Abstract
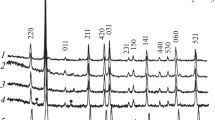
In a fusion reactor, tritium is produced in the blanket and recovered the tritium through extraction system. Tritium is one of the isotope of hydrogen, and strontium- and cerium-based perovskite materials are extremely useful for measuring hydrogen isotopes. Reliable and fast hydrogen isotope measurement is critical for effective tritium recovery, and Sr2CeO4–SrCe0.85Y0.15O3−δ could be a promising candidate for hydrogen isotope sensors based on proton-conducting ceramic membranes. The mixed-phase Sr2CeO4–SrCe0.85Y0.15O3−δ were synthesized using a solid-state reaction involving mixing–milling and high-temperature calcination. The mixture of strontium, cerium, and yttrium oxides were ground inside a high-energy ball mill and measured their particle size distribution using the dynamic light scattering method. The thermal analysis (TGA/DSC) was carried out on a mixture of SrCO3–CeO2–Y2O3 from room temperature to 1200 °C at the same time. TGA analysis revealed that the mixed materials reaction temperature ranged between 875 and 994 °C, which is supported by the endothermic peak of DSC. A proportional conversion curve is generated after estimating the temperature-dependent mass loss at 14.2% of the initial mass. TGA and DSC analysis were used to estimate the side reactions that contribute to the formation of Sr2CeO4. Mixed-ground raw materials were isothermally calcined for 2 h inside the muffle furnace at 800, 1000, 1100, and 1200 °C. TGA and stoichiometric estimates are used to compare the total mass loss of the reactions. The resulting products are examined using X-ray diffraction, and the lattice parameters are estimated using the cell refinement method. The materials are two-phase materials composed of Sr2CeO4 and SrCe0.85Y0.15O3−δ. The raw and synthesized material's Raman spectra were also measured, revealing the mixed-phase material. The Raman analysis supported the diffraction data by revealing the possible modes in the compounds. This paper discusses the effect of calcination parameters on the synthesis of SrCe0.85Y0.15O3−δ.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
A. Shrivastava, M. Makwana, P. Chaudhuri, E. Rajendrakumar, Fusion Sci. Technol. 65, 319 (2014)
A. Shrivastava, T. Kumar, R. Shukla, P. Chaudhuri, Fusion Eng. Des. 168, 112411 (2021)
A. Shrivastava, R. Shukla, P. Chaudhuri, Fusion Eng. Des. 166, 112318 (2021)
A. Sircar, S.K. Sharma, R.B. Patel, P.A. Rayjada, Fusion Eng. Des. 89, 1223 (2014)
G. Müller, A. Heinzel, J. Konys, G. Schumacher, A. Weisenburger, F. Zimmermann, V. Engelko, A. Rusanov, V. Markov, J. Nucl. Mater. 301, 40 (2002)
F.J. Martín, L. Soler, F. Hernández, D. Gómez-Briceño, J. Nucl. Mater. 335, 194 (2004)
F. Barbier, G. Benamati, C. Fazio, A. Rusanov, J. Nucl. Mater. 295, 149 (2001)
Z.J. Li, R.Q. Liu, Y.H. Xie, S. Feng, J. De Wang, Solid State Ion. 176, 1063 (2005)
H. Matsumoto, H. Hayashi, H. Iwahara, J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 39, 367 (2002)
H. Matsumoto, K. Takeuchi, H. Iwahara, J. Electrochem. Soc. 146, 1486 (1999)
S. Liu, K. Li, R. Hughes, Mater. Res. Bull. 39, 119 (2004)
A. Volkov, E. Gorbova, A. Vylkov, D. Medvedev, A. Demin, P. Tsiakaras, Sens. Actuators B 244, 1004 (2017)
P. Serret, S. Colominas, G. Reyes, J. Abellà, Fusion Eng. Des. 86, 2446 (2011)
H. Borland, L. Llivina, S. Colominas, J. Abellà, Fusion Eng. Des. 88, 2431 (2013)
L. Llivina, S. Colominas, G. Reyes, J. Abella, Fusion Eng. Des. 87, 979 (2012)
E. Juhera, S. Colominas, J. Abellà, Fusion Eng. Des. 98–99, 1710 (2015)
J. Ramírez-Rico, M.J. López-Robledo, A.R. de Arellano-López, J. Martínez-Fernández, A. Sayir, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 3705 (2006)
J. Ranløv, B. Lebech, K. Nielsen, J. Mater. Chem. 5, 743 (1995)
I. Arvanitidis, D.U. Sichen, H.Y. Sohn, S. Seetharaman, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 28, 1063 (1997)
T.S. Krishnan, Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. A 44, 96 (1956)
J. Cui and G. A. Hope, J. Spectrosc. 2015, (2015).
M.A. Małecka, L. Kepiński, W. Miśta, Appl. Catal. B 74, 290 (2007)
D. Yadav, G. Nirala, U. Kumar, and S. Upadhyay, Res. Sq. Preprint (2020)
M. Sahu, S.K. Gupta, D. Jain, M.K. Saxena, R.M. Kadam, Spectrochim. Acta A 195, 113 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Mr. Vrushabh Lambade for his support during the sample preparation. We are also grateful to Dr. Nirav Jamnapara and Mr. Vyom Desai for their help in X-ray diffraction characterization and Dr. Rudrasingh Panda for Raman characterization.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the manuscript “High-temperature Solid-state Synthesis and Characterization of Mixed-phase Sr2CeO4–SrCe0.85Y0.15O3−δ Ceramic: A Potential Proton-Conducting Ceramic Membrane.” Conceptualization: AS, DY; Methodology: AS, DY; Formal analysis and investigation: AS, DY; Writing—original draft preparation: AS; Writing—review and editing: DY, PC, AS; Supervision: AS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shrivastava, A., Yadav, D., Chaudhuri, P. et al. High-temperature solid-state synthesis and characterization of mixed-phase Sr2CeO4–SrCe0.85Y0.15O3−δ ceramic: a potential proton-conducting ceramic membrane. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 455 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09900-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09900-y