Abstract
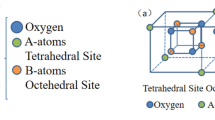
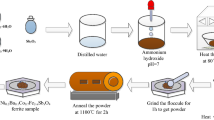
Ce3+-doped Mg-Co ferrite powder can be prepared by sol–gel spontaneous combustion method. The chemical formula for Mg0.2Co0.8Fe2-xCexO4 (x = 0.00, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1). X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Scanning electron microscope (SEM), and Vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) were used for a series of structural and magnetism analysis of the samples. XRD results show that all samples were spinel structures, the lattice constants of the samples increased first and then decreased, and the sizes of all the samples were 66 ~ 88 nm. FTIR shows that the characteristic peaks and absorption bands of pure and doped samples are consistent with the characteristics of spinel, which further confirms the cubic spinel structure of the samples. SEM confirmed that the samples were spherical spinel. VSM confirmed that the saturation magnetization (Ms) and remanent magnetization (Mr) increased first and then decreased with the increase of Ce3+ content, indicating that Ce3+ content has an effect on the magnetism of ferrite. When the concentration of Ce3+ is 0.025, the values of saturation magnetization and remanent magnetization of samples are the best, and the samples have the best magnetic properties.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Data sharing and data citation is encouraged.
References
L. Bozadgiev, T. Dimova, T. Mitev, Classifications of ferrospinel structures and textures. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. (1985). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1985.tb15250.x
M. Rostami, M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M.R. Ganjali et al., Facile synthesis and characterizations of TiO2-graphene–ZnFe2−xTbxO4 ternary nano-hybrids. J. Mater. Sci. 52, 7008–7016 (2017)
M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M. Behpour, A. Sobhani-Nasab, S.M. Hosseinpour-Mashkani, ZnFe2–xLaxO4 nano structure:synthesis, characterization, and its magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 9776–9781 (2015)
A. Baykal, N. Kasapoglu, Y.K. Seoglu, A. Basaran, H. Kavas, M. Toprak, Microwave-induced combustion synthesis and characterization of NixCo1-xFe2O4 nanocrystals (x=0.0, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0). Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 6, 125–135 (2008)
S. Sakka, Sol-gel processing of insulating electroconducting and superconducting fibers. J. Non-Cryst Solids. 121, 417–423 (1990)
Y.I. Kim, D. Kim, C.S. Lee, Synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles prepared by temperature-controlled coprecipitation method. Phys. 337, 42–51 (2003)
P. Sivagurunathan, S.R. Gibin, Preparation and characterization of nickel ferrite nano particles by co-precipitation method with citrate as chelating agent. J. Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 27, 8891–8898 (2016)
B.S. Kim, S.Y. Chang, Microstructure and magnetic properties of nano-sized ba-al ferrite particles by high energy ball milling. J. Nanosci. Nanotechno. 12, 1301–1304 (2012)
Influence of fuel to oxidizer ratio, Sudheesh, V. D. Thomas et al., Synthesis of nanocrystalline spinel ferrite (MFe2O4, M=Zn and Mg) by solution combustion method. J. Alloy. Compd. 742, 577–586 (2018)
V. D. Sudheesh, Nygil Thomas et al., Synthesis, characterization and influence of fuel to oxidizer ratio on the properties of spinel ferrite (MFe2O4, M = Co and Ni) prepared by solution combustion method. Ceram. Int. 43, 15002–15009 (2017)
K. Neiati, R. Zzbihi, Preparation and magnetic properties of nano size nickel ferrite particles using hydrothermal method. Chem. Cent. J. 6, 23–29 (2012)
Q. Zhang, Z. Li, X. Li, Yu. Laigui, Z. Zhang, Wu. Zhishen, Preparation of Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticle-Decorated Boron Nitride Nanosheet Flame Retardant and Its Flame Retardancy in Epoxy Resin. J. Nano. 14(05), 1950063 (2019)
K. Anitha Rani, V. Senthol Kumar, Preparation and Characterization of Nickel and Copper Ferrite Nanoparticles by Sol-Gel Auto-Combustion Method. International Journal of Innovative Research in Scienc. 2347–3207 (2015)
E. Roohani, H. Arabi, R. Sarhaddi, Influence of nickel substitution on crystal structure and magnetic properties of strontium ferrite preparation via sol-gel auto-combustion route. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B. 32(01), 1750271 (2018)
M.K. Satheeshkumar, E. Ranjith Kumar, Ch. Srinivas, G. Prasad, S.S. Meena, I. Pradeep, N. Suriyanarayanan, D.L. Sastry, Structural and magnetic properties of CuFe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by cow urine assisted combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 484(15), 120–125 (2019)
S. Amiri, H. Shokrollahi, Magnetic and structural properties of RE doped Co-ferrite (RE=Nd, Eu, and Gd) nano-particles synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 345, 18–23 (2013)
Li qiong Shao, Ai min Sun, Li chao Yu, Zhuo Zuo., et al., Cr3+-doped nanocrystalline nickel–magnesium–cobalt spinel ferrite microstructural and magnetic. Appl. Phys. A 127, 199 (2021)
A.T. Ravichandran, J. Srinivas, R. Karthick et al., Facile combustion synthesis, structural, morphological, optical and antibacterial studies of Bi1−xAlxFeO3 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 0.15) nanoparticles. J. Ceram. Int. 44, 13247–13252 (2018)
C.E. Demirci et al., A comparison of the magnetism of cobalt-, manganese-, and nickel-ferrite nanoparticles. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 51 (2018).
Mohd Firdaus Malek, Mohamad Hafiz Mamat, Mohd Zainizan Sahdan, Musa Mohamed Zahidi, Zuraida Khusaimi, Mohamad Rusop Mahmood, Influence of various sol concentrations on stress/strain and properties of ZnO thin films synthesised by sol–gel technique. Thin Solid Films 527, 102–109 (2013)
R.N. Gayen, K. Sarkar, ZnO films prepared by modified sol-gel technique. Indian. J. Pure. Ap. Phy. 49, 470–477 (2011)
Mohd Shahadan Mohd Suan, Chew Ke Chin, Jeefferie Abd Razak, Hazman Hasib et al., Synthesis and Characterizations of Fe3O4 Added with Al2O3 Nanoparticles via Sol-Gel Technique. I. Co. S. M. 957,01204 (2020)
Kwang Pyo Chae, Won-Ok Choi, Byung-Sub Kang, and Young Bae Lee, effects of ga substitution on crystallographic and magnetic properties of Co Ferrites. J. Magn 20(1), 26–30 (2015)
N. Rannah, Y. Melikhov, I.C. Nlebedim, D.C. Jiles, J.E. Snyder, A.J. Moses, P.I. Williamms, Temperature dependence of magnetic anisotropy of germanium/cobalt cosubstituted cobalt ferrite [J]. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 5181–5183 (2009)
S.U. Bhasker, M.R. Reddy, Effect of chromium substitution on structueal, magnetic and electrical properties of magneto ceramic cobalt ferrite nano-particles [J]. J. Sol Techn. 73, 396–402 (2015)
M. Hamedoun, A. Benyoussef, M. Bousmina, Magnetic properties of magnetic Co1-xMgxFe2O4 spinel by HTSE method. Physica B. 406, 1633–1638 (2011)
Z. Ahmad, S. Shahid Atiq, K. Abbas, S.M. Ramay, S. Riaz, S. Naseem, Structural and complex impedanee spectroscopic studies of Mg-substituted CoFe2O4. Ceram. Int. 42(16), 18271–18282 (2016)
E. Uyanga, H. Hirazawa, T. Sakai et al., Correlation between synthesis and physical properties of magnesium ferrite. J. Sol-Gel. Technol. 95, 223–229 (2020)
R. Arilasita, B.P. Utari, The effect of low-temperature annnealing on the structural and the magnetic characteristics of co-precipitated strontium cobalt ferrite. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 74, 498–501 (2019)
A. Godlyn, A. Manikandan, Enhanced magneto-optical and photo-catalytic properties of transition metal (Co2+ ions) doped spinel MgFe2O4 ferrite nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 25, 380–388 (2018)
W. Zhang, A. Sun, Magnetic transformation of Zn-substituted Mg-Co ferriet nanoparticles: hard magnetism-soft magnetism. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 32, 3286–3302 (2021)
J. Balavijayalakshim, C. Annie Josphine, Impact of annealing on structural and magnetic properties of manganese co-doped magnesium-cobalt ferrute. Nanoparticles. 189, 233–243 (2017)
Xu. Jun, HE Xiao-Ping, Effects of rare earth elements yttrium and holmium doping on magnetic properties of bismuth ferrite. J. Mol. Struct. 05, 57–60 (2013)
D.V. Phugate, B.B. Rameshwar, Effect of Ho3+Ion doping on thermal, structural, and morphological properties of Co-Ni ferrite synthesized by sol-gel method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33, 3545–3554 (2020)
G. Mustafa, M. Ulslam, Temperature dependent structural and magnetic properties of Cerium substituted Co–Cr ferrite prepared by auto-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 378, 409–416 (2015)
K. Muthuraman, V. Naidu, Study of Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Cerium Doped Nano Smart Magnesium Ferrite Material. International Journal of Computer Applications, 65–23, (2013)
G. E. Schulze, R. R. W. Cahn(ed). Physical Metallurgy. Second revised edition. North Holland Publishing Comp. Amsterdam-London 1970 Format 18 -25cm, Hfl. 160.00; $, 47.00 [J]. 7(4), 49–50 (2010)
S. Manouchehri et al., Effect of aluminum doping on the structural and magnetic properties of Mg–Mn ferrite nanoparticles prepared by coprecipitation method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 29, 2179–2188 (2016)
L. Kalina et al., Structural, magnetic, dielectric, and electrical properties of NiFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by honey-mediated sol–gel combustion. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 107, 150–161 (2017)
N. Sharma, P. Aghamkar, S. Kumar, M. Bansal, R.P. Tondon Anji, Study of structural and magnetic properties of Nd doped zinc ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 369, 162–167 (2014)
K. Siraj, M. Khaleeq-ur-Rahman, S.I. Hussain, M.S. Rafque, S. Anjum, Effect of deposition temperature on structural, surface, optical and magnetic properties of pulsed laser deposited Al doped CdO thin flms. J. Alloy. Compd. 509(24), 6756–6762 (2011)
B.D. Cullity, J.W. Weymouth, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction. Am. J. Phys 25, 394 (1957)
Xi Qian Zhao, Ai min Sun, Wei Zhang, Li chaoYu, Zhaxi nan Suo, Enhancement of the magnetic properties of Ni-Cu-Co ferrites by the magnetic Ce3+-ions substitution. J. Mater Sci 31, 762–778 (2020)
ZhaoFeng Shang, WeiHua Qi et al., Cation distributions estimated using the magnetic moments of the spinel ferrites C1-xCrxFe2O4 at 10 k. Chin Phys B 23(10), 107503 (2014)
C.A.F. Vaz, J. Hoffman, C.H. Anh, R. Ramesh, Magnetoelectric coupling effects in multiferroic complex oxide composite structures. Adv. Mater. 22, 2900–2918 (2010)
Q.M. Wei, J.B. Li, Y.J. Chen, Cation distribution and infrared properties of NixMn1-xFe2O4 ferrite. J. Mater. Sci. 36, 5115 (2001)
M. Kryszewski, J.K. Jeszka, Nano structured conducting polymer composites super paramagnetic particles in conducting polymers. Synth. Met. 94, 99 (1998)
S. Maensiri, C. Masingboon, B. Boonchom, S. Seraphin, A simple route to synthesize nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) nanoparticles using egg white. Scripta Mater. 56, 797–800 (2007)
P.P. Sarangi, S.R. Vadera et al., Synthesis and characterization of pure single phase Ni–Zn ferrite nanopowders by oxalate based precursor method. Powder Technol. 203(2), 348–353 (2010)
T.K. Bromho et al., Understanding the impacts of Al+3- substitutions on the enhancement of magnetic, dielectric and electrical behaviors of ceramic processed nickel-zinc mixed ferrites: FTIR assisted studies—ScienceDirect. Mater. Res. Bull. 97, 444–451 (2018)
S.R. Aid, N.N.A.A.N. Zain, N.N.M. Rashid, H. Hara, K. Shameli, I. Koji, A study on biological sample preparation for high resolution imaging of scanning electron microscope. J. Phy. Conf. Ser. 1447, 012 (2020)
M.A. Gabal, R.M. Shishtawy, Y.M.A. Angari, Structural and magnetic properties of nano-crystalline Ni–Zn ferrites synthesized using egg-white precursor. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 2258–2264 (2012)
I.P. Muthuselvam, R.N. Bhowmil, Mechanical alloyed Ho3+doping in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite and understanding of magnetic nanodomains [J]. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322(7), 767–776 (2010)
S. Bhukal, T. Namgyal, S. Mor et al., Magnetic, physical and electical, optical and magnrtic properties of chromium substituted Co-Zn nanoferrites Co0.6Zn0.4CexFe2-xO4 (0≤x≤1.0) prepared via sol-gel auto-combustion method. J. Mol. Struct. 1012, 162–167 (2012)
G. Kumar et al., Cation distribution in mixed Mg–Mn ferrite systems from X-ray diffraction technique and saturation magnetization. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 44(12), 930–934 (2006)
P.A. Shaikh, R.C. Kambale, A.V. Rao, Y.D. Kolekar, Effect of Ni doping on structural and magnetic properties of Co1–xNixFe1.9Mn0.1O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 718 (2010)
R.H. Kadam, A.P. Birajdar, S.T. Alone, S.E. Shirsath, Fabrication of materials via sol–gel method and their characterizations. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 327, 167–171 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW contributed to experiment, conceptualization, investigation, writing-original draft, and visualization; AS checked the manuscript; YJ and XH helped checking the table, LS and YZ helped in measurement of data and experimental process and helped checking the figure.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author states that there is no conflict of interest with other institutions (financial or non-financial, directly or indirectly related to work, in all scientific fields).
Ethical approval
The author states that the manuscript complies with the ethical rules applicable to the journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Sun, A., Jiang, Y. et al. Structural and magnetic properties of Ce3+doped Mg-Co ferrite prepared by sol–gel method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 11881–11895 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08150-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08150-8