Abstract
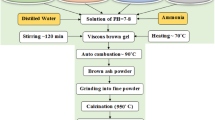
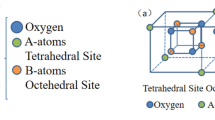
Nanocrystalline spinel ferrites with the general chemical formula Cu1−xCoxEu0.1Fe1.9O4 with x = 0, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, and 1.0 were synthesized using the flash auto-combustion technique. X-ray diffraction, Scanning electron microscopy and Raman spectroscopy techniques were used to analyses the structural properties of samples of produced spinel ferrite. The magnetic characteristics of the obtained spinel ferrite samples have been examined using the vibration sample magnetometers measurements. According to X-ray diffraction analysis, the main cubic phase with space group Fd3m ocuured in all of the prepared samples and the lattice parameter of the cubic phase increases with increase in the amount of Co content. The cation distributions in Cu1−xCoxEu0.1Fe1.9O4 spinel ferrite were identified using the X-ray diffraction data. The majority of the particles were found to be agglomerated and spherical by scanning electron microscopy. The emission peaks of its separate component elements can be observed in the spectra obtained using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Raman spectroscopy revealed that the samples with higher Co content displayed sharp and strong Raman bands for tetrahedral sites and octahedral sites. According to VSM measurements, the saturation magnetization (Ms) and magnetic moment (μB) were improved as the Co concentration increased.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
M.A. Soler et al., Aging investigation of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles in low pH magnetic fluid. Langmuir 23(19), 9611–9617 (2007)
E. Manova et al., Mechano-synthesis, characterization, and magnetic properties of nanoparticles of cobalt ferrite, CoFe2O4. Chem. Mater. 16(26), 5689–5696 (2004)
K. Sakthipandi et al., Investigation of magnetic phase transitions in Ni0.5Cu0.25Zn0.25Fe2-xLaxO4 nanoferrites using magnetic and in-situ ultrasonic measurements. Phys. B Cond. Matter. 645(15), 414280 (2022)
S. Ayyappan, J. Philip, B. Raj, Effect of digestion time on size and magnetic properties of spinel CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 113(2), 590–596 (2009)
A. Hossain et al., Optical, magnetic and magneto-transport properties of Nd1-xAxMn0.5Fe0.5O3-δ (A=Ca, Sr, Ba; x=0, 0.25). J. Alloys Comp. 847(20), 156297 (2020)
R.R. Kanna et al., Neodymium doped on the manganese-copper nanoferrites: analysis of structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 4473–4486 (2019)
D.S. Nikam et al., Cation distribution, structural, morphological and magnetic properties of Co1–xZnxFe2O4 (x= 0–1) nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 5(3), 2338–2345 (2015)
K. Patil et al., Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of (Cu/Co) Fe2O4 spinel ferrite materials. Appl. Phys. A 128(11), 988 (2022)
A.G. Abraham et al., Enhanced magneto-optical and photo-catalytic properties of transition metal cobalt (Co2+ ions) doped spinel MgFe2O4 ferrite nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 452, 380–388 (2018)
A. Manikandan, J.J. Vijaya, L.J. Kennedy, Comparative investigation of NiO nano-and microstructures for structural, optical and magnetic properties. Physica E 49, 117–123 (2013)
G. Mathubala et al., Enhanced photocatalytic activity of spinel CuxMn1–xFe2O4 nanocatalysts for the degradation of methylene blue dye and opto-magnetic properties. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 8(5), 375–381 (2016)
D. Maruthamani et al., Fine cutting edge shaped Bi2O3rods/reduced graphene oxide (RGO) composite for supercapacitor and visible-light photocatalytic applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 498, 449–459 (2017)
S. Asiri et al., Hydrothermal synthesis of CoyZnyMn1-2yFe2O4 nanoferrites: magneto-optical investigation. Ceram. Int. 44(5), 5751–5759 (2018)
K. Haneda, A. Morrish, Noncollinear magnetic structure of CoFe2O4 small particles. J. Appl. Phys. 63(8), 4258–4260 (1988)
N. Moumen, P. Veillet, M. Pileni, Controlled preparation of nanosize cobalt ferrite magnetic particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 149(1–2), 67–71 (1995)
V. Blaskov et al., Magnetic properties of nanophase CoFe2O4 particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 162(2–3), 331–337 (1996)
S.A. Faghidian, Flexure mechanics of nonlocal modified gradient nano-beams. J. Comput. Design Eng. 8(3), 949–959 (2021)
R. Waldron, Infrared spectra of ferrites. Phys. Rev. 99(6), 1727 (1955)
K. Davies et al., The observation of multi-axial anisotropy in ultrafine cobalt ferrite particles used in magnetic fluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 149(1–2), 14–18 (1995)
V. Pillai, D. Shah, Synthesis of high-coercivity cobalt ferrite particles using water-in-oil microemulsions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 163(1–2), 243–248 (1996)
P. Sinuhaji et al., Influences of Co compositions in CoFe2O4 on microstructures, thermal, and magnetic properties. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering 26, 101040 (2021)
P.A. Vinosha et al., Review on recent advances of synthesis, magnetic properties, and water treatment applications of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and nanocomposites. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 34, 995–1018 (2021)
S.A. Faghidian, K.K. Żur, J.N. Reddy, A mixed variational framework for higher-order unified gradient elasticity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 170, 103603 (2022)
S.A. Faghidian, Contribution of nonlocal integral elasticity to modified strain gradient theory. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136(5), 559 (2021)
M. Darvish et al., Biosynthesis of Zn-doped CuFe2O4 nanoparticles and their cytotoxic activity. Sci. Rep. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-13692-2
K. Sangsuriyonk et al., Synthesis and characterization of CoxFe1−xFe2O4 nanoparticles by anionic, cationic, and non-ionic surfactant templates via co-precipitation. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 4611 (2022)
M.A. Gabal, Y. Al Angari, Effect of diamagnetic substitution on the structural, magnetic and electrical properties of NiFe2O4. Mater. Chem. Phys. 115(2–3), 578–584 (2009)
X. Tan et al., The effect of Cu content on the structure of Ni1−xCuxFe2O4 spinels. Mater. Res. Bull. 44(12), 2160–2168 (2009)
T. Marinca, I. Chicinaş, O. Isnard, Synthesis, structural and magnetic characterization of nanocrystalline CuFe2O4 as obtained by a combined method reactive milling, heat treatment and ball milling. Ceram. Int. 38(3), 1951–1957 (2012)
A. Rais et al., Copper substitution effect on the structural properties of nickel ferrites. Ceram. Int. 40(9), 14413–14419 (2014)
N. Sanpo et al., Transition metal-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 9(3), 5830–5837 (2013)
M. Hashim et al., Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Co–Cu ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 518, 11–18 (2012)
S. Jesus Mercy et al., Microstructural, thermal, electrical and magnetic analysis of Mg2+ substituted cobalt ferrite. Appl. Phys. A 126, 1–13 (2020)
K. Sinkó et al., Liquid-phase syntheses of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 1–14 (2012)
D.D. Andhare et al., Effect of Zn doping on structural, magnetic and optical properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized via Co-precipitation method. Phys. B: Cond. Matter 583, 412051 (2020)
C. Lee, H. Chang, H.D. Jang, Preparation of CoFe2O4-graphene composites using aerosol spray pyrolysis for supercapacitors application. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 19(3), 443–448 (2019)
P.D. Thang, G. Rijnders, D.H. Blank, Spinel cobalt ferrite by complexometric synthesis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 295(3), 251–256 (2005)
M.M. Naik et al., Multifunctional properties of microwave-assisted bioengineered nickel doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 91, 578–595 (2019)
P. Monisha et al., Influence of Mn dopant on the crystallite size, optical and magnetic behaviour of CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 148, 109654 (2021)
L. Yao et al., Synthesis of cobalt ferrite with enhanced magnetostriction properties by the sol–gel–hydrothermal route using spent Li-ion battery. J. Alloy. Compd. 680, 73–79 (2016)
S. Fayazzadeh et al., Magnetic properties and magnetic hyperthermia of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by hydrothermal method. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 33, 2227–2233 (2020)
R. Massart et al., Preparation and properties of monodisperse magnetic fluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 149(1–2), 1–5 (1995)
A. Abouhaswa et al., Investigation of crystal structure, electrical and magnetic properties of Spinel Mn–Cd ferrite nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02116-9
S. Saleem et al., Investigating the impact of Cu2+ doping on the morphological, structural, optical, and electrical properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles for use in electrical devices. Materials 15(10), 3502 (2022)
J.R. Dasari, Comparison of the effect of Cr3+ substituted Co–Cu and Cu-Co nano ferrites on structural, Dc electrical resistivity and magnetic properties. Dc Elect. Resist. Magn. Prop. (2023). https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.44854196
S.H. Trier, M.S. Abdali, The structural, magnetic, and optical properties of Cu1-xCoxFe2O4 spinel ferrite and its applications. Al-Qadisiyah J. Pure Sci. 25(3), 1–15 (2020)
R.R. Kanna et al., Doping effect of rare-earth (lanthanum, neodymium and gadolinium) ions on structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of copper nanoferrites. J. Rare Earths 36(12), 1299–1309 (2018)
A. Abouhaswa et al., Investigation of crystal structure, electrical and magnetic properties of spinel Mn-Cd ferrite nanoparticles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02116-9
A. Balagurov et al., Structural phase transition in CuFe2O4 spinel. Crystallogr. Rep. 58, 710–717 (2013)
M. Manikandan, N. Sundaramurthy, S.J.S.O. Rajalakshmi, Structure magnetic and dielectric properties of Mg-Co-Cu nano ferrite powder synthesized by sol-gel auto combustion method. Semicond. Optoelect. 42(1), 58–74 (2023)
E. O’Quinn et al., Inversion in Mg1-xNixAl2O4 spinel: new insight into local structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b04370
T.R. Tatarchuk et al., Structural characterization and antistructure modeling of cobalt-substituted zinc ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 694, 777–791 (2017)
T. Tatarchuk et al., Spinel ferrite nanoparticles: synthesis, crystal structure, properties, and perspective applications (Springer, Cham, 2017), pp.305–325
K. Khalaf et al., Infrared and structural studies of Mg1–xZnxFe2O4 ferrites. Phys B 407, 795–804 (2013)
D.R. Mane et al., Structural and magnetic characterizations of Mn–Ni–Zn ferrite nanoparticles. Phys. Status Solidi 207(10), 2355–2363 (2010)
S.N. Kane, M. Satalkar, Correlation between magnetic properties and cationic distribution of Zn0.85−xNixMg0.05Cu0.1Fe2O4 nano spinel ferrite: effect of Ni doping. J. Mater. Sci. 52(6), 3467–3477 (2017)
K.E. Sickafus, J.M. Wills, N.W. Grimes, Structure of spinel. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 82(12), 3279–3292 (1999)
S.I. Ahmad, S.A. Ansari, D. Ravi Kumar, Structural, morphological, magnetic properties and cation distribution of Ce and Sm co-substituted nano crystalline cobalt ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 208, 248–257 (2018)
M.A. Amer et al., Spectral studies of Co substituted Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323(11), 1445–1452 (2011)
I. Ahmad et al., Study of cation distribution for Cu–Co nanoferrites synthesized by the sol–gel method. Ceram. Int. 39(6), 6735–6741 (2013)
R. Kadam et al., A thorough investigation of rare-Earth Dy3+ substituted cobalt-chromium ferrite and its magnetoelectric nanocomposite. Nanomaterials 13, 1165 (2023)
S. Kane, M. Satalkar, Correlation between magnetic properties and cationic distribution of Zn0.85−xNixMg0.05Cu0.1Fe2O4 nano spinel ferrite: effect of Ni doping. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 3467–3477 (2017)
S. Shaat, H. Dawoud, Influence of variation of structural parameters on magnetic properties of Al-substituted Ni spinel ferrite. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32(9), 11536–11546 (2021)
P. Chandramohan et al., Cation distribution and particle size effect on Raman spectrum of CoFe2O4. J. Solid State Chem. 184(1), 89–96 (2011)
R. Kambale et al., The effect of Mn substitution on the magnetic and dielectric properties of cobalt ferrite synthesized by an autocombustion route. Smart Mater. Struct. 18(11), 115028 (2009)
L. Phor, S. Chahal, V. Kumar, Zn2+ substituted superparamagnetic MgFe2O4 spinel-ferrites: investigations on structural and spin-interactions. J. Adv. Ceram. 9, 576–587 (2020)
S.C. Suman et al., Zn doped α-Fe2O3: an efficient material for UV driven photocatalysis and electrical conductivity. Crystals 10(4), 273 (2020)
O. Hemeda, M. Barakat, Effect of hopping rate and jump length of hopping electrons on the conductivity and dielectric properties of Co–Cd ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 223(2), 127–132 (2001)
A. Goldman, Ferrite transformers and inductors at high power. Modern Ferrite Technol. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-29413-1_13
R. Tiwari et al., Structural and magnetic properties of tailored NiFe2O4 nanostructures synthesized using auto-combustion method. Results Phys. 16, 102916 (2020)
D. Varshney, K. Verma, A. Kumar, Substitutional effect on structural and magnetic properties of AxCo1−xFe2O4 (A= Zn, Mg and x= 0.0, 0.5) ferrites. J. Mol. Struct. 1006(1–3), 447–452 (2011)
P. Pulišová et al., Structure and magnetic properties of Co and Ni nano-ferrites prepared by a two step direct microemulsions synthesis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 341, 93–99 (2013)
Ü. Özgür, Y. Alivov, H. Morkoç, Microwave ferrites, part 1: fundamental properties. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 20, 789–834 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RSD, AAE-H and ASA performed all the experimental work (sample preparation and its characterization) and prepared manuscript. MHN and LMSE-D helped significantly in the explanation of experimental results.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest among the contributing authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Diab, R.S., El-Deen, L.M.S., Nasr, M.H. et al. Structural, cation distribution, Raman spectroscopy, and magnetic features of Co-doped Cu–Eu nanocrystalline spinel ferrites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 35, 290 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12047-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-024-12047-z