Abstract
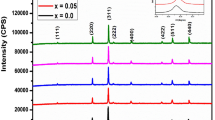
The correlation among magnetic properties and cationic distribution of Ni-doped Zn0.85−x Ni x Mg0.05Cu0.1Fe2O4 (x = 0.00, 0.17, 0.34, 0.51, 0.85) ferrite, synthesized using sol–gel auto-combustion process is studied by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDAX), and magnetic measurements. XRD patterns revealed a pure phase spinel ferrite structure for all samples with Scherrer’s grain diameter (D) ranging from 33.55 to 42.07 nm. Experimental, theoretical lattice constant (a exp. , a th.), specific surface area (S), and the distances between cations (Me–Me) (b, c, d, e, f) of the annealed Zn–Ni–Mg–Cu ferrite decrease with the increase in Ni doping. Elemental analysis, particle diameter, and surface morphology were examined by EDAX and SEM. Coercivity (H c) and saturation magnetization (M s) of Zn–Ni–Mg–Cu ferrite ranges between 0.97–167.5 Oe and 47.63–136.93 Am2 kg−1, respectively, signifying the soft character of annealed samples. Magnetic parameters such as H c, magnetocrystalline anisotropy (K 1), remanence (M r), and reduced remanent magnetization (M r/M s) increase up to x = 0.51 and then reduce thereafter with Ni doping. Particle size dependence of H c reveals superparamagnetic, single domain, and multi-domain nature of the studied ferrite. Observed similar trend of M s, Néel/experimental magnetic moment (n NB , n eB ) with Ni content (x) follows the Néel’s two-sublattice model of ferrimagnetism and is accredited to the cationic distribution and B–B exchange interaction. All these results establish a strong connection between magnetic properties and cationic distribution of Zn0.85−x Ni x Mg0.05Cu0.1Fe2O4 ferrite.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Y, Zhong Y, Zhang J, Ren Z, Cao S, Yang Z, Gao T (2011) Structure and magnetic properties of MnZn nanoferrites synthesized under a high magnetic field. J Appl Phys 110:074310–074314
Eshraghi M, Kameli P (2011) Magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by thermal treatment of ball-milled precursors. Curr Appl Phys 11:476–481
Goldman A (2006) Modern ferrite technology. Springer, Pittsburgh
Roy PK, Bera J (2006) Effect of Mg substitution on electromagnetic properties of (Ni0.25Cu0.20Zn0.55)Fe2O4 ferrite prepared by auto combustion method. J Magn Magn Mater 298:38–42
Mahalakshmi S, SrinivasaManja K, Nithiyanantham S (2014) Electrical properties of nanophase ferrites doped with rare earth ions. J Supercond Novel Magn 27:2083–2088
Reddy MP, Balakrishnaiah G, Madhuri W, Ramana MV, Reddy NR, Siva Kumar KV, Murthy VRK, Reddy RR (2010) Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of NiCuZn ferrites prepared by microwave sintering method suitable for MLCI applications. J Phys Chem Solids 71:1373–1380
Bachhava SG, Patil RS, Ahirrao PB, Patil AM, Patil DR (2011) Microstructure and magnetic studies of Mg–Ni–Zn–Cu ferrites. Mater Chem Phys 129:1104–1109
Sujatha Ch, Reddy KV, Babu KS, Reddy ARC, Suresh MB, Rao KH (2012) Structural and magnetic properties of Mg substituted NiCuZn nano ferrites. Phys B 407:1232–1237
Sujatha Ch, Reddy KV, Babu KS, Reddy ARC, Suresh MB, Rao KH (2013) Effect of Mg substitution on electromagnetic properties of NiCuZn ferrite. J Magn Magn Mater 340:38–45
Sujatha Ch, Reddy KV, Babu KS, Reddy ARC, Suresh MB, Rao KH (2013) Effect of co substitution of Mg and Zn on electromagnetic properties of NiCuZn ferrites. J Phys Chem Solids 74:917–923
Dar MA, Verma V, Gairola SP, Siddiqui WA, Singh RK, Kotnal RK (2012) Low dielectric loss of Mg doped Ni–Cu–Zn nano-ferrites for power applications. Appl Surf Sci 258:5342–5347
Chinnasamy CN, Yang A, Yoon SD, Hsu K, Shultz MD, Carpenter EE, Mukerjee S, Vittoria C, Harris VG (2007) Size dependent magnetic properties and cation inversion in chemically synthesized MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. J Appl Phys 101:09M509–09M511
Kapse VD, Ghosh SA, Raghuwanshi FC, Kapse SD (2009) Nanocrystalline spinel Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4: a novel material for H2S sensing. Mater Chem Phys 113:638–644
Weil L, Bertaut EF, Bochirol L (1950) Propriétés magnétiques et structure de la phase quadratique du ferrite de cuivre. J Phys Radium 11:208–212
Tanna AR, Joshi HH (2013) Computer aided X-ray diffraction intensity analysis for spinels: hands-on computing experience. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 75:78
Smit J, Wijn HPJ (1959) Ferrites: Philips Technical Library. Eindhoven, The Netherlands
Sickafus KE, Wills JM, Grimes NW (1999) Spinel compounds: structure and property relations. J Am Ceram Soc 82:3279–3292
Shannon RD (1976) Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst A32:751–767
Qi X, Zhou J, Yue Z, Gui Z, Li L (2003) Permeability and microstructure of manganese modified lithium ferrite prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion method. Mater Sci Eng B 99:278–281
Satalkar M, Kane SN, Ghosh A, Ghodke N, Barrera G, Celegato F, Coisson M, Tiberto P, Vinai F (2014) Synthesis and soft magnetic properties of Zn0.8−x Ni x Mg0.1Cu0.1Fe2O4 (x = 0.0–0.8) ferrites prepared by sol-gel auto-combustion method. J Alloys Compd 615:S313–S316
Lutterotti L, Scardi P (1990) Simultaneous structure and size-strain refinement by the Rietveld method. J Appl Cryst 23:246–252
Batra AS, Satalkar M, Kane SN, Ghosh A, Ghodke N (2014) Influence of Ni substitution on structural and magnetic properties of Zn0.85−x Ni x Mg0.05Cu0.1Fe2O4. AIP Conf Proc 1591:537–539
Costa ACFM, Lula RT, Kiminami RHGA, Gama LFV, de Jesus AA, Andrade HMC (2006) Preparation of nano structured NiFe2O4 catalysts by combustion reaction. J Mater Sci 41:4871–4875. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-0048-1
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Chikazumi S (2005) Physics of ferromagnetism. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Stoner EC, Wohlfarth EP (1948) A mechanism of magnetic hysteresis in heterogeneous alloys. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A 240:599–642
Tirosh E, Shemer G, Markovich G (2006) Optimizing cobalt ferrite nanocrystal synthesis using a magneto-optical probe. Chem Mater 18:465–470
Muthuselvam IP, Bhowmik RN (2010) Mechanical alloyed Ho3+ doping in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite and understanding of magnetic nanodomains. J Magn Magn Mater 322:767–776
Pearson RF, Annis AD (1968) Anisotropy of Fe3+ ions in Yttrium iron garnet. J Appl Phys 39:1338–1339
George M, Nair SS, John AM, Joy PA, Anantharaman MR (2006) Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of the sol-gel prepared Li0.5Fe2.5O4 fine particles. J Phys D Appl Phys 39:900–910
Berkowitz AE, Schuele WJ (1959) Magnetic properties of some ferrite Micropowders. J Appl Phys 30:S134–S135
Verma A, Chatterjee R (2006) Effect of zinc concentration on the structural, electrical and magnetic properties of mixed Mn–Zn and Ni–Zn ferrites synthesized by the citrate precursor technique. J Magn Magn Mater 306:313–320
Panchal S, Raghuvanshi S, Gehlot K, Mazaleyrat F, Kane SN (2016) Cationic distribution assisted tuning of magnetic properties of Li0.5−x/2Zn x Fe2.5−x/2O4. AIP Adv 6:055930–055936
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by MPCST Project No. 1783/CST/R & D/Phy and Engg Sc and by UGC-DAE CSR, Indore [CSR-IC/CRS-74/2014-15/2104]. Authors thank Dr. M. Gupta and Mr. L. Behra and Dr. A. Banerjee and Mr. K. Kumar, respectively, for XRD and magnetic measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kane, S.N., Satalkar, M. Correlation between magnetic properties and cationic distribution of Zn0.85−x Ni x Mg0.05Cu0.1Fe2O4 nano spinel ferrite: effect of Ni doping. J Mater Sci 52, 3467–3477 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0636-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0636-7