Abstract
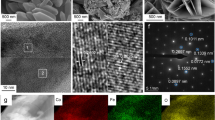
Environmental pollution and energy exhaustion threaten human existence, and the exploitation of nanocatalysts offers new efficient ways to solve the pollution and energy crisis. However, the nanophotocatalysts are difficult to recycle because of its small size and low density. In this work, the magnetically recyclable ZnFe2O4-Fe2O3-Ag hollow nanophotocatalyst was successfully prepared via the process of impregnating, calcination and photoreduction. ZnFe2O4-Fe2O3-Ag possesses a hollow nanocore-shell structure with a particle size distribution of about 240 nm and a shell thickness of about 15 nm. In the hollow nanoternary complex of ZnFe2O4-Fe2O3-Ag, ZnFe2O4 and Fe2O3 have photocatalytic properties and magnetic properties, playing a recyclable and photocatalytic role, and both of them can form a matching heterojunction each other, which can further improve the photodegradation performance. Ag can capture electrons to inhibit photogenerated carrier recombination. The hollow core-shell structure can improve the utilization rate of light and the contact frequency with pollutants. The results of the photocatalytic activity to decompose rhodamine B under visible light irradiation as driving force reveal the sequence: ZnFe2O4-Fe2O3-Ag > ZnFe2O4-Fe2O3 > ZnFe2O4. ZnFe2O4-Fe2O3-Ag can be conveniently separated from water in magnetic environment and recycled. This work also affords a new method to prepare ZnFe2O4-based hollow nanoatalysts with facile recovery and form an excellent ternary composite.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable.
References
X. Yang, J. Tian, Y. Guo et al., ZnO nano-rod arrays synthesized with exposed {0001} facets and the investigation of photocatalytic activity. Crystals 11, 522 (2021)
T. Liu, L. Wang, X. Liu et al., Dynamic photocatalytic membrane coated with ZnIn2S4 for enhanced photocatalytic performance and antifouling property. Chem. Eng. J. 379, 122379 (2020)
L. Han, P. Zhang, L. Li et al., Nitrogen-containing carbon nano-onions-like and graphene-like materials derived from biomass and the adsorption and visible photocatalytic performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 543, 148752 (2021)
H. Fang, B. Wu, X. Sheng et al., A nano heterostructure with step-accelerated system toward optimized photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 47, 1656–1668 (2021)
J.M.D. Rodríguez, E.P. Melián, Nano-photocatalytic materials: possibilities and challenges. Nanomaterials 11, 668 (2021)
Z. Jiang, C. Xiao, X. Yin et al., Facile preparation of a novel Bi24O31Br10/nano-ZnO composite photocatalyst with enhanced visible light photocatalytic ability. Ceram. Int. 46, 10771–10778 (2020)
Y. Wang, F. Xin, Y. Ideng et al., Nano-Zn2SnO4/reduced graphene oxide composites for enhanced photocatalytic performance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 254, 123505 (2020)
P. Cao, Z. Zhang, X. Bai et al., Complecting the BiOCl nano-roundels based hollow microbasket induced by chitosan for dramatically enhancing photocatalytic activity. J. Mol. Struct. 1254, 132339 (2022)
C. Peng, Y. Liu, J. Cui et al., Preparation and photocatalytic activity of silver phosphate modified by nano-silver metal. Digest J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 15, 991–999 (2021)
D.M. Imran, N. Jawayria, H. Zaib et al., Biogenic scale up synthesis of ZnO nano-flowers with superior nano-photocatalytic performance. Inorg. Nano-Metal Chem. 50, 613–619 (2020)
Z. Guo, C. Huang, A.Y. Chen, Experimental study on photocatalytic degradation eflciency of mixed crystal nano-TiO2 concrete. Nanatechnol. Rev. 9, 219–229 (2020)
H.S. Jarusheh, A. Yusuf, F. Banat et al., Integrated photocatalytic technologies in water treatment using ferrites nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 10, 108204 (2022)
Z.H. Jabbar, S.E. Ebrahim, Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic degradation activity of core/shell magnetic nanocomposites (Fe3O4@SiO2@Ag2WO4@Ag2S) under visible light irradiation. Opt. Mater. 122, 111818 (2021)
A. Lassoued, J. Li, Structure and optical, magnetic and photocatalytic properties of Cr3+ substituted zinc nano-ferrites. J. Mol. Struct. 1262, 133021 (2022)
Y. Cui, J. Zheng, Z. Wang et al., Magnetic induced fabrication of core-shell structure Fe3O4@TiO2 photocatalytic membrane: enhancing photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline and antifouling performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 9, 106666 (2021)
A. Navidpour, M. Fakhrzad, Photocatalytic and magnetic properties of ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesised by mechanical alloying. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 102, 690–706 (2022)
J. Luo, Y. Wu, X. Chen et al., Synergistic adsorption-photocatalytic activity using Z-scheme based magnetic ZnFe2O4/CuWO4 heterojunction for tetracycline removal. J. Alloys Compd. 910, 164954 (2022)
L. Nguyen, D. Vo, L. Nguyen et al., Synthesis, characterization, and application of ZnFe2O4@ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B under visible-light illumination. Evironmental Technol. Innov. 25, 102130 (2022)
W. Zhao, Y. Huang, C. Su et al., Fabrication of magnetic and recyclable In2S3/ZnFe2O4 nanocomposites for visible light photocatalytic activity enhancement. Materals Res. Exp. 7, 015080 (2020)
C. Zhang, X. Han, F. Wang et al., A facile fabrication of ZnFe2O4/Sepiolite composite with excellent photocatalytic performance on the removal of tetracycline hydrochloride. Oiginal Res. 9, 736369 (2021)
Z. Azam, S.M. Seyed, M. Alireza, Synthesis, characterization and investigation of photocatalytic activity of ZnFe2O4@MnO-GO and ZnFe2O4@MnO-rGO nanocomposites for degradation of dye Congo red from wastewater under visible light irradiation. Res. Chem. Intermed. 46, 33–61 (2020)
M. Bohra, V. Alman, R. Arras, Nanostructured ZnFe2O4: an exotic energy material. Nanomaterials 11, 1–24 (2021)
D. Wang, J. Chen, H. Che et al., Flexible g-C3N4-based photocatalytic membrane for efficient inactivation of harmful algae under visible light irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 60, 154270 (2022)
M.M. Faisal, A. Ejaz, A. Mukhtar et al., Enhanced photocatalytic activity of hydrogen evolution through Cu incorporated ZnO nano composites. Mater. Sci. Semiconduct. Process 120, 105278 (2020)
X. Cheng, L. Li, L. Jia et al., Preparation of K+ doped ZnO nanorods with enhanced photocatalytic performance under visible light. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 53, 035301 (2020)
Z. Li, L. Zhou, L. Lu, Enhanced photocatalytic properties of ZnO/Al2O3 nanorod heterostructure. Mater. Res. Exp. 8, 045505 (2021)
B. Yu, H. Yu, B. Song, Preparation and Study of ZnAl2O4/CeO2 water remediation photocatalyst and its photocatalytic activity. Rus. Phys. Chem. A 95, 2523–2529 (2021)
S. Hussain, S. Hussain, A. Waleed et al., Spray pyrolysis deposition of ZnFe2O4/Fe2O3 Composite Thin Films on hierarchical 3-D nanospikes for efficient photoelectrochemical oxidation of Water. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 18360–18368 (2017)
X. Zhang, B. Lin, X. Li et al., MOF-derived magnetically recoverable Z-scheme ZnFe2O4/Fe2O3 perforated nanotube for efficient photocatalytic ciprofloxacin removal. Chem. Eng. J. 430, 132728 (2022)
P. Wei, S. Yin, T. Zhou et al., Rational design of Z-scheme ZnFe2O4/Ag@Ag2CO3 hybrid with enhanced photocatalytic activity, stability and recovery performance for tetracycline degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 266, 118544 (2021)
Z.X. Liu, Q.Q. Yu, J. Liu et al., Enhanced visible photocatalytic activity in flower-like CuO-WO3-Bi2WO6 ternary hybrid through the cascadal electron transfer. Micro Nano Lett. 12, 195–200 (2017)
X. Yuan, L. Jiang, X. Chen et al., Highly efficient visible-light-induced photoactivity of Z-scheme Ag2CO3/Ag/WO3 photocatalysts for organic pollutant degradation. Environ. Sci.: Nano 4, 2175–2185 (2017)
X. Wu, Y. Hu, Y. Wang et al., In-situ synthesis of Z-scheme Ag2CO3/Ag/AgNCO heterojunction photocatalyst with enhanced stability and photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci 464, 108–114 (2019)
T. Sobahi, M. Amin, Synthesis of ZnO/ZnFe2O4/Pt nanoparticles heterojunction photocatalysts with superior photocatalytic activity. Ceram. Int. 46, 3558–3564 (2020)
C. Shipra, B. Aditi, M. Satyabrata, Microwave-assisted synthesis of alpha-Fe2O3/ZnFe2O4/ZnO ternary hybrid nanostructures for photocatalytic applications. Ceram. Int. 47, 3833–3841 (2021)
M.O. Abdalla, A. Ludwick, Boron-modified phenolic resins for high performance applications. Polymer 44, 7353–7359 (2003)
S. Ito, P. Chen, P. Comte, Fabrication of Screen-Printing Pastes from TiO2 powders for dye-sensitised solar cells. Prog. Photovoltaics Res. Appl. 15, 603–612 (2007)
Z. Zhang, L. Li, Y. Jiang et al., Step-Scheme Photocatalyst of CsPbBr3 Quantum Dots/BiOBr nanosheets for efficient CO2 photoreduction. Inorg. Chem. 61, 3351–3360 (2022)
D. Li, J. Zhou, Z. Zhang et al., Enhanced photocatalytic activity for CO2 reduction over a CsPbBr3/CoAl-LDH composite: insight into the S-Scheme charge transfer mechanism. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 5, 6238–6247 (2022)
Z. Zhang, Y. Jiang, Z. Dong et al., 2D/2D Inorganic/Organic hybrid of lead-free Cs2AgBiBr6 double Perovskite/Covalent triazine frameworks with boosted charge separation and efficient CO2 photoreduction. Inorg. Chem. 61, 16028–16037 (2022)
X. Wang, J. Feng, Z.Q. Zhang et al., Pt enhanced the photo-Fenton activity of ZnFe2O4/alpha-Fe2O3 heterostructure synthesized via one-step hydrothermal method. J. Colloid Interface Sci 561, 793–800 (2020)
X.H. Zhang, B.Y. Lin, X.Y. Li et al., MOF-derived magnetically recoverable Z-scheme ZnFe2O4/Fe2O3 perforated nanotube for efficient photocatalytic ciprofloxacin removal. Chem. Eng. J. 430, 132728 (2022)
N.N. Yang, P.F. Hu, C.C. Chen et al., Ternary Composite of g-C3N4/ZnFe2O4/Fe2O3: hydrothermal synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic performance. ChemistrySelect 4, 7308–7316 (2019)
Funding
I am grateful for the financial support of the 2022 General Special Scientific Research Program of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education and the 2023 research project of Shaanxi Institute of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhenxing Liu completes all the work of the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest in this paper.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z. Magnetically recyclable ZnFe2O4-Fe2O3-Ag hollow nanophotocatalysts to decompose rhodamine B. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 413 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09849-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09849-y