Abstract
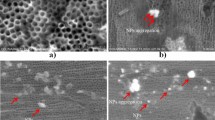
Implanted materials are susceptible to bacterial colonization and biofilm formation, which can result in severe infection and lost implant function. UV induced photocatalytic disinfection on TiO2 and release of Ag+ ions are two promising strategies to combat such events, and can be combined for improved efficiency. In the current study, a combinatorial physical vapor deposition technique was utilized to construct a gradient coating between Ag and Ti oxide, and the coating was evaluated for antibacterial properties in darkness and under UV light against Staphylococcus epidermidis. The findings revealed a potent antibacterial effect in darkness due to Ag+ release, with near full elimination (97 %) of viable bacteria and visible cell lysis on Ag dominated surfaces. The photocatalytic activity, however, was demonstrated poor due to low TiO2 crystallinity, and UV light irradiation of the coating did not contribute to the antibacterial effect. On the contrary, bacterial viability was in several instances higher after UV illumination, proposing a UV induced SOS response from the bacteria that limited the reduction rate during Ag+ exposure. Such secondary effects should thus be considered in the development of multifunctional coatings that rely on UV activation.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campoccia D, Montanaro L, Arciola CR. A review of the clinical implications of anti-infective biomaterials and infection-resistant surfaces. Biomaterials. 2013;34:8018–29.
Neu HC. The crisis in antibiotic resistance. Science. 1992;257:1064–73.
Yu J, Xiong J, Cheng B, Liu S. Fabrication and characterization of Ag–TiO2 multiphase nanocomposite thin films with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal B Environ. 2005;60:211–21.
Yu B, Leung KM, Guo Q, Lau WM, Yang J. Synthesis of Ag–TiO2 composite nano thin film for antimicrobial application. Nanotechnology. 2011;22:115603.
Maness P, Smolinski S, Blake D, Huang Z, Wolfrum E, Jacoby W. Bactericidal activity of photocatalytic TiO2 reaction: toward an understanding of its killing mechanism. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999;65:4094–8.
Feng QL, Wu J, Chen GQ, Cui FZ, Kim TN, Kim JO. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;52:662–8.
Morones JR, Elechiguerra JL, Camacho A, Holt K, Kouri JB, Ramírez JT, et al. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology. 2005;16:2346–53.
Sung-Suh HM, Choi JR, Hah HJ, Koo SM, Bae YC. Comparison of Ag deposition effects on the photocatalytic activity of nanoparticulate TiO2 under visible and UV light irradiation. J Photoch Photobiol A. 2004;163:37–44.
Page K, Palgrave RG, Parkin IP, Wilson M, Savin SLP, Chadwick AV. Titania and silver-titania composite films on glass-potent antimicrobial coatings. J Mater Chem. 2006;17:95–104. doi:10.1039/b611740f.
Seery MK, George R, Floris P, Pillai SC. Silver doped titanium dioxide nanomaterials for enhanced visible light photocatalysis. J Photoch Photobio A. 2007;189:258–63. doi:10.1016/j.jphotochem.2007.02.010.
Mai L, Wang D, Zhang S, Xie Y, Huang C, Zhang Z. Synthesis and bactericidal ability of Ag/TiO2 composite films deposited on titanium plate. Appl Surf Sci. 2010;257:974–8.
Necula BS, Fratila-Apachitei LE, Zaat SAJ, Apachitei I, Duszczyk J. In vitro antibacterial activity of porous TiO2–Ag composite layers against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Biomater. 2009;5:3573–80.
Machida M, Norimoto K, Kimura T. Antibacterial activity of photocatalytic titanium dioxide thin films with photodeposited silver on the surface of sanitary ware. J Am Ceram Soc. 2004;88:95–100.
Ewald A, Glückermann SK, Thull R, Gbureck U. Antimicrobial titanium/silver PVD coatings on titanium. Biomed Eng Online. 2006;5:22.
Unosson E, Rodriguez D, Welch K, Engqvist H. Reactive combinatorial synthesis and characterization of a gradient Ag-Ti oxide thin film with antibacterial properties. Acta Biomater. 2015;11:503–10.
McFarland E, Weinberg W. Combinatorial approaches to materials discovery. Trends Biotechnol. 1999;17:107–15.
Amis EJ, Xiang X-D, Zhao J-C. Combinatorial materials science: What’s new since Edison? MRS Bull. 2002;27:295–300.
Unosson E, Tsekoura EK, Engqvist H, Welch K. Synergetic inactivation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Streptococcus mutansin a TiO2/H2O2/UV system. Biomatter. 2013;3:e26727.
Unosson E, Cai Y, Jiang X, Lööf J, Welch K, Engqvist H. Antibacterial properties of dental luting agents: potential to hinder the development of secondary caries. Int J Dent. 2012;2012:1–7.
Sarker SD, Nahar L, Kumarasamy Y. Microtitre plate-based antibacterial assay incorporating resazurin as an indicator of cell growth, and its application in the in vitro antibacterial screening of phytochemicals. Methods. 2007;42:321–4.
Simchi A, Tamjid E, Pishbin F, Boccaccini AR. Recent progress in inorganic and composite coatings with bactericidal capability for orthopaedic applications. Nanomedicine. 2011;7:22–39.
Foster HA, Ditta IB, Varghese S, Steele A. Photocatalytic disinfection using titanium dioxide: spectrum and mechanism of antimicrobial activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011;90:1847–68.
Zhao L, Wang H, Huo K, Cui L, Zhang W, Ni H, et al. Antibacterial nano-structured titania coating incorporated with silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2010;32:5706–16.
Lan M-Y, Liu C-P, Huang H-H, Lee S-W. Both enhanced biocompatibility and antibacterial activity in Ag-decorated TiO2 nanotubes. PLoS One. 2013;8:e75364.
Unosson E, Welch K, Persson C, Engqvist H. Stability and prospect of UV/H2O2 activated titania films for biomedical use. Appl Surf Sci. 2013;285:317–23.
Carp O, Huisman C, Reller A. Photoinduced reactivity of titanium dioxide. Prog Solid State Chem. 2004;32:33–177.
Lindenauer KG, Darby JL. Ultraviolet disinfection of wastewater: Effect of dose on subsequent photoreactivation. Water Res. 1993;28:805–17.
United States Environmental Protection Agency. Ultraviolet disinfection guidance manual for the final long term 2 enhanced surface water treatment rule. http://www.epa.gov/ogwdw000/disinfection/lt2/pdfs/guide_lt2_uvguidance.pdf; 2006 Nov pp. 1–436.
Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, Kim J-H, Park SJ, Lee HJ, et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine. 2007;3:95–101.
Sant SB, Gill KS, Burrell RE. Nanostructure, dissolution and morphology characteristics of microcidal silver films deposited by magnetron sputtering. Acta Biomater. 2007;3:341–50.
Crowley DJ, Courcelle J. Answering the call: coping with DNA damage at the most inopportune time. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2002;2:66–74.
Erill I, Campoy S, Barbé J. Aeons of distress: an evolutionary perspective on the bacterial SOS response. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2007;31:637–56.
Gallardo-Moreno AM, Pacha-Olivenza MA, Fernández-Calderon M-C, Pérez-Giraldo C, Bruque JM, González-Martín M-L. Bactericidal behaviour of Ti6Al4V surfaces after exposure to UV-C light. Biomaterials. 2010;31:5159–68.
Lilja M, Forsgren J, Welch K, Åstrand M, Engqvist H, Strømme M. Photocatalytic and antimicrobial properties of surgical implant coatings of titanium dioxide deposited though cathodic arc evaporation. Biotechnol Lett. 2012;34:2299–305.
Cooper VS, Bennett AF, Lenski RE. Evolution of thermal dependence of growth rate of Escherichia coli populations during 20,000 generations in a constant environment. Evolution. 2001;55:889–96.
Guillobel H, Leitão AC. Characterization of Staphylococcus epidermidis mutants sensitive to ultraviolet radiation. Mutat Res. 1988;193:1–10.
Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J Colloid Interf Sci. 2004;275:177–82.
Gao A, Hang R, Huang X, Zhao L, Zhang X, Wang L, et al. The effects of titania nanotubes with embedded silver oxide nanoparticles on bacteria and osteoblasts. Biomaterials. 2014;35:4223–35.
Jung WK, Koo HC, Kim KW, Shin S, Kim SH, Park YH. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008;74:2171–8.
Kalishwaralal K, BarathManiKanth S, Pandian SRK, Deepak V, Gurunathan S. Silver nanoparticles impede the biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Colloids Surf B. 2009;79:340–4.
Mohanty S, Mishra S, Jena P, Jacob B, Sarkar B, Sonawane A. An investigation on the antibacterial, cytotoxic, and antibiofilm efficacy of starch-stabilized silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine. 2012;8:916–24.
Qin H, Cao H, Zhao Y, Zhu C, Cheng T, Wang Q, et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-biofilm effects of silver nanoparticles immobilized on titanium. Biomaterials. 2014;35:9114–25.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research (SSF), through the ProViking Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Unosson, E., Morgenstern, M., Engqvist, H. et al. In vitro antibacterial properties and UV induced response from Staphylococcus epidermidis on Ag/Ti oxide thin films. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 27, 49 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-015-5662-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-015-5662-5