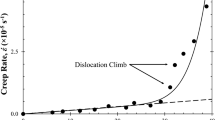
Creep behavior of cast lead-free Sn-5%Sb solder in unhomogenized and homogenized conditions was investigated by long time Vickers indentation testing under a constant load of 15 N and at temperatures in the range 321–405 K. Based on the steady-state power law creep relationship, the stress exponents were found for both conditions of the material. The creep behavior in the unhomogenized condition can be divided into two stress regimes, with a change from the low-stress regime to the high-stress regime occurring around 11.7 × 10−4 < (H V /E) < 18 × 10−4. The low stress regime activation energy of 54.2 kJ mol−1, which is close to 61.2 kJ mol−1 for dislocation pipe diffusion in the Sn, and stress exponents in the range 5.0–3.5 suggest that the operative creep mechanism is dislocation viscous glide. This behavior is in contrast to the high stress regime in which the average values of n = 11.5 and Q = 112.1 kJ mol−1 imply that dislocation creep is the dominant deformation mechanism. Homogenization of the cast material resulted in a rather coarse recrystallized microstructure with stress exponents in the range 12.5–5.7 and activation energy of 64.0 kJ mol−1 over the whole ranges of temperature and stress studied, which are indicative of a dislocation creep mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D.G. Kim and S.B. Jung, J. Alloys Compd. 386, 151 (2005).
R.A. Islam, B.Y. Wu, M.O. Alam, Y.C. Chan, and W. Jillek, J. Alloys Compd. 392, 149 (2005).
F. Ochoa, X. Deng, and N. Chawala, J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1596 (2004).
M.D. Mathew, H. Yang, S. Movva, and K.L. Murty, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36A, 99 (2005).
N. Wade, K. Wu, J. Kunii, S. Yamada, and K. Miyahara, J. Electron. Mater. 30, 1228 (2001).
K.L. Murty, F.M. Haggag, and R.K. Mahidhara, J. Electron. Mater. 26, 839 (1997).
P.T. Vianco and D.R. Frear, JOM 45(7), 14 (1993).
D. Mitlin, C.H. Raeder, and R.W. Messler, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30A, 115 (1999).
H. Mavoori, JOM 52(6), 29 (2000).
R.J. McCabe and M.E. Fine, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 33A, 1531 (2002).
A. de La Torre, P. Adeva, and M. Aballe, J. Mater. Sci. 26, 4351 (1991).
B.N. Lucas and W.C. Oliver, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30A, 601 (1999).
M. Fujiwara and M. Otsuka, Mater. Sci. Eng., A A319-321, 929 (2001).
F. Yang and J.C.M. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng., A A201, 40 (1995).
A. Juhasz, P. Tasnadi, and I. Kovacs, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 5, 35 (1986).
I. Dutta, C. Park, and S. Choi, Mater. Sci. Eng., A A379, 401 (2004).
R. Mahmudi and A. Rezaee-Bazzaz, Mater. Lett. 59, 1705 (2005).
T.T. Fang, R.R. Cola, and K.L. Murty, Metall. Trans. A 17A, 1447 (1986).
R. Roumina, B. Raeisinia, and R. Mahmudi, Scripta Mater. 51, 497 (2004).
R. Mahmudi, R. Roumina, and B. Raeisinia, Mater. Sci. Eng., A A382, 15 (2004).
A.R. Geranmayeh and R. Mahmudi, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 1002 (2005).
A.R. Geranmayeh and R. Mahmudi, J. Mater. Sci. 40, 3361 (2005).
R. Mahmudi, A.R. Geranmayeh, and A. Rezaee-Bazzaz, Mater. Sci. Eng., A A448, 287 (2007).
P.M. Sargent andM.F. Ashby, Mater. Sci. Technol. 8, 594 (1992).
L. Rotherham, A.D.N. Smith, and G.B. Greenough, J. Inst. Met. 79, 439 (1951).
T.G. Langdon, Strength of Metals and Alloys. Proc. 6th Int. Conf., August 1982, ICSMA 6, ed. R.C. Gifkins (Pergamon Press, NY, 1982), p. 1105.
T. Reinikainen and J. Kivilahti, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30A, 123 (1999).
J.D. Meakin and E. Klokholm, Trans. TMS-AIME, 218, 463 (1960).
B. Walser and O.D. Sherby, Scripta Matell. 16, 213 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmudi, R., Geranmayeh, A., Allami, M. et al. Effect of Homogenization on the Indentation Creep of Cast Lead-Free Sn-5%Sb Solder Alloy. J. Electron. Mater. 36, 1703–1710 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-007-0275-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-007-0275-5