Abstract
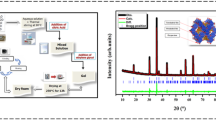
Cobalt-substituted zinc spinel ferrites having chemical composition Zn1−xCoxFe2O4 with stoichiometric proportion ‘x’ equals 0.00, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, and 1.00 have been synthesized by sol–gel citrate route sintered at 1000 °C for 6 h. All the fabricated specimens have been characterized by using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, energy-dispersive spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and vector network analyzer. The XRD patterns ensured the existence of a cubic spinel crystal structure having single phase of space group Fd-3m. Decline in crystallite size (Dc) from 48.016 to 45.314 nm with an increase in cobalt content displayed the nanocrystalline nature of the synthesized specimens. The values of lattice constant (\({a}_{\mathrm{avg}}, {a}_{\mathrm{px}}, {a}_{\mathrm{true}},\; \mathrm{and}\; {a}_{\mathrm{th}}\)) obtained from four different approaches are perfectly coordinating with each other. The complex electromagnetic parameters (\({\varepsilon }_{r}\;{\mathrm{ and }\;\mu }_{r}\)) measured by VNA are found to be increasing with Co2+ doping in K-band (18–26.5 GHz) frequency range. The reflection loss study revealed that all the synthesized compositions have yielded more than 90% absorption intensity in the studied frequency band due to higher magnetic and dielectric losses of the synthesized ferrites thereby making them a potential candidate for the implementation of microwave absorbers at higher frequencies.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Yes.
Code availability
No.
References
X. Ren, G. Xu, Electromagnetic and microwave absorbing properties of NiCoZn-ferrites doped with La3+. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 354, 44–48 (2014)
A. Poorbafrani, E. Kiani, Enhanced microwave absorption properties in cobalt–zinc ferrite based nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 416, 10–14 (2016)
J. Zhang, R. Shu, Y. Wu, Z. Wan, X. Li, Facile synthesis of Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles decorated reduced graphene oxide hybrid nanocomposites with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Ceram. Int. 46, 15925–15934 (2020)
V.K. Chakradhary, M.J. Akhtar, Absorption properties of CNF mixed cobalt nickel ferrite nanocomposite for radar and stealth applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 525, 167592 (2021)
Y. Gao, Z. Wang, R. Shi, J. Pei, H. Zhang, X. Zhou, Electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of Ti doped Li–Zn ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 805, 934–941 (2019)
P. Kaur, S. Bahel, S.B. Narang, Broad-band microwave absorption of Sr0.85La0.15(MnZr)xFe12−2xO19 hexagonal ferrite in 18–40 GHz frequency range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 460, 489–494 (2018)
A.N. Hapishah, M.M. Syazwan, M.N. Hamidon, Synthesis and characterization of magnetic and microwave absorbing properties in polycrystalline cobalt zinc ferrite (Co0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4) composite. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 20573–20579 (2018)
T.J. Shinde, A.B. Gadkari, P.N. Vasambekar, Magnetic properties and cation distribution study of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 333, 152–155 (2013)
H. Harzali, F. Saida, A. Marzouki, A. Megriche, F. Baillon, F. Espitalier, A. Mgaidi, Structural and magnetic properties of nano-sized NiCuZn ferrites synthesized by co-precipitation method with ultrasound irradiation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 419, 50–56 (2016)
Hirthna, S. Sendhilnathan, Enhancement in dielectric and magnetic properties of Mg2+ substituted highly porous super paramagnetic nickel ferrite nanoparticles with Williamson–Hall plots mechanistic view. Ceram. Int. 43, 15447–15453 (2017)
Z.Ž Lazarević, Č Jovalekić, D.L. Sekulić, A. Milutinović, S. Baloš, M. Slankamenac, N.Ž Romčević, Structural, electrical and dielectric properties of spinel nickel ferrite prepared by soft mechanochemical synthesis. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 4368–4378 (2013)
S.C. Tolani, A.R. Golhar, K.G. Rewatkar, A review of morphological, structural behaviour and technological applications of ferrites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2104, 030032 (2019)
V.G. Patil, S.E. Shirsath, S.D. More, S.J. Shukla, K.M. Jadhav, Effect of zinc substitution on structural and elastic properties of cobalt ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 488, 199–203 (2009)
Y. Sun, Y. Diao, H. Wang, G. Chen, M. Zhang, M. Guo, Synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of spinel ferrite (Ni, Cu, Co) Fe2O4 from low nickel matte. Ceram. Int. 43, 16474–16481 (2017)
M.N. Ashiq, S. Saleem, M.A. Malana, A.U. Rehman, Physical, electrical and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Zr–Ni doped Mn-ferrite synthesized by the co-precipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 486, 640–644 (2009)
S.A.V. Prasad, M. Deepty, P.N. Ramesh, G. Prasad, K. Srinivasarao, Ch. Srinivas, K.V. Babu, E.R. Kumar, N.K. Mohan, D.L. Sastry, Synthesis of MFe2O4 (M=Mg2+, Zn2+, Mn2+) spinel ferrites and their structural, elastic and electron magnetic resonance properties. Ceram. Int. 44, 10517–10524 (2018)
H.S. Aziz, R.A. Khan, F. Shah, B. Ismail, J. Nisar, S.M. Shah, A. Rahim, A.R. Khan, Improved electrical, dielectric and magnetic properties of Al–Sm co-doped NiFe2O4 spinel ferrites nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 243, 47–53 (2019)
D.S. Mathew, R.-S. Juang, An overview of the structure and magnetism of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and their synthesis in microemulsions. Chem. Eng. J. 129, 51–65 (2007)
P. Thakur, D. Chahar, S. Taneja, N. Bhalla, A. Thakur, A review on MnZn ferrites: synthesis, characterization and applications. Ceram. Int. 46, 15740–15763 (2020)
N. Boda, K.C.B. Naidu, D.B. Basha, D. Ravinder, Structural and magnetic properties of CdCoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33, 1039–1044 (2020)
B. Nandan, M.C. Bhatnagar, S.C. Kashyap, Cation distribution in nanocrystalline cobalt substituted nickel ferrites: x-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopic investigations. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 129, 298–306 (2019)
S.R. Bhongale, H.R. Ingawale, T.J. Shinde, K. Pubby, S.B. Narang, P.N. Vasambekar, Nano-crystalline magnesium substituted cadmium ferrites as X-band microwave absorbers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 441, 475–481 (2017)
K.C.B. Naidu, W. Madhuri, Microwave processed bulk and nano NiMg ferrites: a comparative study on X-band electromagnetic interference shielding properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 187, 164–176 (2017)
X. Huang, J. Zhang, W. Wang, T. Sang, B. Song, H. Zhu, W. Rao, C. Wong, Effect of pH value on electromagnetic loss properties of Co–Zn ferrite prepared via coprecipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 405, 36–41 (2016)
M. Deepty, C. Srinivas, K.V. Babu, E.R. Kumar, S.S. Meena, C.L. Prajapat, N.K. Mohan, D.L. Sastry, Structural and electron spin resonance spectroscopic studies of MnxZn1−xFe2O4 (x = 0.5, 0.6, 0.7) nanoferrites synthesized by sol–gel auto combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 466, 60–68 (2018)
A. Pradeep, P. Priyadharsini, G. Chandrasekaran, Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of nanocrystalline zinc ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 3917–3923 (2011)
J. Venturini, R. Young, S. Zampiva, S. Arcaro, C.P. Bergmann, Sol–gel synthesis of substoichiometric cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) spinels: influence of additives on their stoichiometry and magnetic properties. Ceram. Int. 44, 12381–12388 (2018)
M. Atif, W. Asghar, M. Nadeem, W. Khalid, Z. Ali, S. Badshah, Synthesis and investigation of structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of zinc substituted cobalt ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 123, 36–42 (2018)
S. Agrawal, A. Parveen, A. Azam, Structural, electrical, and optomagnetic tweaking of Zn doped CoFe2−xZnxO4−δ nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 414, 144–152 (2016)
J. Feng, R. Xiong, Y. Liu, F. Su, X. Zhang, Preparation of cobalt substituted zinc ferrite nanopowders via autocombustion route: an investigation to their structural and magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 18358–18371 (2018)
K. Pubby, S.S. Meena, S.M. Yusuf, S.B. Narang, Cobalt substituted nickel ferrites via Pechini’s sol–gel citrate route: X-band electromagnetic characterization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 466, 430–445 (2018)
B. Nandan, M.C. Bhatnagar, S.C. Kashyap, Cation distribution in nanocrystalline cobalt substituted nickel ferrites: X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopic investigations. J. Phys. Chem. 129, 298–306 (2019)
L.C. Sonia, M. Victory, S. Phanjoubam, A comparative study of the properties of zinc ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by different techniques for nanofluid preparation. Integr. Ferroelectr. 204, 100–111 (2020)
M.A. Gabal, A.A. Al-Juaid, S.M. Al-Rashed, M.A. Hussein, F. Al-Marzouki, Synthesis, characterization and electromagnetic properties of Zn-substituted CoFe2O4 via sucrose assisted combustion route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 426, 670–679 (2017)
D.D. Andhare, S.R. Patade, J.S. Kounsalye, K.M. Jadhav, Effect of Zn doping on structural, magnetic and optical properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized via Co-precipitation method. Physica B 583, 412051 (2020)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, 2nd edn. (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company Inc., Boston, 1978)
F. Gözüak, Y. Köseoğlu, A. Baykal, H. Kavas, Synthesis and characterization of CoxZn1−xFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles via a PEG-assisted route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2170–2177 (2009)
T.R. Tatarchuk, M. Bououdina, N.D. Paliychuk, I.P. Yaremiy, V.V. Moklyak, Structural characterization and antistructure modeling of cobalt substituted zinc ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 694, 777–791 (2017)
R.D. Shannon, Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. A 32, 751–767 (1976)
S.B. Somvanshi, M.V. Khedkar, P.B. Kharat, K.M. Jadhav, Influential diamagnetic magnesium (Mg2+) ion substitution in nano-spinelzinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4): thermal, structural, spectral, optical and physisorption analysis. Ceram. Int. 46, 8640–8650 (2020)
A. Manikandan, J.J. Vijaya, M. Sundararajan, C. Meganathan, L.J. Kennedy, M. Bououdina, Optical and magnetic properties of Mg-doped ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles prepared by rapid microwave combustion method. Superlattices Microstruct. 64, 118–131 (2013)
N.M. Deraz, A. Alarifi, Structural, morphological and magnetic properties of nano-crystalline zinc substituted cobalt ferrite system. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 94, 41–47 (2012)
M. Sharif, J. Jacob, M. Javed, A. Manzoor, K. Mahmood, M.A. Khan, Impact of Co and Mn substitution on structural and dielectric properties of lithium soft ferrites. Phys. Rev. B 567, 45–50 (2019)
N. Aggarwal, S.B. Narang, Effect of co-substitution of Co–Zr on electromagnetic properties of Ni–Zn spinel ferrites at microwave frequencies. J. Alloys Compd. 866, 157461 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157461
R.S. Yadav, I. Kuřitka, J. Havlica, M. Hnatko, C. Alexander, J. Masilko, L. Kalina, M. Hajdúchová, J. Rusnak, V. Enev, Structural, magnetic, elastic, dielectric and electrical properties of hot-press sintered Co1−xZnxFe2O4 (x=0.0, 0.5) spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 447, 48–57 (2017)
A. Hossain, I.N. Esha, I.B. Elius, M.N.I. Khan, K.H. Maria, Interrelation between cationic distribution and electromagnetic properties of vanadium substituted Mn–Zn ferrites. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 977–992 (2021)
Y. Slimani, H. Güngüneş, M. Nawaz, A. Manikandan, H.S. EL Sayed, M.A. Almessiere, H. Sözeri, S.E. Shirsath, I. Ercan, A. Baykal, Magneto-optical and microstructural properties of spinel cubic copper ferrites with Li–Al co-substitution. Ceram. Int. 44, 14242–14250 (2018)
P. Coppola, F.G. da Silva, G. Gomide, F.L.O. Paula, A.F.C. Campos, R. Perzynski, C. Kern, J. Depeyrot, R. Aquino, Hydrothermal synthesis of mixed zinc–cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: structural and magnetic properties. J. Nanopart. Res. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3430-1
F.G. da Silva, J. Depeyrot, A.F.C. Campos, R. Aquino, D. Fiorani, D. Peddis, Structural and magnetic properties of spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 19, 4888–4902 (2019)
M.A. Amer, M.E. Hiti, Mössbauer and X-ray studies for Ni0.2ZnxMg0.8−xFe2O4 ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 234, 118–125 (2001)
A.M. Wahba, M.B. Mohamed, Structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties of nanocrystalline Cr-substituted Co0.8Ni0.2Fe2O4 ferrite. Ceram. Int. 40, 6127–6135 (2014)
Aakash, R. Choubey, D. Das, S. Mukherjee, Effect of doping of manganese ions on the structural and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 668, 33–39 (2016)
Z. Wang, D. Schiferl, Y. Zhao, HSt.C. O’Neill, High pressure Raman spectroscopy of spinel-type ferrite ZnFe2O4. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 64, 2517–2523 (2003)
F.A. Wahaab, L.L. Adebayo, A.A. Adekoya, I.G. Hakeem, B. Alqasem, A.M. Obalalu, Physiochemical properties and electromagnetic wave absorption performance of Ni0.5Cu0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles at X-band frequency. J. Alloys Compd. 836, 155272 (2020)
K. Pubby, S.B. Narang, Influence of grain size and porosity on X-band properties of Mn–Zr substituted Ni–Co ferrites. Mater. Lett. 244, 186–191 (2019)
P. Kaur, S.B. Narang, S. Bahel, Complex permittivity, complex permeability and reflection loss of Co–Zr substituted La–Sr hexaferrites in 18–40 GHz frequency range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 502, 166456 (2020)
K.C.B. Naidu, S.R. Kiran, W. Madhuri, Microwave processed NiMgZn ferrites for electromagnetic intereference shielding applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 53, 1–7 (2017)
W. Wang, C. Zang, Q. Jiao, Synthesis, structure and electromagnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrite by sol–gel combustion technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 349, 116–120 (2014)
X. Huang, J. Zhang, W. Rao, T. Sang, B. Song, C. Wong, Tunable electromagnetic properties and enhanced microwave absorption ability of flaky graphite/cobalt zinc ferrite composites. J. Alloys Compd. 662, 409–414 (2016)
K. Pubby, K.V. Babu, S.B. Narang, Magnetic, elastic, dielectric, microwave absorption and optical characterization of cobalt-substituted nickel spinel ferrites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 255, 114513 (2020)
Z. Hou, J. Xiang, X. Zhang, L. Gong, J. Mi, X. Shen, K. Zhang, Microwave absorption properties of single- and double-layer absorbers based on electrospun nickel–zinc spinel ferrite and carbon nanofibers. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 12258–12268 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge UGC (University Grants Commission) India for providing fellowship through the MANF (Maulana Azad National Fellowship) scheme.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Synthesis, characterization, data collection, analysis, and writing of manuscript by MK. Review, edit, and supervision by SB and PK.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, M., Kaur, P. & Bahel, S. K-band microwave absorption analysis of sol–gel synthesized cobalt-substituted zinc spinel ferrites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 12182–12200 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08178-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08178-w