuclear magnetic resonance in one and two dimensions. Oxford Science Publications, Oxford
Felli I, Brutscher B (2009) Recent advances in solution NMR: fast methods and heteronuclear direct detection. ChemPhysChem 10:1356–1368
Frueh DP, Arthanari H, Wagner G (2005) Unambiguous assignment of NMR protein backbone signals with a time-shared triple-resonance experiment. J Biomol NMR 33:187–196
Goddard TD, Kneller DG (2004) SPARKY 3 University of California, San Francisco
Grzesiek S, Bax A (1993) Amino acid type determination in the sequential assignment procedure of uniformly 13C/15N-enriched proteins. J Biomol NMR 3:185–204
Hsu S-TD, Bertoncini CW, Dobson CM (2009) Use of protonless NMR spectroscopy to alleviate the loss of information resulting from exchange-broadening. J Am Chem Soc 131:7222–7223
Hyberts SG, Takeuchi K, Wagner G (2010) Poisson-gap sampling and forward maximum entropy reconstruction for enhancing the resolution and sensitivity of protein NMR Data. J Am Chem Soc 132:2145–2147
John M, Park AY, Dixon NE, Otting G (2006) NMR detection of protein 15N spins near paramagnetic lanthanide ions. J Am Chem Soc 129:462–463
Kupče, Freeman R (1995) Adiabatic pulses for wideband inversion and broadband decoupling. J Magn Reson A 115:273–276
Kupče E, Freeman R, Wider G, Wüthrich K (1996) Figure of merit and cycling sidebands in adiabatic decoupling. J Magn Reson A 120:264–268
Lee D, Vögeli B, Pervushin K (2005) Detection of C′, Cα correlations in proteins using a new time- and sensitivity-optimal experiment. J Biomol NMR 31:273–278
Lin IJ, Xia B, King DS, Machonkin TE, Westler WM, Markley JL (2009) Hyperfine-shifted 13C and 15N NMR signals from costridium pasteurianum rubredoxin: extensive assignments and quantum chemical verification. J Am Chem Soc 131:15555–15563
Logan TM, Olejniczak ET, Xu RX, Fesik SW (1993) A general method for assigning NMR spectra of denatured proteins using 3D HC(CO)NH-TOCSY triple resonance experiments. J Biomol NMR 3:225–231
Machonkin TE, Westler WM, Markley JL (2004) Strategy for the study of paramagnetic proteins with slow electronic relaxation rates by NMR spectroscopy: application to oxidized human [2Fe-2S] ferredoxin. J Am Chem Soc 126:5413–5426
Marintchev A, Frueh D, Wagner G (2007) NMR methods for studying protein-protein interactions involved in translation initiation. Methods Enzymol 430:283–331
Marion D, Ikura M, Tschudin R, Bax A (1989) Rapid recording of 2D NMR spectra without phase cycling. Application to the study of hydrogen exchange in proteins. J Magn Reson 85:393–399
Pervushin K, Riek R, Wider G, Wüthrich K (1997) Attenuated T2 relaxation by mutual cancellation of dipole-dipole coupling and chemical shift anisotropy indicates an avenue to NMR structures of very large biological macromolecules in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:12366–12371
Rao A, Luo C, Hogan PG (1997) Transcription factors of the NFAT family: regulation and function. Annu Rev Immunol 15:707–747
Rovnyak D, Hoch JC, Stern AS, Wagner G (2004) Resolution and sensitivity of high field nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 30:1–10
Ruaro EM, Collavin L, Del Sal G, Haffner R, Oren M, Levine AJ, Schneider C (1997) A proline-rich motif in p53 is required for transactivation-independent growth arrest as induced by Gas1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:4675–4680
Serber Z, Richter C, Dötsch V (2001) Carbon-detected NMR experiments to investigate structure and dynamics of biological macromolecules. Chembiochem 2:247–251
Shaka AJ, Keeler J, Frenkiel T, Freeman R (1983) An improved sequence for broadband decoupling: WALTZ-16. J Magn Reson 52:335–338
Shaka AJ, Barker PB, Freeman R (1985) Computer-optimized decoupling scheme for wideband applications and low-level operation. J Magn Reson 64:547–552
Shimba N, Stern AS, Craik CS, Hoch JC, Dötsch V (2003) Elimination of 13Calpha splitting in protein NMR spectra by deconvolution with maximum entropy reconstruction. J Am Chem Soc 125:2382–2383
Takeuchi K, Sun ZY, Wagner G (2008) Alternate 13C–12C labeling for complete main chain resonance assignments using Ca direct-detection with applicability toward fast relaxing protein systems. J Am Chem Soc 130:17210–17211
Takeuchi K, Frueh DP, Hyberts SG, Sun ZJ, Wagner G (2010) High-resolution 3D CANCA NMR experiments for complete main chain assignments using Ca direct-detection. J Am Chem Soc (in press)
Vance CK, Kang YM, Miller A-F (1997) Selective 15N labeling and direct observation by NMR of the active-site glutamine of Fe-containing superoxide dismutase. J Biomol NMR 9:201–206
Vasos PR, Hall JB, Kummerle R, Fushman D (2006) Measurement of 15N relaxation in deuterated amide groups in proteins using direct nitrogen detection. J Biomol NMR 36:27–36
Venot C, Maratrat M, Dureuil C, Conseiller E, Bracco L, Debussche L (1998) The requirement for the p53 proline-rich functional domain for mediation of apoptosis is correlated with specific PIG3 gene transactivation and with transcriptional repression. EMBO J 17:4668–4679
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NIH (grants AI37581, GM47467 and EB 002026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takeuchi, K., Heffron, G., Sun, ZY.J. et al. Nitrogen-detected CAN and CON experiments as alternative experiments for main chain NMR resonance assignments. J Biomol NMR 47, 271–282 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-010-9430-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-010-9430-z