Abstract
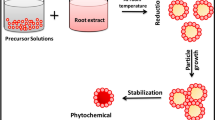
Gum kondagogu (GK), a natural biopolymer was successfully employed in the synthesis of trimetallic (AgAuPd) nanocomposites and characterized for their physicochemical properties in comparison with the monometallic nanoparticles. The UV–visible spectrum of GK-Ag nanoparticles (NPs) and GK-AuNPs showed distinctive surface plasmon peaks at 418 and 546 nm, respectively. In contrast, GK-PdNPs and the trimetallic nanoparticles did not exhibit any specific absorbance within the region of 200–800 nm. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy revealed that hydroxyl, acetyl, and carboxylate functional groups are responsible for the formation of GK-NPs. The scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray analysis depicted the surface morphology and elemental composition of GK-based nanoparticles in comparison with native gum. Further, the GK-trimetallic nanocomposite was crystalline in nature with face-centered cubic geometry based on X-ray diffraction analysis and oxidation state zero as analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The zeta potential (mV) for the GK-AgAuPdNPs was recorded as − 4.97 ± 1.25 when compared to native gum − 25.25 ± 2.64. The transmission electron microscopy analysis displayed the average sizes for GK-AgNPs (13 ± 4.8 nm), GK-AuNPs (8 ± 3.0 nm), GK-PdNPs (6 ± 1.1 nm), and the trimetallic GK-AgAuPdNPs (28 ± 8.1 nm). The synthesized GK-NPs exhibited enhanced catalytic efficiencies in the reduction of an anthropogenic agent 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) by NaBH4 to 4-aminophenol with rate constants k (min−1) 0.180 for (GK-AgNPs), 0.158 (GK-AuNPs), 0.293 (GK-PdNPs), and 0.287 (GK-AgAuPdNPs). Our findings disclosed that GK-trimetallic NPs are more efficient catalysts in the reduction of 4-NP as compared to monometallic nanoparticles.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.J.S. Costa, L.M. Rossi, Synthesis of supported metal nanoparticle catalysts using ligand assisted methods. Nanoscale 4, 5826–5834 (2012)
P. Dauthal, M. Mukhopadhyay, Noble metal nanoparticles: plant mediated synthesis, mechanistic aspects of synthesis and applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55, 9557–9577 (2016)
I. Ijaz, E. Gilani, A. Nazir, A. Bukhari, Detail review on chemical, physical and green synthesis, classification, characterizations, and applications of nanoparticles. Green. Chem. Lett. Rev. 13, 223–245 (2020)
P. Anastas, N. Eghbali, Green chemistry: principles and practice. Chem. Soc. Rev. 39, 301–312 (2010)
H. Duan, D. Wang, Y. Li, Green chemistry for nanoparticle synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44, 5778–5792 (2015)
V.T.P. Vinod, R.B. Sashidhar, V.U.M. Sarma, U.V.R. Vijaya Saradhi, Compositional analysis and rheological properties of gum kondagogu (Cochlospermum gossypium): a tree gum from India. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 56, 2199–2207 (2008)
I. Chung, I. Park, K. Seung-Hyun, M. Thiruvengadam, G. Rajakumar, Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: their characteristic properties and therapeutic applications. Nanoscale. Res. Lett. 11, 40 (2016)
M. Goudarzi, N. Mir, M. Mousavi-Kamazani, S. Bagheri, M. Salavati-Niasari, Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles prepared from two novel natural precursors by facile thermal decomposition methods. Sci. Rep. 6, 32539 (2016)
Y. Zhong, C. Deng, Y. He, Y. Ge, G. Song, Glutathione-protected silver nanoclusters for sensing trace-level Hg2+ in a wide pH range. Anal. Methods 7, 1558–1562 (2015)
V.K. Sharma, R.A. Yngard, Y. Lin, Silver nanoparticles: green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 145, 83–96 (2009)
N. Elahi, M. Kamali, M.H. Baghersad, Recent biomedical applications of gold nanoparticles: a review. Talanta 184, 537–556 (2018)
X. Hu, Y. Zhang, T. Ding, J. Liu, H. Zhao, Multifunctional gold nanoparticles: a novel nanomaterial for various medical applications and biological activities. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8, 990 (2020)
N. Tepale, V.V.A. Fernández-Escamilla, C. Carreon-Alvarez, V.J. González-Coronel, A. Luna-Flores, A. Carreon-Alvarez, J. Aguilar, Nanoengineering of gold nanoparticles: green synthesis, characterization, and applications. Crystals 9, 612 (2019)
L. Biao, S. Tan, Q. Meng, J. Gao, X. Zhang, Z. Liu, Y. Fu, Green synthesis, characterization and application of proanthocyanidins-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 8, 53 (2018)
M. Hazarika, D. Borah, P. Bora, A.R. Silva, P. Das, Biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles and their applications as catalyst and antimicrobial agent. PLoS ONE 9, 12 (2017)
V. Kandathil, R.B. Dateer, B.S. Sasidhar, S.A. Patil, S.A. Patil, Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: applications in aryl halide cyanation and hiyama cross-coupling reaction under ligand free conditions. Catal. Lett. 148, 1562–1578 (2018)
F. Qazi, Z. Hussain, M.N. Tahir, Advances in biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles. RSC. Adv. 6, 60277–60286 (2016)
P. Vishnukumar, S. Vivekanandhan, S. Muthuramkumar, Plant-mediated biogenic synthesis of palladium nanoparticles: recent trends and emerging opportunities. Chem. Bio. Eng. Rev. 4, 18–36 (2017)
A.J. Kora, L. Rastogi, Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using gum ghatti (Anogeissus latifolia) and its application as an antioxidant and catalyst. Arab. J. Chem. 11, 1097–1106 (2018)
J. Jana, M. Ganguly, T. Pal, Enlightening surface plasmon resonance effect of metal nanoparticles for practical spectroscopic application. RSC Adv. 6, 86174–86211 (2016)
G. Sharma, D. Kumar, A. Kumar, A.H. Al-Muhtaseb, D. Pathania, M. Naushad, G.T. Mola, Revolution from monometallic to trimetallic nanoparticle composites, various synthesis methods and their applications: a review. Mat. Sci. Eng. C. 71, 1216–1230 (2017)
K. Pyrzynska, Nanomaterials in speciation analysis of metals and metalloids. Talanta 212, 120784 (2020)
H.B. Ahmed, H.E. Emam, Seeded growth core-shell (Ag–Au–Pd) ternary nanostructure at room temperature for potential water treatment. Polym. Test. 89, 106720 (2020)
R.B. Sashidhar, S.K. Selvi, V.T.P. Vinod, K. Tanuja, D. Raju, R. Karuna, Bioprospecting of gum kondagogu (Cochlospermum gossypium) for bioremediation of uranium (VI) from aqueous solution and synthetic nuclear power reactor effluents. J. Environ. Radioact. 148, 33–41 (2015)
K.Y. Cho, H.Y. Seo, Y.S. Yeom, P. Kumar, A.S. Lee, K. Baek, H.G. Yoon, Stable 2D-structured supports incorporating ionic block copolymer-wrapped carbon nanotubes with graphene oxide toward compact decoration of metal nanoparticles and high-performance nano-catalysis. Carbon 105, 340–352 (2016)
B. Khodadadi, M. Bordbar, A. Yeganeh-Faal, M. Nasrollahzadeh, Green synthesis of Ag nanoparticles/clinoptilolite using Vaccinium macrocarpon fruit extract and its excellent catalytic activity for reduction of organic dyes. J. Alloys Compd. 719, 82–88 (2017)
M. Tajbakhsh, H. Alinezhad, M. Nasrollahzadeh, T.A. Kamali, Green synthesis of the Ag/HZSM-5 nanocomposite by using Euphorbia heterophylla leaf extract: a recoverablecatalyst for reduction of organic dyes. J. Alloys Compd. 685, 258–265 (2016)
A.M. Mostafa, E.A. Mwafy, Synthesis of ZnO and Au@ ZnO core/shell nano-catalysts by pulsed laser ablation in different liquid media. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 3241–3248 (2020)
A. Mostafa, E. Mwafy, N. Awwad, H. Ibrahium, Catalytic activity of Ag nanoparticles and Au/Ag nanocomposite prepared by pulsed laser ablation technique against 4-nitrophenol for environmental applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 11978–11988 (2021)
M.A. Zakria, A.A. Menazea, A.M. Mostafa, E.A. Al-Ashkar, Ultra-thin silver nanoparticles film prepared via pulsed laser deposition: synthesis, characterization, and its catalytic activity on reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Surf. Interfaces 19, 100438 (2020)
B. Jaleh, M. Nasrollahzadeh, A. Nasri, M. Eslamipanah, A. Moradi, Z. Nezafat, Biopolymer-derived (nano)catalysts for hydrogen evolution via hydrolysis of hydrides and electrochemical and photocatalytic techniques: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 182, 1056–1090 (2021)
J. Arjomandi, N.K.I. Mossa, B. Jaleh, Electrochemical synthesis and In situ spectroelectrochemistry of conducting NMPy-TiO2 and ZnO polymer nanocomposites for Li secondary battery applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 132, 41526 (2015)
V.T.P. Vinod, P. Saravanan, B. Sreedhar, D.K. Devi, R.B. Sashidhar, A facile synthesis and characterization of Ag, Au and Pt nanoparticles using a natural hydrocolloid gum kondagogu (Cochlospermum gossypium). Colloids Surf. B. 83, 291–298 (2011)
K.V. Pasha, C.V. Ratnavathi, J. Ajani, D. Raju, S.M. Kumar, S.R. Beedu, Proximate, mineral composition and antioxidant activity of traditional small millets cultivated and consumed in Rayalaseema region of south India. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 98, 652–660 (2017)
L. Rastogi, S.R. Beedu, A.J. Kora, Facile synthesis of palladium nanocatalysts using gum kondagogu (Cochlospermum gossypium): a natural biopolymer. IET Nanobiotechnology 9, 362 (2015)
S. Velpula, S.R. Beedu, K. Rupula, Bimetallic nanocomposite (Ag-Au, Ag-Pd, Au-Pd) synthesis using gum kondagogu a natural biopolymer and their catalytic potentials in the degradation of 4-nitrophenol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 190, 159–169 (2021)
N. Berahim, W.J. Basirun, B.F. Leo, M.R. Johan, Synthesis of bimetallic gold-silver (Au-Ag) nanoparticles for the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. Catalysts 8, 412 (2018)
L. Rastogi, R.B. Sashidhar, D. Karunasagar, J. Arunachalam, Gum kondagogu reduced/stabilized silver nanoparticles as direct colorimetric sensor for the sensitive detection of Hg2+ in aqueous system. Talanta 118, 111–117 (2014)
D. Muchintala, V. Suresh, D. Raju, R.B. Sashidhar, Synthesis and characterization of cecropin peptide-based silver nanocomposites: Its antibacterial activity and mode of action. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 110, 110712 (2020)
J. Singh, T. Dutta, K. Kim, M. Rawat, P. Samddar, P. Kumar, Green synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 16, 84 (2018)
P. Venkatesan, J. Santhanalakshmi, Synthesis and characterization of surfactant stabilized trimetallic Au-Ag-Pd nanoparticles for heck coupling reaction. Phys. Chem. 2, 12–15 (2012)
H.B. Ahmed, H.E. Emam, Layer by layer assembly of nanosilver for high performance cotton fabrics. Fibers Polym. 17, 418–426 (2016)
H.E. Emam, Arabic gum as bio-synthesizer for Ag–Au bimetallic nanocomposite using seed-mediated growth technique and its biological efficacy. J. Polym. Environ. 27, 210–223 (2019)
H.E. Emam, M.A. Attia, F.M.S.E. El-Dars, H.B. Ahmed, Emerging use of homogenic and heterogenic nano-colloids synthesized via size-controllable technique in catalytic potency. J. Polym. Environ. 28, 553–565 (2020)
B. Janaki, R.B. Sashidhar, Subchronic (90-day) toxicity study in rats fed gum kondagogu (Cochlospermum gossypium). Food Chem. Toxicol. 38, 523–534 (2000)
H.B. Ahmed, H.E. Emam, Synergistic catalysis of monometallic (Ag, Au, Pd) and bimetallic (Ag\\Au, Au\\Pd) versus trimetallic (Ag-Au-Pd) nanostructures effloresced via analogical techniques. J. Mol. Liq. 287, 110975 (2019)
S. Tsai, Y.-H. Liu, P. Wu, C. Yeh, Preparation of Au–Ag–Pd trimetallic nanoparticles and their application as catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. 13, 978–980 (2003)
Y.M. Mohan, K.M. Raju, K. Sambasivudu, S. Singh, B. Sreedhar, Preparation of acacia-stabilized silver nanoparticles: a green approach. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 106, 3375–3381 (2007)
K. Suwannarat, K. Thongthai, S. Ananta, L. Srisombat, Synthesis of hollow trimettallic Ag/Au/Pd nanoparticles for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 540, 73–80 (2018)
H. Tan, T. Zhan, W.Y. Fan, A simple route to water-soluble size-tunable monodispersed Pd nanoparticles from the light decomposition of Pd(PPh3)4. Chem. Phys. Lett. 428, 352–355 (2006)
Y. Suo, I. Hsing, Synthesis of bimetallic PdAu nanoparticles for formic acid oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 56, 2174–2183 (2011)
S. Li, Y. Ping, J. Yan, H. Wang, M. Wu, Q. Jiang, Facile synthesis of AgAuPd/Graphene with high performance for hydrogen generation from formic acid. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 14535–14538 (2011)
A.J. Kora, S.R. Beedu, A. Jayaraman, Size-controlled green synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by gum ghatti (Anogeissus latifolia) and its biological activity. Org. Med. Chem. Lett. 2, 17 (2012)
T.S. Rodrigues, A.G.M. da Silva, P.H.C. Camargo, Nanocatalysis by noble metal nanoparticles: controlled synthesis for the optimization and understanding of activities. J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 5857–5874 (2019)
T. Li, S. Vongehr, S. Tang, Y. Dai, X. Huang, X. Meng, Scalable synthesis of Ag networks with optimized sub-monolayer Au-Pd nanoparticle covering for highly enhanced SERS detection and catalysis. Sci. Rep. 6, 37092 (2016)
C. He, Y. Hu, L. Yin, C. Tang, C. Yin, Effects of particle size and surface charge on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31, 3657–3666 (2010)
M. Liang, L. Wang, R. Su, W. Qi, M. Wang, Y. Yu, Z. He, Synthesis of silver nanoparticles within cross-linked lysozyme crystals as recyclable catalysts for 4-nitrophenol reduction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 3, 1910–1914 (2013)
A. Gangula, R. Podila, M. Ramakrishna, L. Karanam, C. Janardhana, A.M. Rao, Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol using biogenic gold and silver nanoparticles derived from Breynia rhamnoides. Langmuir 27, 15268–15274 (2011)
H.I. Salaheldin, Comparative catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol by polyacrylamide-gold nanocomposite synthesized by hydrothermal autoclaving and conventional heating routes. Adv. Nat. Sci: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8, 045002 (2018)
T. Pradeep, Anshup, Noble metal nanoparticles for water purification: a critical review. Thin Solid Films 517, 6441–6478 (2009)
H.A. Oualid, O. Amadine, Y. Essamlali, I.M. Kadmiri, H.E. Arroussi, M. Zahouily, Highly efficient catalytic/sonocatalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and antibacterial activity through a bifunctional Ag/ZnO nanohybrid material prepared via a sodium alginate method. Nanoscale Adv. 1, 3151–3163 (2019)
P. Dauthal, M. Mukhopadhyay, Biosynthesis of palladium nanoparticles using delonix regia leaf extract and its catalytic activity for nitro-aromatics hydrogenation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52, 18131–18139 (2013)
A.S. Kumari, M. Venkatesham, D. Ayodhya, G. Veerabhadram, Green synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity of palladium nanoparticles by xanthan gum. Appl. Nanosci. 5, 315–320 (2015)
K. Kalantari, A.B.M. Afifi, S. Bayat, K. Shameli, S. Yousefi, N. Mokhtar, A. Kalantari, Heterogeneous catalysis in 4-nitrophenol degradation and antioxidant activities of silver nanoparticles embedded in Tapioca starch. Arab. J. Chem. 12, 5246–5252 (2019)
S.J.M. Gavade, G.H. Nikam, S.R. Sabale, B.V. Tamhankar, Green synthesis of fluorescent silver nanoparticles using Acacia nilotica gum extract for kinetic studies of 4-nitrophenol reduction. Mater. Today. 3, 4109–4114 (2016)
R.R. Palem, G. Shimoga, T.J. Kang, S. Lee, Fabrication of multifunctional guar gum-silver nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical and environmental applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 159, 474–486 (2020)
Y.S. Seo, E. Ahn, J. Park, T.Y. Kim, J.E. Hong, K. Kim, Y. Park, Y. Park, Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol with gold nanoparticles synthesized by caffeic acid. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 12, 7 (2017)
G. Wu, X. Liu, P. Zhou, L. Wang, M. Hegazy, X. Huang, Y. Huang, A facile approach for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and degradation of congo red using gold nanoparticles or laccase decorated hybrid inorganic nanoparticles/polymer-biomacromolecules vesicles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 94, 524–533 (2019)
M. Khoshnamvand, Z. Hao, C. Huo, J. Liu, Photocatalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol pollutant and in vitro antioxidant assay of gold nanoparticles synthesized from Apium graveolens leaf and stem extracts. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 17, 2433–2442 (2020)
A.I. Ayad, D. Luart, A.O. Dris, E. Guénin, Kinetic analysis of 4-nitrophenol reduction by “water-soluble” palladium nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 10, 1169 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi for providing infrastructural facilities under PURSE programs phase-I & II at Osmania University, Hyderabad. Mr. Velpula Suresh would like to thank the University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi for awarding Basic Scientific Research (BSR) fellowship (JRF and SRF) at the Department of Biochemistry, Osmania University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SV: Investigation, methodology, acquisition of data, analysis, and interpretation of data, drafting the article. SRB: The conception of the idea, and introducing novel biopolymer for development of metal nanocomposites; In addition, to reviewing the study critically for important intellectual inputs. KR: The conception and design of the study, critically reviewing experimental data, research supervision and administration, final approval of the version to be submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velpula, S., Beedu, S.R. & Rupula, K. Biopolymer-based trimetallic nanocomposite synthesis, characterization and its application in the catalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 2677–2698 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07476-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07476-z