Abstract
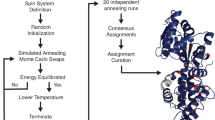
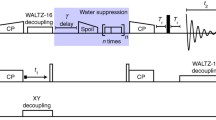
We describe an approach for the signal assignment and structural analysis with a suite of two-dimensional 13C–13C magic-angle-spinning solid-state NMR spectra of uniformly 13C-labeled peptides and proteins. We directly fit the calculated spectra to experimental ones by simulated annealing in restrained molecular dynamics program CNS as a function of atomic coordinates. The spectra are calculated from the conformation dependent chemical shift obtained with SHIFTX and the cross-peak intensities computed for recoupled dipolar interactions. This method was applied to a membrane-bound 14-residue peptide, mastoparan-X. The obtained C′, Cα and Cβ chemical shifts agreed with those reported previously at the precisions of 0.2, 0.7 and 0.4 ppm, respectively. This spectral fitting program also provides backbone dihedral angles with a precision of about 50° from the spectra even with resonance overlaps. The restraints on the angles were improved by applying protein database program TALOS to the obtained chemical shifts. The peptide structure provided by these restraints was consistent with the reported structure at the backbone RMSD of about 1 Å.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrof NS, Griffin RG (2002) Soft-triple resonance solid-state NMR experiments for assignments of U-13C, 15N labeled peptides and proteins. J Magn Reson 158:157–163
Baldus M, Petkova AT, Herzfeld J, Griffin RG (1998) Cross polarization in the tilted frame: assignment and spectral simplification in heteronuclear spin systems. Mol Phys 95:1197–1207
Bak M, Rasmussen JT, Nielsen NC (2000) SIMPSON: A general simulation program for solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 147:296–330
Bennett AE, Rienstra CM, Griffiths JM, Zhen W, Lansbury PT Jr, Griffin RG (1998) Homonuclear radio frequency-driven recoupling in rotating solids. J Chem Phys 108:9463–9479
Brünger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, Read RJ, Rice LM, Simonson T, Warren GL (1998) Crystallography & NMR System: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D54:905–921
Buchler NEG, Zuiderweg ERP, Wang H, Goldstein RA (1997) Protein heteronuclear NMR assignments using mean-field simulated annealing. J Magn Reson 125:34–42
Cadars S, Lesage A, Emsley L (2005) Chemical shift correlations in disordered solids. J Am Chem Soc 127:4466–4476
Castellani F, van Rossum BJ, Diehl A, Rehbein K, Oschkinat H (2003) Determination of solid-state NMR structures of proteins by means of three-dimensional 15N-13C-13C dipolar correlation spectroscopy and chemical shift analysis. Biochemistry 42:11476–11483
Cieslar C, Clore GM, Gronenborn AM (1988) Computer-aided sequential assignment of protein 1H NMR spectra. J Magn Reson 80:119–127
Cornilescu G, Delaglio F, Bax A (1999) Protein backbone angle restraints from searching a database for chemical shift and sequence homology. J Biomol NMR 13:289–302
de Dios AC, Pearson JG, Oldfield E (1993) Chemical shifts in proteins: an ab initio study of carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shielding in glycine, alanine, and valine residues. J Am Chem Soc 115:9768–9773
Eccles C, Güntert P, Billeter M, Wüthrich K (1991) Efficient analysis of protein 2D NMR spectra using the software package EASY. J Biomol NMR 1:111–130
Egawa A, Fujiwara T, Mizoguchi T, Kakitani Y, Koyama Y, Akutsu H (2007) Structure of the light-harvesting bacteriochlorophyll c assembly in chlorosomes from Chlorobium limicola determined by solid-state NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:790–795
Elena B, Pintacuda G, Mifsud N, Emsley L (2006) Molecular structure determination in powders by NMR crystallography from proton spin diffusion. J Am Chem Soc 128:9555–9560
Etzkorn M, Martell S, Andronesi OC, Seidel K, Engelhard M, Baldus M (2007) Secondary structure, dynamics, and topology of a seven-helix receptor in native membranes, studied by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:459–462
Franks WT, Zhou DH, Wylie BJ, Money BG, Graesser DT, Frericks HL, Sahota G, Rienstra CM (2005) Magic-angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy of the β1 immunoglobulin binding domain of protein G (GB1): 15N and 13C chemical shift assignments and conformational analysis. J Am Chem Soc 127:12291–12305
Fujiwara T, Todokoro Y, Yanagishita H, Tawarayama M, Kohno T, Wakamatsu K, Akutsu H (2004) Signal assignments and chemical-shift structural analysis of uniformly 13C, 15N-labeled peptide, mastoparan-X, by multidimensional solid-state NMR under magic-angle spinning. J Biomol NMR 28:311–325
Grommek A, Meier BH, Ernst M (2006) Distance information from proton-driven spin diffusion under MAS. Chem Phys Lett 427:404–409
Güntert P, Mumenthaler C, Wüthrich K (1997) Torsion angle dynamics for NMR structure calculation with the new program DYANA. J Mol Biol 273:283–298
Harada E, Todokoro Y, Akutsu H, Fujiwara T (2006) Detection of peptide-phospholipid interaction sites in bilayer membranes by 13C NMR spectroscopy: Observation of 2H/31P-selective 1H-depolarization under magic-angle spinning. J Am Chem Soc 128:10654–10655
Havlin RH, Tycko R (2005) Probing site-specific conformational distributions in protein folding with solid-state NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:3284–3289
Heise H, Luca S, de Groot BL, Grubmüller H, Baldus M (2005) Probing conformational disorder in neurotensin by two-dimensional solid-state NMR and comparison to molecular dynamics simulations. Biophys J 89:2113–2120
Hohwy M, Jakobsen HJ, Edén M, Levitt MH, Nielsen NC (1998) Broadband dipolar recoupling in the nuclear magnetic resonance of rotating solids: a compensated C7 pulse sequence. J Chem Phys 108:2686–2694
Hong M (1999) Solid-state dipolar INADEQUATE NMR spectroscopy with a large double-quantum spectral width. J Magn Reson 136:86–91
Hughes CE, Luca S, Baldus M (2004) Radio-frequency driven polarization transfer without heteronuclear decoupling in rotating solids. Chem Phys Lett 385:435–440
Jakeman DL, Mitchell DJ, Shuttleworth WA, Evans JNS (1998) Effects of sample preparation conditions on biomolecular solid-state NMR lineshapes. J Biomol NMR 12:417–421
Kainosho M, Torizawa T, Iwashita Y, Terauchi T, Ono AM, Güntert P (2006) Optimal isotope labelling for NMR protein structure determinations. Nature 440:52–57
Kleywegt GJ (2000) Validation of protein crystal structures. Acta Cryst D56:249–265
Kleywegt GJ, Boelens R, Cox M, Llinás M, Kaptein R (1991) Computer-assisted assignment of 2D 1H NMR spectra of proteins: basic algorithms and application to phoratoxin B. J Biomol NMR 1:23–47
Kobayashi M, Matsuki Y, Yumen I, Fujiwara T, Akutsu H (2006) Signal assignment and secondary structure analysis of a uniformly [13C, 15N]-labeled membrane protein, H+-ATP synthase subunit c, by magic-angle spinning solid-state NMR. J Biomol NMR 36:279–293
Lange A, Giller K, Hornig S, Martin-Eauclaire M-F, Pongs O, Becker S, Baldus M (2006) Toxin-induced conformational changes in a potassium channel revealed by solid-state NMR. Nature 440:959–962
Le HB, Pearson JG, de Dios AC, Oldfield E (1995) Protein structure refinement and prediction via NMR chemical shifts and quantum chemistry. J Am Chem Soc 117:3800–3807
Le H, Oldfield E (1994) Correlation between 15N NMR chemical shifts in proteins and secondary structure. J Biomol NMR 4:341–348
Leopold MF, Urbauer JK, Wand AJ (1994) Resonance assignment strategies for the analysis of NMR spectra of proteins. Mol Biotechnol 2:61–93
Leutner M, Gschwind RM, Liermann J, Schwarz C, Gemmecker G, Kessler H (1998) Automated backbone assignment of labeled proteins using the threshold accepting algorithm. J Biomol NMR 11:31–43
Liu G, Shen Y, Atreya HS, Parish D, Shao Y, Sukumaran DK, Xiao R, Yee A, Lemak A, Bhattacharya A, Acton TA, Arrowsmith CH, Montelione GT, Szypersk T (2005) NMR data collection and analysis protocol for high-throughput protein structure determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:10487–10492
Marulanda D, Tasayco ML, McDermott A, Cataldi M, Arriaran V, Polenova T (2004) Magic angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy for structural studies of protein interfaces Resonance assignments of differentially enriched Escherichia coli thioredoxin reassembled by fragment complementation. J Am Chem Soc 126:16608–16620
Matsuki Y, Akutsu H, Fujiwara T (2004) Precision 1H-1H distance measurement via 13C NMR signals: Utilization of 1H-1H double-quantum dipolar interactions recoupled under magic angle spinning conditions. Magn Reson Chem 42:291–300
Mertens HDT, Gooley PR (2005) Validating the use of database potentials in protein structure determination by NMR. FEBS Lett 579:5542–5548
Meiler J (2003) PROSHIFT: Protein chemical shift prediction using artificial neural networks. J Biomol NMR 26:25–37
Morcombe CR, Zilm KW (2003) Chemical shift referencing in MAS solid state NMR. J Magn Reson 162:479–486
Moseley HNB, Montelione GT (1999) Automated analysis of NMR assignments and structures for proteins. Curr Opin Struct Biol 9:635–642
Neal S, Berjanskii M, Zhang H, Wishart DS (2006) Accurate prediction of protein torsion angles using chemical shifts and sequence homology. Magn Reson Chem 44:S158–S167
Neal S, Nip AM, Zhang H, Wishart DS (2003) Rapid and accurate calculation of protein 1H, 13C and 15N chemical shifts. J Biomol NMR 26:215–240
Nederveen AJ, Doreleijers JF, Vranken W, Miller Z, Spronk CAEM, Nabuurs SB, Güntert P, Livny M, Markley JL, Nilges M, Ulrich EL, Kaptein R, Bonvin AMJJ (2005) RECOORD: A recalculated coordinate database of 500+ proteins from the PDB using restraints from the BioMagResBank. Proteins 59:662–672
Nilges M, O’Donoghue SI (1998) Ambiguous NOEs and automated NOE assignment. Prog Nucl Magn Reson 32:107–139
Oas TG, Hartzell CJ, Dahlquist FW, Drobny GP (1987) The amide nitrogen-15 chemical shift tensors of four peptides determined from carbon-13 dipole-coupled chemical shift powder patterns. J Am Chem Soc 109:5962–5966
Oldfield E (2002) Chemical shifts in amino acids, peptides, and proteins: from quantum chemistry to drug design. Annu Rev Phys Chem 53:349–378
Ösapay K, Case DA (1994) Analysis of proton chemical shifts in regular secondary structure of proteins. J Biomol NMR 4:215–230
Pang Y, Zuiderweg ERP (2000) Determination of protein backbone 13CO chemical shift anisotropy tensors in solution. J Am Chem Soc 122:4841–4842
Shoji A, Ozaki T, Fujito T, Deguchi K, Ando I, Magoshi J (1998) 15N chemical shift tensors and conformation of solid polypeptides containing 15N-labeled glycine residue by 15N NMR. J Mol Struct 441:251–266
Sun H, Sanders LK, Oldfield E (2002) Carbon-13 NMR shielding in the twenty common amino acids: comparisons with experimental results in proteins. J Am Chem Soc 124:5486–5495
Thomas PD, Basus VJ, James TL (1991) Protein solution structure determination using distances from two-dimensional nuclear overhauser effect experiments: effect of approximations on the accuracy of derived structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:1237–1241
Todokoro Y, Yumen I, Fukushima K, Kang SW, Park JS, Kohno T, Wakamatsu K, Akutsu H, Fujiwara T (2006) Structure of tightly membrane-bound mastoparan-X, a g-protein-activating peptide, determined by solid-state NMR. Biophys J 91:1368–1379
Veshtort M, Griffin RG (2006) SPINEVOLUTION: a powerful tool for the simulation of solid and liquid state NMR experiments. J Magn Reson 178:248–282
Wagner G, Pardi A, Wüthrich K (1983) Hydrogen bond length and proton NMR chemical shifts in proteins. J Am Chem Soc 105:5948–5949
Wang Y, Jardetzky O (2004) Predicting 15N chemical shifts in proteins using the preceding residue-specific individual shielding surfaces from ϕ, ψi-1, and χ1 torsion angles. J Biomol NMR 28:327–340
Wei Y, Lee DK, Ramamoorthy A (2001) Solid-state 13C NMR chemical shift anisotropy tensors of polypeptides. J Am Chem Soc 123:6118–6126
Wishart DS, Case DA (2001) Use of chemical shifts in macromolecular structure determination. Meth Enzymol 338:3–34
Wishart DS, Nip AM (1998) Protein chemical shift analysis: a practical guide. Biochem Cell Biol 76:153–163
Xu XP, Case DA (2002) Probing multiple effects on 15N, 13Cα, 13Cβ, and 13C′ chemical shifts in peptides using density functional theory. Biopolymers 65:408–423
Xu Y, Wang X, Yang J, Vaynberg J, Qin J (2006) PASA – A program for automated protein NMR backbone signal assignment. J Biomol NMR 34:41–56
Zimmerman DE, Kulikowski CA, Huang Y, Feng W, Tashiro M, Shimotakahara S, Chien CY, Powers R, Montelione GT (1997) Automated analysis of protein NMR assignments using methods from artificial intelligence. J Mol Biol 269:592–610
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Prof. D. S. Wishart for releasing the source program of SHIFTX to us. We also thank Dr. Y. Todokoro for the sample preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Software availability
The program described in this paper is available from the authors upon request.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuki, Y., Akutsu, H. & Fujiwara, T. Spectral fitting for signal assignment and structural analysis of uniformly 13C-labeled solid proteins by simulated annealing based on chemical shifts and spin dynamics. J Biomol NMR 38, 325–339 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-007-9170-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-007-9170-x