Abstract
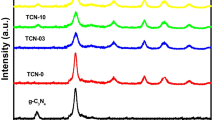
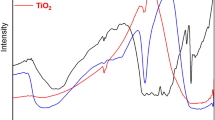
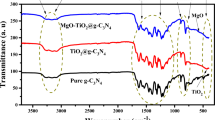
A ternary TiO2/Y2O3@g-C3N4 nanocomposite was fabricated by a simple sonochemical method and its photocatalytic activity for organic pollutants was examined. X-ray diffraction analysis, transmission electron microscopy coupled with elemental chemical composition confirmed the formation of network-like nanostructure composed of Y2O3/TiO2 nanoparticles coupled with g-C3N4 nanosheets. Due to its large surface area, low band gap energy, and the presence of photogenerated holes, electrons, and hydroxyl radicals, the nanohybrid composite exhibited excellent photocatalytic degradation of Congo Red dye in an aqueous solution under optimized operational conditions, i.e., 100% for a short time of 60 min. The photodegradation kinetics was validated by the pseudo-first-order model and the photodegradation mechanism was elucidated. This study provides insights into the degradation of hazardous and toxic organic pollutants under visible light illumination.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
X. Cao et al., Band gap opening of graphene by forming heterojunctions with the 2D carbonitrides nitrogenated holey graphene, g-C3N4, and g-CN: electric field effect. J. Phys. Chem. C 120(20), 11299–11305 (2016)
J. Liu et al., Adsorption of Congo red dye on FexCo3-xO4 nanoparticles. J. Environ. Manag. 238, 473–483 (2019)
H. Hou et al., Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution with hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite. Chem. Eng. J. 211–212, 336–342 (2012)
M. Khadhraoui et al., Discoloration and detoxicification of a Congo red dye solution by means of ozone treatment for a possible water reuse. J. Hazard. Mater. 161(2), 974–981 (2009)
M. Harja, G. Buema, D. Bucur, Recent advances in removal of Congo Red dye by adsorption using an industrial waste. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 6087 (2022)
I. Ali, Z.A. AL-Othman, A. Alwarthan, Molecular uptake of Congo red dye from water on iron composite nano particles. J. Mol. Liq. 224, 171–176 (2016)
A.M.S. Solano et al., Degradation of acidic aqueous solutions of the diazo dye Congo Red by photo-assisted electrochemical processes based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Appl. Catal. B 168, 559–571 (2015)
M.R. Abukhadra, A. Adlii, B.M. Bakry, Green fabrication of bentonite/chitosan@ cobalt oxide composite (BE/CH@ Co) of enhanced adsorption and advanced oxidation removal of Congo red dye and cr (VI) from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 126, 402–413 (2019)
J. Garvasis et al., Efficient removal of Congo red from aqueous solutions using phytogenic aluminum sulfate nano coagulant. Mater. Chem. Phys. 251, 123040 (2020)
K. Sathishkumar et al., Sequential electrochemical oxidation and bio-treatment of the azo dye Congo red and textile effluent. J. Photochem. Photobiol., B 200, 111655 (2019)
M.A.B. Aissa et al., Environmental remediation applications of MxOy-gC3N4 nanocomposites (M = mg, Ti, and zn): photocatalytic activity for Indigo carmine dye degradation. Diam. Relat. Mater. 136, 109988 (2023)
R.A. Abumousa, MgO@ZrO2@g-C3N4 composite for efficient photodegradation of alizarin red dye. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 155, 111086 (2023)
A. Bessadok-Jemai et al., Hybrid CaO@MgO@g-C3N4 nanostructure as a cost-effective sorbent for hazardous organic dyes activated by additives. Diam. Relat. Mater. 133, 109757 (2023)
X. Liu et al., Co3O4-g-C3N4 composites with enhanced peroxidase-like activities for the degradation of environmental rhodamine B. Reaction Kinetics Mech. Catal. 130(2), 1109–1121 (2020)
A. Modwi et al., Superior removal of dyes by mesoporous MgO/g-C3N4 fabricated through ultrasound method: Adsorption mechanism and process modeling. Environ. Res. 205, 112543 (2022)
A. Toghan, A. Modwi, Boosting unprecedented indigo carmine dye photodegradation via mesoporous MgO@ g-C3N4 nanocomposite. J. Photochem. Photobiol., a 419, 113467 (2021)
A. Toghan et al., Mesoporous TiO2@ g-C3N4 composite: construction, characterization, and boosting indigo carmine dye destruction. Diam. Relat. Mater. 118, 108491 (2021)
A.B. Jorge et al., H2 and O2 evolution from water half-splitting reactions by graphitic carbon nitride materials. J. Phys. Chem. C 117(14), 7178–7185 (2013)
P. Audebert et al., State of the art in the preparation and properties of molecular monomeric s-heptazines: syntheses, characteristics, and functional applications. Chem. Rev. 121(4), 2515–2544 (2021)
Y. Zhang et al., Non-covalent doping of graphitic carbon nitride polymer with graphene: controlled electronic structure and enhanced optoelectronic conversion. Energy Environ. Sci. 4(11), 4517–4521 (2011)
B. Guo et al., Numerical study on optoelectronic properties of alkaline-earth metal doped g-C3N4. Chem. Phys. 544, 111104 (2021)
P.P. Gotipamul et al., Impact of piezoelectric effect on the heterogeneous visible photocatalysis of g-C3N4/Ag/ZnO tricomponent. Chemosphere. 287, 132298 (2022)
G. Zhou et al., Switching charge transfer of g-C3N4/BiVO4 heterojunction from type II to Z-scheme via interfacial vacancy engineering for improved photocatalysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 47(14), 8749–8760 (2022)
L. Xu et al., Improvement of Fe2+/peroxymonosulfate oxidation of organic pollutants by promoting Fe2 + regeneration with visible light driven g-C3N4 photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 430, 132828 (2022)
J. Wu et al., g-C3N4 modified Co3O4 as efficient catalysts for aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol. Reaction Kinetics Mech. Catal. 128(1), 109–120 (2019)
L. Yan et al., Tremella-like integrated carbon nitride with polyvinylimine-doped for enhancing photocatalytic degradation and hydrogen evolution performances. Sep. Purif. Technol. 279, 119766 (2021)
X. Ren et al., Effect of hydrogen bond interaction in precursor on photocatalytic oxidation of MB by C-GA/g-C3N4 composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 606, 154941 (2022)
D. Han et al., High-yield and low-cost method to synthesize large-area porous g-C3N4 nanosheets with improved photocatalytic activity for gaseous nitric oxide and 2-propanol photodegradation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 464, 577–585 (2019)
W. Gong et al., Phase equilibria of the TiO2–Y2O3 system. Calphad. 33(3), 624–627 (2009)
T. Rafique et al., Geochemical factors controlling the occurrence of high fluoride groundwater in the Nagar Parkar area, Sindh, Pakistan. J. Hazard. Mater. 171(1–3), 424–430 (2009)
X. Jiang et al., Preparation and visible-light photocatalytic activity of ag-loaded TiO2@ Y2O3 hollow microspheres with double-shell structure. Powder Technol. 377, 621–631 (2021)
S.J. Schrauben et al., Association of multiple plasma biomarker concentrations with progression of prevalent diabetic kidney disease: findings from the chronic renal insufficiency cohort (CRIC) study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 32(1), 115–126 (2021)
R. Srinivasan, R. Yogamalar, A.C. Bose, Structural and optical studies of yttrium oxide nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Mater. Res. Bull. 45(9), 1165–1170 (2010)
C.A. Traina, T.J. Dennes, J. Schwartz, A modular monolayer coating enables cell targeting by luminescent yttria nanoparticles. Bioconjug. Chem. 20(3), 437–439 (2009)
T. Berger et al., Photocatalytic degradation of organic dye via atomic layer deposited TiO2 on ceramic membranes in single-pass flow-through operation. J. Membr. Sci. 604, 118015 (2020)
Y. Zhao et al., Removal of Escherichia Coli from water using functionalized porous ceramic disk filter coated with Fe/TiO2 nano-composites. J. Water Process. Eng. 33, 101013 (2020)
A.L. Kozlovskiy et al., Phase transformations and photocatalytic activity of nanostructured Y2O3/TiO2-Y2TiO5 ceramic such as doped with carbon nanotubes. Molecules 25(8), 1943 (2020)
A. El-Maaref et al., Enhancement of spectroscopic parameters of Er3+-doped cadmium lithium gadolinium silicate glasses as an active medium for lasers and optical amplifiers in the NIR-region. Solid State Sci. 113, 106539 (2021)
Y. Ren et al., Preparation of Y2O3/TiO2-Loaded polyester fabric and its Photocatalytic properties under visible light irradiation. Polymers. 14(14), 2760 (2022)
M. Youssry, D. Guyomard, B. Lestriez, Carbon black dispersions in surfactant-based microemulsion–CORRIGENDUM. J. Mater. Res. 33(9), 1309–1309 (2018)
Y. Li, P.D. Hodgson, C. Wen, The effects of calcium and yttrium additions on the microstructure, mechanical properties and biocompatibility of biodegradable magnesium alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 46(2), 365–371 (2011)
A.A. Manda et al., Highly Efficient UV-Visible Absorption of TiO2/Y2O3 Nanocomposite Prepared by Nanosecond Pulsed Laser Ablation Technique. Arab. J. Chem. 15, 104004 (2022)
Y. Li et al., Synergetic removal of oppositely charged dyes by co-precipitation and amphoteric self-floating capturer: mechanism investigation by molecular simulation. Chemosphere. 296, 134033 (2022)
W. Han et al., The promoting role of different carbon allotropes cocatalysts for semiconductors in photocatalytic energy generation and pollutants degradation. Front. Chem. 5, 84 (2017)
S. Zhang et al., Recent developments in fabrication and structure regulation of visible-light-driven g-C3N4-based photocatalysts towards water purification: a critical review. Catal. Today. 335, 65–77 (2019)
Z. Abaker et al., Superior uptake of Cu (II) from aquatic media via Y2O3-ZnO nanostructures. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 30, 100879 (2022)
G. Chen et al., Temperature-dependent emission color and temperature sensing behavior in Tm3+/Yb3+: Y2O3 nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 77, 233–239 (2018)
M.Y. Ye et al., 0D/2D heterojunctions of vanadate quantum dots/graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for enhanced visible-light‐driven photocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56(29), 8407–8411 (2017)
L. Khezami et al., Mesoporous Sn@ TiO2 nanostructures as excellent adsorbent for Ba ions in aqueous solution. Ceram. Int. 48(4), 5805–5813 (2022)
B.C. Lippens, J. De Boer, Studies on pore systems in catalysts: V. The t method. J. Catal. 4(3), 319–323 (1965)
F.J. Sotomayor, K.A. Cychosz, M. Thommes, Characterization of micro/mesoporous materials by physisorption: concepts and case studies. Acc. Mater. Surf. Res. 3(2), 34–50 (2018)
M.A. Al-Ghouti, D.A. Da’ana, Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: a review. J. Hazard. Mater. 393, 122383 (2020)
C.S.D. Rodrigues et al., Nitrophenol degradation by heterogeneous Fenton’s oxidation over activated carbon-based catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 219, 109–122 (2017)
O. Długosz et al., Synthesis of Fe3O4/ZnO nanoparticles and their application for the photodegradation of anionic and cationic dyes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18(3), 561–574 (2021)
A. Modwi et al., Efficient pb (II) adsorption in aqueous solution by hierarchical 3D/2D TiO2/CNNS nanocomposite. Mater. Sci. Engineering: B 289, 116191 (2023)
B. Zhang et al., Molten salt assisted in-situ synthesis of TiO2/g-C3N4 composites with enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity and adsorption ability. J. Photochem. Photobiol., a 362, 1–13 (2018)
C. Zhang et al., Multistage polymerization design for g-C3N4 nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic activity by modifying the polymerization process of melamine. ACS Omega. 4(17), 17148–17159 (2019)
Q. Wang, S. Guan, B. Li, 2D graphitic-C 3 N 4 hybridized with 1D flux-grown Na-modified K 2 Ti 6 O 13 nanobelts for enhanced simulated sunlight and visible-light photocatalytic performance. Catal. Sci. Technol. 7(18), 4064–4078 (2017)
S. Hu et al., Enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance of g-C3N4 photocatalysts co-doped with iron and phosphorus. Appl. Surf. Sci. 311, 164–171 (2014)
C. Li et al., Porous carbon networks derived from graphitic carbon nitride for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 14(1), 1–9 (2019)
G. Zhao et al., Single atom Fe-dispersed graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) as a highly efficient peroxymonosulfate photocatalytic activator for sulfamethoxazole degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 430, 132937 (2022)
Y. Li et al., Seed-induced growing various TiO2 nanostructures on g-C3N4 nanosheets with much enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light. J. Hazard. Mater. 292, 79–89 (2015)
G. Zhou et al., Size-dependent cytotoxicity of yttrium oxide nanoparticles on primary osteoblasts in vitro. J. Nanopart. Res. 18(5), 1–14 (2016)
L. Ge et al., gC 3 N 4/MgO nanosheets: light-independent, metal-poisoning-free catalysts for the activation of hydrogen peroxide to degrade organics. J. Mater. Chem. A 6(34), 16421–16429 (2018)
F. Mukhtar et al., Highly efficient tri-phase TiO2–Y2O3–V2O5 nanocomposite: structural, optical, photocatalyst, and antibacterial studies. J. Nanostructure Chem. 12(4), 547–564 (2022)
L. Tan et al., Synthesis of g-C3N4/CeO2 nanocomposites with improved catalytic activity on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 356, 447–453 (2015)
Q. Sun et al., Effect of contact interface between TiO2 and g-C3N4 on the photoreactivity of g-C3N4/TiO2 photocatalyst:(0 0 1) vs (1 0 1) facets of TiO2. Appl. Catal. B 164, 420–427 (2015)
S. Wang et al., Defective black Ti3 + self-doped TiO2 and reduced graphene oxide composite nanoparticles for boosting visible-light driven photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 467, 45–55 (2019)
S. Gong et al., The synthesis of graphene-TiO2/g-C3N4 super-thin heterojunctions with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activities. J. Nanopart. Res. 20(11), 1–13 (2018)
G. Yuan et al., In situ synthesis, enhanced luminescence and application in dye sensitized solar cells of Y2O3/Y2O2S: Eu3 + nanocomposites by reduction of Y. Eu3+ Sci. Rep. 2O3(1), 1–9 (2016)
S. Renukadevi, A.P. Jeyakumari, Microwave induced inverse spinel NiFe2O4 decorated g-C3N4 nanosheet for enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. J. Cluster Sci. 33, 1–11 (2021)
B. Khanizadeh et al., Mg and La Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method: synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity. Periodica Polytech. Chem. Eng. 64(1), 61–74 (2020)
R.J. Tayade, R.G. Kulkarni, R.V. Jasra, Transition metal ion impregnated mesoporous TiO2 for photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants in water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 45(15), 5231–5238 (2006)
Z.H. Jabbar et al., Photocatalytic destruction of Congo red dye in wastewater using a novel Ag2WO4/Bi2S3 nanocomposite decorated g-C3N4 nanosheet as ternary S-scheme heterojunction: improving the charge transfer efficiency. Diam. Relat. Mater. 133, 109711 (2023)
X. Xue et al., Facile fabrication of three-dimensional nanofibrous foams of cellulose@ g-C3N4@ Cu2O with superior visible-light photocatalytic performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 303, 120455 (2023)
M. Shemeena, N. Binitha, Visible light active ZnO–g-C3N4 photocatalyst for dye pollutant degradation. Mater. Today 25, 107–110 (2020)
A. Modwi et al., Scalable fabrication and characterization of Y2O3@ g-C3N4 nanocomposite for the enhancement of photocatalytic removal of Congo red dye under visible light. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 34(4), 298 (2023)
J. Wang et al., Sulfur-doped g-C3N4/TiO2 S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst for Congo Red photodegradation. Chin. J. Catal. 42(1), 56–68 (2021)
L.G. Devi, R. Kavitha, A review on plasmonic metal TiO2 composite for generation, trapping, storing and dynamic vectorial transfer of photogenerated electrons across the Schottky junction in a photocatalytic system. Appl. Surf. Sci. 360, 601–622 (2016)
H. Li et al., Intercorrelated superhybrid of AgBr supported on graphitic-C3N4‐decorated nitrogen‐doped graphene: high engineering photocatalytic activities for water purification and CO2 reduction. Adv. Mater. 27(43), 6906–6913 (2015)
H. Yu et al., Significant improvement of photocatalytic hydrogen evolution rate over g-C3N4 with loading CeO2@ Ni4S3. J. Solid State Chem. 272, 102–112 (2019)
H. Tang et al., Construction of Ag3PO4/Ag2MoO4 Z-scheme heterogeneous photocatalyst for the remediation of organic pollutants. Chin. J. Catal. 38(2), 337–347 (2017)
X. Yan et al., Construction of novel ternary dual Z-scheme Ag3VO4/C3N4/reduced TiO2 composite with excellent visible-light photodegradation activity. J. Mater. Res. 34(12), 2024–2036 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of Prince Sultan University for overall support of this publication.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Rasha A. Abumousa, M. Bououdina, Mohamed Ali Ben Aissa, Lotfi Khezami and A. Modwi. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Rasha A. Abumousa and A. Modwi, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abumousa, R.A., Bououdina, M., Ben Aissa, M.A. et al. Efficient photocatalytic degradation of Congo red and other dyes by ternary TiO2/Y2O3@g-C3N4 nanohybrid. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 486 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12264-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12264-6