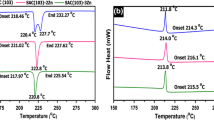
Abstract
Electronic devices need to work at high temperature in some fields for a long time, peculiarly step soldering technology, primary packaging and flip–chip connections, etc., along with the application of electronic products more and more widely. These phenomena promote the further development of high-temperature solders. Because of the high melting temperatures of Sn-Ag and Sn-Sb, they are suitable for high-temperature fields such as automotive electronics and avionics. In this review, the influences of trace elements and nanoparticles on microstructure, intermetallic components (IMC) growth, mechanical properties, wettability, melting behavior, and creep behavior of Sn-Ag and Sn-Sb solders have been summarized systematically. It was found that the addition of trace elements or nanoparticles into solders to be beneficial in improving the performance of Sn-Ag and Sn-Sb solders. Besides, the melting behavior of the solder at high temperatures can be further improved if Sn-Ag and Sn-Sb are used better as high-temperature solders.
































Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article.
References
H.R. Kotadia, P.D. Howes, H.M. Mannan et al., A review: On the development of low melting temperature Pb-free solders[J]. Microelectron. Reliab. 54(6–7), 1253–1273 (2014)
M. Zhao, L. Zhang, Z.Q. Liu et al., Structure and properties of Sn-Cu lead-free solders in electronics packaging[J]. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 20(1), 421–444 (2019)
Z. Liang, K.N. Tu, Structure and properties of lead-free solders bearing micro and nano particles[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. Rep. 82, 1–32 (2014)
S. Cheng, C.M. Huang, M. Pecht, A review of lead-free solders for electronics applications [J]. Microelectron. Reliab. 75, 77–95 (2017)
M.L. Li, L. Zhang, N. Jiang et al., Materials modification of the lead-free solders incorporated with micro/nano-sized particles: A review [J]. Mater. Design 197, 109224 (2021)
Y.B. Park, G.T. Park, B.R. Lee et al., Solder volume effect on electromigration failure mechanism of Cu/Ni/Sn-Ag Microbump [J]. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packaging Manuf. Technol. 99, 1–1 (2020)
Y. Wang, Y. Wang, L. Ma et al., Effect of Sn grain c -axis on Cu atomic motion in Cu reinforced composite solder joints under electromigration [J]. J. Electron. Mater. 49(3), 2159–2163 (2020)
Z. Yao, S. Jiang, L. Yin et al., Effects of joint height on the interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-Cored SAC305 solder joints[J]. J. Electron. Mater. 49(9), 5391–5398 (2020)
L. Zhang, W.M. Long, F.J. Wang, Microstructures, interface reaction, and properties of Sn–Ag–Cu and Sn–Ag–Cu–0.5CuZnAl solders on Fe substrate[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(9), 6645–6653 (2020)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, Nanoindentation creep, elastic properties, and shear strength correlated with the structure of Sn-9Zn-0.5nano-Ag alloy for advanced green electronics[J]. Metals 10(9), 1137 (2020)
Q. Zhang, F. Hu, Z. Song, Transient soldering reaction mechanisms of SnCu solder on CuNi nano conducting layer and fracture behavior of the joint interfaces[J]. J. Electron. Mater. 49(5), 3383–3390 (2020)
N. Jiang, L. Zhang, W.M. Long et al., Influence of doping Ti particles on intermetallic compounds growth at Sn58Bi/Cu interface during solid–liquid diffusion[J]. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32(1), 3341–3351 (2021)
Y. Wei, Y. Liu, L. Zhang et al., Effects of endogenous Al and Zn phases on mechanical properties of Sn58Bi eutectic alloy[J]. Mater. Charact. 175(5), 111089 (2021)
V. Chidambaram, J. Hattel, J. Hald, High-temperature lead-free solder alternatives[J]. Microelectron. Eng. 88(6), 981–989 (2010)
G. Zeng, S. McDonald, K. Nogita, Development of high-temperature solders: Review[J]. Microelectron. Reliab. 52(7), 1306–1322 (2012)
K. Tatsuya, S. Ikuo, N. Yusuke, Effect of power cycling and heat aging on reliability and IMC growth of Sn-5Sb and Sn-10Sb solder joints[J]. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 1–6 (2018)
S.W. Chen, C.H. Wang, S.K. Lin et al., Phase diagrams of Pb-free solders and their related materials systems[J]. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 18(1/3), 19–37 (2007)
Z. Liang, C.W. He, Y.H. Guo et al., Development of SnAg-based lead free solders in electronics packaging—ScienceDirect[J]. Microelectron. Reliab. 52(3), 559–578 (2012)
K. Kobayashi, I. Shohji, H. Hokazono, Tensile and fatigue properties of miniature size specimens of Sn-5Sb lead-free solder[J]. Mater. Sci. Forum 879, 2377–2382 (2017)
M. Hasnine, B. Tolla, N. Vahora, Microstructural evolution and mechanical behavior of high-temperature solders: Effects of high-temperature aging[J]. J. Electron. Mater. 6, 1–11 (2017)
R.M. Shalaby, M. Kamal, E.A.M. Ali et al., Microstructural and mechanical characterization of melt spun process Sn-3.5Ag and Sn-35.Ag-xCu lead-free solders for low cost electronic assembly[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. 690, 446–452 (2017)
F. Guo, S. Choi, J.P. Lucas et al., Microstructural characterisation of reflowed and isothermally-aged Cu and Ag particulate reinforced Sn-3.5Ag composite solders[J]. Solder. Surf. Mount Technol. 13(1), 7–18 (2001)
R. Mahmudi, S. Mahin-Shirazi, Effect of Sb addition on the tensile deformation behavior of lead-free Sn–3.5Ag solder alloy[J]. Mater. Design 32(10), 5027–5032 (2011)
J. Wan, Y. Liu, W. Chen et al., Effect of the addition of In on the microstructural formation of Sn–Ag–Zn lead-free solder[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 463(1–2), 230–237 (2008)
J. Peng, Y. Liu, W. Chen et al., Effect of high-temperature annealing on the microstructural formation of Sn–3.7Ag–0.9Zn– x Al lead-free solder[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 20(2), 139–143 (2009)
J. Shen, Y.C. Liu, Y.J. Han et al., Strengthening effects of ZrO2 nanoparticles on the microstructure and microhardness of Sn-3.5Ag lead-free solder[J]. J Electro Mater 35(8), 1672–1679 (2006)
M. Sobhy, Effects of torsional oscillation on tensile behavior of Sn–3.5wt% Ag alloy with and without adding ZnO nanoparticles[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 610, 237–242 (2014)
S. Wiese, K.J. Wolter, Microstructure and creep behaviour of eutectic SnAg and SnAgCu solders[J]. Microelectron. Reliab. 44(12), 1923–1931 (2004)
S. Liu, Z. Hu, J. Xiong et al., Effects of forming processes on the microstructure and solderability of Sn-3.5Ag eutectic solder ribbons as well as the mechanical properties of solder joints[J]. J. Electron. Mater. 46(11), 6737 (2017)
A.A. El-Daly, A.Z. Mohamad, A. Fawzy et al., Creep behavior of near-peritectic Sn-5Sb solders containing small amount of Ag and Cu[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528(3), 1055–1062 (2011)
A.A. El-Daly, Y. Swilem, A.E. Hammad, Creep properties of Sn-Sb based lead-free solder alloys[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 471(1–2), 98–104 (2009)
A.A. El-Daly, A. Fawzy, A.Z. Mohamad et al., Microstructural evolution and tensile properties of Sn-5Sb solder alloy containing small amount of Ag and Cu[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 509(13), 4574–4582 (2011)
M. Kamal, E.S. Gouda, Decomposition behavior and properties for tin-antimony alloy with bismuth content[J]. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 161(7), 427–431 (2006)
A.R. Geranmayeh, G. Nayyeri, R. Mahmudi, Microstructure and impression creep behavior of lead-free Sn–5Sb solder alloy containing Bi and Ag[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 547, 110–119 (2012)
R.M. Shalaby, Influence of indium addition on structure, mechanical, thermal and electrical properties of tin–antimony based metallic alloys quenched from melt[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 480(2), 334–339 (2009)
M.M. Mansour, G. Saad, L.A. Wahab et al., Indentation creep behavior of thermally aged Sn-5wt%Sb-1.5wt%Ag solder integrated with ZnO nanoparticles[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 8348–8357 (2019)
M.M. Mansour, A. Fawzy, L.A. Wahab et al., Tensile characteristics of Sn–5wt%Sb–1.5wt%Ag reinforced by nano-sized ZnO particles[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 4831–4841 (2019)
M. Sobhy, A.M. El-Refai, A. Fawzy, Effect of graphene oxide nano-sheets (GONSs) on thermal, microstructure and stress–strain characteristics of Sn-5wt% Sb-1wt% Ag solder alloy[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27(3), 2349–2359 (2016)
E.A. Eid, A.M. Deghady, A.N. Fouda, Enhanced microstructural, thermal and tensile characteristics of heat treated Sn-50Sb-03Cu (SSC-503) Pb-free solder alloy under high pressure[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. 743, 726–732 (2019)
M. Dias, T.A. Costa, B.L. Silva et al., A comparative analysis of microstructural features, tensile properties and wettability of hypoperitectic and peritectic Sn-Sb solder alloys[J]. Microelectronics Reliability 81, 150–158 (2018)
L. Zhang, Z.Q. Liu, Inhibition of intermetallic compounds growth at Sn–58Bi/Cu interface bearing CuZnAl memory particles (2–6 μm) [J]. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(1), 2466–2480 (2020)
J.J. Yu, C.A. Yang, Y.F. Lin et al., Optimal Ag addition for the elimination of voids in Ni/SnAg/Ni micro joints for 3D IC applications[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 629, 16–21 (2015)
B. Guo, A. Kunwar, C. Jiang et al., Synchrotron radiation imaging study on the rapid IMC growth of Sn–xAg solders with Cu and Ni substrates during the heat preservation stage[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29(1), 589–601 (2018)
H. Ma, A. Kunwar, B. Guo et al., Effect of cooling condition and Ag on the growth of intermetallic compounds in Sn-based solder joints[J]. Appl. Phys. A122(12), 1052.1-1052.10 (2016)
C. Yu, J.S. Chen, K.Y. Wang et al., Suppression effect of Cu and Ag on Cu3Sn layer in solder joints[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24(11), 4630–4635 (2013)
M.O. Alam, Y.C. Chan, Solid-state growth kinetics of Ni3Sn4 at the Sn–3.5Ag solder/Ni interface[J]. J. Appl. Phys. 98(12), 14–485 (2005)
A. Kumar, C. Zhong, Influence of solid-state interfacial reactions on the tensile strength of Cu/electroless Ni–P/Sn–3.5Ag solder joint[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 423(1–2), 175–179 (2006)
J.W. Yoon, J.H. Bang, C.W. Lee et al., Interfacial reaction and intermetallic compound formation of Sn–1Ag/ENIG and Sn–1Ag/ENEPIG solder joints[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 627, 276–280 (2015)
S. Tian, Y. Liu, Q. Ma et al., Intermetallics-induced directional growth of Sn whiskers in Sn-3.5Ag coating on Al substrate[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci. 539, 148135 (2021)
Y. Yao, J. Zhou, F. Xue et al., Interfacial structure and growth kinetics of intermetallic compounds between Sn-3.5Ag solder and Al substrate during solder process[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 682, 627–633 (2016)
M.Y. Xiong, L. Zhang, Interface reaction and intermetallic compound growth behavior of Sn-Ag-Cu lead-free solder joints on different substrates in electronic packaging[J]. J. Mater. Sci. 54(3), 1741–1768 (2019)
A. Kunwar, H. Ma, H. Ma et al., On the increase of intermetallic compound’s thickness at the cold side in liquid Sn and SnAg solders under thermal gradient[J]. Mater. Lett. 172, 211–215 (2016)
D.T. Chu, Y.C. Chu, J.A. Lin et al., Growth competition between layer-type and porous-type Cu3Sn in microbumps[J]. Microelectron. Reliab. 79, 32–37 (2017)
F.Y. Ouyang, Y.P. Su, Growth kinetic of Ag3Sn intermetallic compound in micro-scale Pb-free solder alloys under a temperature gradient[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 655, 155–164 (2016)
F.Y. Ouyang, G.L. Hong, Y.R. Hsu et al., Thermomigration in Co/SnAg/Co and Cu/SnAg/Co sandwich structure[J]. Microelectron. Reliab. 97, 16–23 (2019)
Y.S. Yang, C.J. Yang, F.Y. Ouyang, Interfacial reaction of Ni3Sn4 intermetallic compound in Ni/SnAg solder/Ni system under thermomigration[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 674, 331–340 (2016)
Y.S. Huang, H.Y. Hsiao, C. Chen et al., The effect of a concentration gradient on interfacial reactions in microbumps of Ni/SnAg/Cu during liquid-state soldering[J]. Scripta Mater. 66(10), 741–744 (2012)
Y.W. Wang, Y.W. Lin, C.R. Kao, Kirkendall voids formation in the reaction between Ni-doped SnAg lead-free solders and different Cu substrates[J]. Microelectron. Reliab. 49(3), 248–252 (2009)
J.G. Lee, K.N. Subramanian, Microstructural features contributing to enhanced behaviour of Sn-Ag based solder joints[J]. Solder. Surf. Mount Technol. 17(1), 33–39 (2005)
C.Y. Ho, M.T. Tsai, J.G. Duh et al., Bump height confinement governed solder alloy hardening in Cu/SnAg/Ni and Cu/SnAgCu/Ni joint assemblies[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 600, 199–203 (2014)
H.R. Kotadia, O. Mokhtari, M. Bottrill et al., Reactions of Sn-3.5Ag-Based Solders Containing Zn and Al Additions on Cu and Ni(P) Substrates[J]. J. Electron. Mater. 39(12), 2720–2731 (2010)
M. Lu, D.Y. Shih, S.K. Kang et al., Effect of Zn doping on SnAg solder microstructure and electromigration stability[J]. J. Appl. Phys. 106(5), 1611–1615 (2009)
S. Tikale, K.N. Prabhu, Effect of multiple reflow cycles on the shear strength of nano-Al2O3 particles reinforced Sn3.6Ag lead-free solder alloy[J]. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 71, 2855–2859 (2018)
C. Yu, Y. Yang, K. Wang et al., Relation between Kirkendall voids and intermetallic compound layers in the SnAg/Cu solder joints[J]. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 23(1), 124–129 (2012)
C. Lee, C.Y. Lin, Y.W. Yen, The 260 °C phase equilibria of the Sn–Sb–Cu ternary system and interfacial reactions at the Sn–Sb/Cu joints[J]. Intermetallics 39(35), 1027–1037 (2010)
J.P. Curtulo, M. Dias, F. Bertelli et al., The application of an analytical model to solve an inverse heat conduction problem: Transient solidification of a Sn-Sb peritectic solder alloy on distinct substrates[J]. J. Manuf. Process. 48, 164–173 (2019)
X.N. Du, J.D. Guo, J.K. Shang, Effect of electromigration on interfacial reactions in 90Sn-10Sb Pb-free solder joints[J]. J. Electron. Mater. 38(11), 2398–2404 (2009)
C.H. Lee, W.T. Chen, C.N. Liao, Effect of antimony on vigorous interfacial reaction of Sn–Sb/Te couples[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 509(16), 5142–5146 (2011)
B.Y. Han, F.L. Sun, T.H. Li et al., Microstructure evolution of Au/SnSb-CuNiAg/(Au)Ni during high temperature aging[J]. Solder. Surf. Mount Technol. 32(2), 57–64 (2020)
T.T. Dele-Afolabi, M. Hanim, M. Norkhairunnisa et al., Growth kinetics of intermetallic layer in lead-free Sn–5Sb solder reinforced with multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26(10), 8249–8259 (2015)
N. Jiang, L. Zhang, Z.Q. Liu et al., Reliability issues of lead-free solder joints in electronic devices[J]. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 20(1), 876–901 (2019)
B. Yeung, J.W. Jang, Correlation between mechanical tensile properties and microstructure of eutectic Sn-3.5Ag solder[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 21(9), 723–726 (2002)
W.M. Chen, P. Mccloskey, S.C. O’Mathuna, Isothermal aging effects on the microstructure and solder bump shear strength of eutectic Sn37Pb and Sn3.5Ag solders[J]. Microelectron. Reliab. 46(5–6), 896–904 (2006)
H. Rhee, K.N. Subramanian, A. Lee et al., Mechanical characterization of Sn-3.5Ag solder joints at various temperatures[J]. Solder. Surf. Mount Technol. 15(3), 21–26 (2003)
M.Y. Guo, C.K. Lin, C. Chen et al., Asymmetrical growth of Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compounds due to rapid thermomigration of Cu in molten SnAg solder joints - ScienceDirect[J]. Intermetallics 29(10), 155–158 (2012)
J. Keller, D. Baither, U. Wilke et al., Mechanical properties of Pb-free SnAg solder joints[J]. Acta Mater. 59(7), 2731–2741 (2011)
I. Shohji, T. Yoshida, T. Takahashi et al., Tensile properties of Sn-Ag based lead-free solders and strain rate sensitivity[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 366(1), 50–55 (2004)
D.B. Witkin, Influence of microstructure on quasistatic and dynamic mechanical properties of bismuth-containing lead-free solder alloys-ScienceDirect[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 532(3), 212–220 (2012)
P. Babaghorbani, S.M.L. Nai, M. Gupta, Development of lead-free Sn-3.5Ag/SnO2 nanocomposite solders[J]. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 20(6), 571–576 (2009)
P. Babaghorbani, S.M.L. Nai, M. Gupta, Reinforcements at nanometer length scale and the electrical resistivity of lead-free solders[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 478(1–2), 458–461 (2009)
M. Lederer, A.B. Kotas, G. Khatibi, A lifetime assessment and prediction method for large area solder joints[J]. Microelectron. Reliab. 114, 113888 (2020)
M.J. Esfandyarpour, R. Mahmudi, Microstructure and tensile behavior of Sn–5Sb lead-free solder alloy containing Bi and Cu[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 530, 402–410 (2011)
T.T. Dele-Afolabi, M.A. Azmah Hanim, M. Norkhairunnisa et al., Investigating the effect of isothermal aging on the morphology and shear strength of Sn-5Sb solder reinforced with carbon nanotubes[J]. J. Alloy. Compd. 649, 368–374 (2015)
A.R. Geranmayeh, R. Mahmudi, M. Kangooie, High-temperature shear strength of lead-free Sn–Sb–Ag/Al2O3 composite solder[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528(12), 3967–3972 (2011)
O.L. Rocha, T.A. Costa, M. Dias et al., Cellular/dendritic transition, dendritic growth and microhardness in directionally solidified monophasic Sn-2%Sb alloy[J]. Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. China 28(8), 1686 (2018)
E.S. Gouda, E.M. Ahmed, F.A.S. Allah, Electrical and mechanical properties of Sn-5wt.% Sb alloy with annealing temperature[J]. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 45(1), 10901 (2009)
K.K. Xu, L. Zhang, L.L. Gao et al., Review of microstructure and properties of low temperature lead-free solder in electronic packaging[J]. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 21(1), 689–711 (2020)
Z. Xu, A. Sharma, S.J. Lee et al., Effect of soldering temperature on wetting and optical density of dip coated Sn and Sn-3.5Ag solders[J]. Adv. Manuf. Process. 30(1), 127–132 (2015)
C.Y. Liu, L. Jian, G.J. Vandentop et al., Wetting reaction of Sn-Ag based solder systems on Cu substrates plated with Au and/or Pd layer[J]. J. Electron. Mater. 30(5), 521–525 (2001)
V.U. Nayak, K.N. Prabhu, N. Stanford et al., Wetting behavior and evolution of microstructure of Sn-3.5Ag solder alloy on electroplated 304 stainless steel substrates[J]. Trans. Indian Inst. Metal. 65(6), 713–717 (2012)
L.Y. Hsiao, J.G. Duh, Synthesis and characterization of lead-free solders with Sn-3.5Ag-xCu (x = 0.2, 0.5, 1.0) alloy nanoparticles by the chemical reduction method[J]. J. Electrochem. Soc. 152(9), J105–J109 (2005)
Peng L, Fu G. Effects of Ni particle addition on microstructure and properties of SnAg based composite solders[C]// Electronics Packaging Technology Conference. IEEE, 2006.
W. Min, X. Su, An investigation on surface tension of Sn-based lead free solders[J]. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26(11), 1–7 (2015)
M.M. El-Bahay, M. Mossalamy, M. Mahdy et al., Study of the mechanical and thermal properties of Sn-5 wt% Sb solder alloy at two annealing temperatures[J]. Phys. Status Solidi 198(1), 76–90 (2003)
J.M. Song, Z.M. Wu, D.A. Huang, Two-stage nonequilibrium eutectic transformation in a Sn–3.5Ag–3In solder[J]. Scr. Mater. 56, 413–416 (2007)
S.W. Chen, P.Y. Chen, C.H. Wang, Lowering of SnSb alloy melting points caused by substrate dissolution[J]. J. Electron. Mater. 35(11), 1982–1985 (2006)
E.M.A. Ahmed, M.A. Amin, N. Tubaylah, Evolution of microstructure and physical properties of lead-free Sn–5Sb-Ag rapidly solidified solder alloys[J]. Appl. Phys. A 127(6), 403 (2021)
E.S. Gouda, Effect of Solidification Conditions on Structure and Properties of Rapidly-Solidified Sn-7.5wt%Sb Alloy[J]. Adv. Manuf. Process. 22(7–8), 842–845 (2007)
Q.K. Zhang, Z.F. Zhang, In situ observations on creep fatigue fracture behavior of Sn–4Ag/Cu solder joints[J]. Acta Mater. 59(15), 6017–6028 (2011)
I. Dutta, C. Park, S. Choi, Impression creep characterization of rapidly cooled Sn–3.5Ag solders[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 379(1/2), 401–410 (2004)
D. Taneja, M. Volpert, F. Hodaj, Further insight into interfacial interactions in nickel/liquid Sn–Ag solder system at 230–350 °C[J]. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28(24), 1–13 (2017)
D. Witkin, Creep behavior of Bi-containing lead-free solder alloys[J]. J. Electron. Mater. 41(2), 190–203 (2012)
Z.J. Yang, S.M. Yang, H.S. Yu et al., IMC and creep behavior in Lead-free solder joints of Sn-Ag and Sn-Ag-Cu alloy system by SP method[J]. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 15(7), 1137–1142 (2014)
X. Huang, Z. Wang, Y. Yu, Thermomechanical properties and fatigue life evaluation of SnAgCu solder joints for microelectronic power module application[J]. J. Market. Res. 9(3), 5533–5541 (2020)
F. Guo, J. Lee, K.N. Subramanian, Creep behaviour of composite lead-free electronic solder joints[J]. Solder. Surf. Mount Technol. 15(1), 39–42 (2003)
L. Zhang, L. Sun, Y.H. Guo et al., Reliability of lead-free solder joints in CSP device under thermal cycling[J]. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25(3), 1209–1213 (2014)
M.D. Mathew, H. Yang, S. Movva et al., Creep deformation characteristics of tin and tin-based electronic solder alloys[J]. Metall. and Mater. Trans. A. 36(1), 99–105 (2005)
R. Mahmudi, A. Maraghi, Shear punch creep behavior of cast lead-free solders[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 599, 180–185 (2014)
R. Mahmudi, A.R. Geranmayeh, M. Allami et al., Effect of homogenization on the indentation creep of cast lead-free Sn-5%Sb solder alloy[J]. J. Electron. Mater. 36(12), 1703–1710 (2007)
A.R. Geranmayeh, R. Mahmudi, Power law indentation creep of Sn-5% Sb solder alloy[J]. J. Mater. Sci. 40(13), 3361–3366 (2005)
R. Mahmudi, A.R. Geranmayeh, A. Rezaee-Bazzaz, Impression creep behavior of lead-free Sn–5Sb solder alloy[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 448(1–2), 287–293 (2007)
Y. Park, J.H. Bang, C.M. Oh et al., The effect of eutectic structure on the creep properties of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu and Sn-8.0Sb-3.0Ag solders[J]. Multidiscip. Digital Publish. Inst. 7(12), 540 (2017)
Z. Liang, S.B. Xue, L.L. Gao et al., Development of Sn–Zn lead-free solders bearing alloying elements[J]. J. Mater. Mater. Electron. 21(1), 1–15 (2010)
S.L. Tay, A. Haseeb, M.R. Johan, Addition of cobalt nanoparticles into Sn-3.8Ag-0.7Cu lead-free solder by paste mixing[J]. Solder. Surf. Mount Technol. 23(1), 10–14 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The present work was under support of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20211351), the Key project of State Key Laboratory of Advanced Welding and Joining (AWJ-19Z04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xi Wang involved in data curation and writing—original draft preparation. Liang Zhang and Mu-lan Li participated in writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Zhang, L. & Li, Ml. Microstructure and properties of Sn-Ag and Sn-Sb lead-free solders in electronics packaging: a review. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 2259–2292 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07437-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07437-6