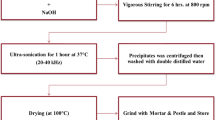
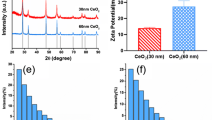
Abstract
Yttrium oxide nanoparticles are an excellent host material for the rare earth metals and have high luminescence efficiency providing a potential application in photodynamic therapy and biological imaging. In this study, the effects of yttrium oxide nanoparticles with four different sizes were investigated using primary osteoblasts in vitro. The results demonstrated that the cytotoxicity generated by yttrium oxide nanoparticles depended on the particle size, and smaller particles possessed higher toxicological effects. For the purpose to elucidate the relationship between reactive oxygen species generation and cell damage, cytomembrane integrity, intracellular reactive oxygen species level, mitochondrial membrane potential, cell apoptosis rate, and activity of caspase-3 in cells were then measured. Increased reactive oxygen species level was also observed in a size-dependent way. Thus, our data demonstrated that exposure to yttrium oxide nanoparticles resulted in a size-dependent cytotoxicity in cultured primary osteoblasts, and reactive oxygen species generation should be one possible damage pathway for the toxicological effects produced by yttrium oxide particles. The results may provide useful information for more rational applications of yttrium oxide nanoparticles in the future.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali AG, Dejene BF, Swart HC (2014) Synthesis and characterization of Y2O3:Eu3+ phosphors using the Sol-Combustion method. Phys B Condens Matter 439(15):181–184
Andelman T, Gordonov S, Busto G, Moghe PV, Riman RE (2010) Synthesis and cytotoxicity of Y2O3 nanoparticles of various morphologies. Nanoscale Res Lett 5(2):263–273
Asare N, Instanes C, Sandberg WJ, Refsnes M, Schwarze P, Kruszewski M, Brunborg G (2012) Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles in testicular cells. Toxicology 291(1–3):65–72
Avalos A, Haza AS, Mateo D, Morales P (2014) Cytotoxicity and ROS production of manufactured silver nanoparticles of different sizes in hepatoma and leukemia cells. J Appl Toxicol 34(4):413–423
Bai CL, Liu MH (2012) Implantation of nanomaterials and nanostructures on surface and their applications. Nano Today 7(4):258–281
Balbus JM, Maynard AD, Colvin VL, Castranova V, Daston GP, Denison RA, Dreher KL et al (2007) Meeting report: hazard assessment for nanoparticles-report from an interdisciplinary workshop. Environ Health Perspect 115:1654–1659
Botelho MC, Costa C, Silva S, Costa S, Dhawan A, Oliveira PA, Teixeira JP (2014) Effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in human gastric epithelial cells in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother 68(1):59–64
Franco-Molina MA, Mendoza-Gamboa E, Sierra-Rivera CA, Gómez-Flores RA, Zapata-Benavides P, Castillo-Tello P et al (2010) Antitumor activity of colloidal silver on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29:148
Ghaznavi H, Najafi R, Mehrzadi S, Hosseini A, Tekyemaroof N, Shakeri-Zadeh A, Rezayat M, Sharifi AM (2015) Neuro-protective effects of cerium and yttrium oxide nanoparticles on high glucose-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in undifferentiated PC12 cells. Neurol Res 37(7):624–632
Hahn MA, Singh AK, Sharma P, Brown SC, Moudgil BM (2011) Nanoparticles as contrast agents for in vivo bioimaging: current status and future perspectives. Anal Bioanal Chem 399(1):3–27
Hilger I (2013) In vivo applications of magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia. Int J Hyperth 29(8):828–834
Hirst SM, Karakoti A, Singh S, Self W, Tyler R, Seal S, Reilly CM (2013) Bio-distribution and in vivo antioxidant effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles in mice. Environ Toxicol 28(2):107–118
Hosseini A, Baeeri M, Rahimifard M, Navaei-Nigjeh M, Mohammadirad A, Pourkhalili N, Hassani S, Kamali M, Abdollahi M (2013) Antiapoptotic effects of cerium oxide and yttrium oxide nanoparticles in isolated rat pancreatic islets. Hum Exp Toxicol 32(5):544–553
Huerta-García E, Pérez-Arizti JA, Márquez-Ramírez SG, Delgado-Buenrostro NL, Chirino YI, Iglesias GG, López-Marure R (2014) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce strong oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage in glial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 73:84–94
Kabir M, Ghahari M, Afarani MS (2014) Co-precipitation synthesis of nano Y2O3:Eu3+ with different morphologies and its photoluminescence properties. Ceram Int 40:10877–10885
Kim J, Piao Y, Hyeon T (2009) Multifunctional nanostructured materials for multimodal imaging, and simultaneous imaging and therapy. Chem Soc Rev 38:372–390
Li TG, Liu SW, Zhang HP, Wang EH, Song LJ, Wang P (2011a) Ultraviolet upconversion luminescence in Y2O3:Yb3+, Tm3+ nanocrystals and its application in photocatalysis. J Mater Sci 46(9):2882–2886
Li Y, Sun L, Jin M, Du Z, Liu X, Guo C, Li Y, Huang P, Sun Z (2011b) Size-dependent cytotoxicity of amorphous silica nanoparticles in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 25(7):1343–1352
Liu SC, Xu LJ, Zhang T, Ren GG, Yang Z (2009) Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by nanosized titanium dioxide in PC12 cells. Toxicology 267(1–3):172–177
Liu HF, Zhang CM, Tan YL, Wang JG, Wang K, Zhao YY, Jia G, Hou YJ, Wang SX, Zhang JC (2014) Biodistribution and toxicity assessment of europium-doped Gd2O3 nanotubes in mice after intraperitoneal injection. J Nanopart Res 16:2303–2313
Lojpur V, Ahrenkiel SP, Dramićanin MD (2014) Yb3+, Er3+ doped Y2O3 nanoparticles of different shapes prepared by self-propagating room temperature reaction method. Ceram Int 40:16033–16039
Marinkovic K, Mancic L, Gomez LS, Rabanal ME, Dramicanin M, Milosevic O (2010) Photoluminescent properties of nanostructured Y2O3:Eu3+ powders obtained through aerosol synthesis. Opt Mater 32:1606–1611
Miethling-Graff R, Rumpker R, Richter M, Verano-Braga T, Kjeldsen F, Brewer J, Hoyland J, Rubahn HG, Erdmann H (2014) Exposure to silver nanoparticles induces size- and dose-dependent oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in human colon carcinoma cells. Toxicol In Vitro 28(7):1280–1289
Mitra RN, Merwin MJ, Han Z, Conley SM, Al-Ubaidi MR, Naash MI (2014) Yttrium oxide nanoparticles prevent photoreceptor death in a light-damage model of retinal degeneration. Free Radic Biol Med 75:140–148
Packiyaraj P, Thangadurai P (2014) Structural and photoluminescence studies of Eu3+ doped cubic Y2O3 nanophosphors. J Lumin 145:997–1003
Park EJ, Yi J, Chung KH, Ryu DY, Choi J, Park K (2008) Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicol Lett 180(3):222–229
Selvaraj V, Bodapati S, Murray E, Rice KM, Winston N, Shokuhfar T, Zhao Y, Blough E (2014) Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity caused by yttrium oxide nanoparticles in HEK293 cells. Int J Nanomedicine 9:1379–1391
Shi ZL, Huang X, Cai YR, Tang RK, Yang DS (2009) Size effect of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on proliferation and apoptosis of osteoblast-like cells. Acta Biomater 5(1):338–345
Shih SJ, Yu YJ, Wu YY (2012) Manipulation of dopant distribution in yttrium-doped ceria particles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 12:7954–7962
Shukla RK, Sharma V, Pandey AK, Singh S, Sultana S, Dhawan A (2011) ROS-mediated genotoxicity induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in human epidermal cells. Toxicol In Vitro 25(1):231–241
Wang JL, Wu JH, Lin JM, Huang ML, Huang YF, Lan Z, Xiao YM, Yue GT, Yin S, Sato T (2012) Application of Y2O3:Er3+ nanorods in dye-sensitized solar cells. ChemSusChem 5(7):1307–1312
Wierzbicka WM, Kolitsch U, Lenz C, Giester G (2015) Structural and photoluminescence properties of doped and REE-endmember mixed-framework rare-earth sorosilicates. J Lumin 168:207–217
Xia GD, Wang SM, Zhou SM, Xu J (2010) Selective phase synthesis of a high luminescence Gd2O3:Eu nanocrystal phosphor through direct solution combustion. Nanotechnology 21(34):345601
Yang KN, Cao WP, Hao XH, Xue X, Zhao J, Liu J, Zhao YL et al (2013) Metallofullerene nanoparticles promote osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells through BMP signaling pathway. Nanoscale 5(3):1205–1212
Yang ER, Li GS, Fu CC, Zheng J, Huang XS, Xu W, Li LP (2015) Eu3+-doped Y2O3 hexagonal prisms: shape-controlled synthesis and tailored luminescence properties. J Alloys Compd 647:648–659
Yokel RA, Au TC, MacPhail R, Hardas SS, Butterfield DA, Sultana R et al (2012) Distribution, elimination, and biopersistence to 90 days of a systemically introduced 30 nm Ceria-Engineered nanomaterial in rats. Toxicol Sci 127(1):256–268
Yoshiura Y, Izumi H, Oyabu T, Hashiba M, Kambara T, Mizuguchi Y, Lee BW et al (2015) Pulmonary toxicity of well-dispersed titanium dioxide nanoparticles following intratracheal instillation. J Nanopart Res 17(6):241–251
Zako T, Yoshimoto M, Hyodo H, Kishimoto H, Ito M, Kaneko K, Soga K, Maeda M (2015) Cancer-targeted near infrared imaging using rare earth ion-doped ceramic nanoparticles. Biomater Sci 3(1):59–64
Zhou GQ, Li Y, Zheng BF, Wang WY, Gao J, Wei HY, Li SH, Wang SX, Zhang JC (2014) Cerium oxide nanoparticles protect primary osteoblasts against hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative damage. Micro Nano Lett 9(2):91–96
Zobeiri E, Bayandori Moghaddam A, Gudarzy F, Mohammadi H, Mozaffari S, Ganjkhanlou Y (2015) Modified Eu-doped Y2O3 nanoparticles as turn-off luminescent probes for the sensitive detection of pyridoxine. Luminescence 30(3):290–295
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21471044 and 21001038), the Youth Talent Fund Project of Hebei Education Department (BJ2014007), and the College Students Innovative Training Project of Hebei University (201410075072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, G., Li, Y., Ma, Y. et al. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of yttrium oxide nanoparticles on primary osteoblasts in vitro. J Nanopart Res 18, 135 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3447-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3447-5