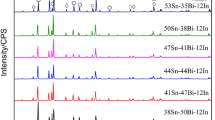
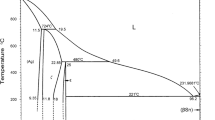
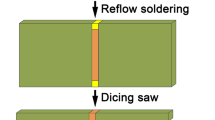
Abstract
With the implementation of legislations on inhibiting the usage of Sn–Pb solder in consumer electronic products, Sn–Ag–Cu series solder has been gotten the most application. However, there are some stimulations from electronic manufacturers to adopt low temperature soldering such as the economic driver from the reduction in manufacturing assembly cost and the reliability driver to avoid the dynamic warpage of area array components caused from Sn–Ag–Cu solder. Sn–Bi series solder is one of the promising candidates, which met the requirements for low melting point, low cost and environment friendly. However, the disadvantage of brittleness characteristic prevented its wide practical application. In order to promote the better application of Sn–Bi based solders, many efforts have been made to improve the wettability, mechanical properties and reliability of Sn–Bi based solders. This paper will summarize the related results about Sn–Bi solder alloys from wettability, interfacial reaction, mechanical properties of Sn–Bi solder and reliabilities of Sn–Bi solder joints. Moreover, in order to improve the properties of Sn–Bi solders, researchers have done lots of works on effect of addition of element dopants. The corresponding works of effect of alloying elements on the properties of Sn–Bi solder were also focused. According to the existing research results, it provides an important basis of understanding the current development of Sn–Bi solders.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.N. Tu, K. Zeng, Tin–lead (SnPb) solder reaction in flip chip technology. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 34, 1–58 (2001)
L. Zhang, K.N. Tu, Structure and properties of lead-free solders bearing micro and nano particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 82, 1–32 (2014)
I.E. Anderson, Development of Sn–Ag–Cu and Sn–Ag–Cu–X alloys for Pb-free electronic solder applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 18, 55–76 (2007)
H. Ma, J.C. Suhling, A review of mechanical properties of lead-free solders for electronic packaging. J. Mater. Sci. 44, 1141–1158 (2009)
D. Amir, S. Walwadkar, S. Aravamudhan, L. May, in The Challenges of Non-wet Open BGA Solder Defect. SMTAI Proceedings, Orlando, FL, 2012, pp. 684–694
B. Sandy, E. Briggs, R. Lasky, Advantages of bismuth-based alloys for low-temperature lead-free soldering and rework. Surf. Mt Technol. Mag. 26, 26–40 (2011)
Z. Zhao, C. Chen, C.Y. Park, Y. Wang, L. Liu, G. Zou, J. Cai, Q. Wang, Effects of package warpage on Head-in-Pillow defect. Mater. Trans. 56, 1037–1042 (2015)
K. Suganuma, K. Niihara, T. Shoutoku, Y. Nakamura, Wetting and interface microstructure between Sn–Zn binary alloys and Cu. J. Mater. Res. 13, 2859–2865 (1998)
S. Liu, S.B. Xue, P. Xue, D.X. Luo, Present status of Sn–Zn lead-free solders bearing alloying elements. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 4389–4411 (2015)
H.R. Kotadia, P.D. Howes, S.H. Mannan, A review: on the development of low melting temperature Pb-free solders. Microelectron. Reliab. 54, 1253–1273 (2014)
Y. Li, F.S. Wu, Y.C. Chan, Electromigration in eutectic In–48Sn ball grid array (BGA) solder interconnections with Au/Ni/Cu pads. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 8522–8533 (2015)
F. Hua, Z. Mei, J. Glazer, in Eutectic Sn–Bi as an Alternative to Pb-Free Solders. 48th Electronic Components and Technology Conference, Seattle, WA, 1998, pp. 277–283
Z. Mei, J.W. Morris, Characterization of eutectic Sn–Bi solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 21, 599–607 (1992)
P.L. Liu, J.K. Shang, Interfacial embrittlement by bismuth segregation copper/tin–bismuth Pb-free solder interconnect. J. Mater. Res. 16, 1651–1659 (2001)
H.F. Zou, Q.K. Zhang, Z.F. Zhang, Transition of Bi embrittlement of SnBi/Cu joint couples with reflow temperature. J. Mater. Res. 26, 449–454 (2010)
X. Chen, F. Xue, J. Zhou, Y. Yao, Effect of In on microstructure, thermodynamic characteristic and mechanical properties of Sn–Bi based lead-free solder. J. Alloy Compd 633, 377–383 (2015)
W.X. Dong, Y.W. Shi, Z.D. Xia, Y.P. Lei, F. Guo, Effects of trace amounts of rare earth additions on microstructure and properties of Sn–Bi-based solder alloy. J. Electron. Mater. 37, 982–991 (2008)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, Interfacial microstructure, wettability and material properties of nickel (Ni) nanoparticle doped tin–bismuth–silver (Sn–Bi–Ag) solder on copper (Cu) substrate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 3982–3994 (2016)
L. Yang, L. Zhu, Y.C. Zhang, P. Liu, N. Zhang, S.Y. Zhou, L.C. Jiang, Microstructure and reliability of Mo nanoparticle reinforced Sn–58Bi-based lead-free solder joints. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34, 992–1002 (2018)
Y. Liu, H. Zhang, F.L. Sun, Solderability of SnBi-nano Cu solder pastes and microstructure of the solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 2235–2241 (2016)
L. Yang, J. Dai, Y.C. Zhang, Y.F. Jing, J.G. Ge, H.X. Liu, Influence of BaTiO3 nanoparticle addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn–58Bi solder. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 2473–2478 (2015)
X.Y. Liu, M.L. Huang, C.M.L. Wu, L. Wang, Effect of Y2O3 particles on microstructure formation and shear properties of Sn–58Bi solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21, 1046–1054 (2010)
L. Yang, C.C. Du, J. Dai, N. Zhang, Y.F. Jing, Effect of nanosized graphite on properties of Sn–Bi solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 4180–4185 (2013)
S.T. Oh, J.H. Lee, Microstructural, wetting, and mechanical characteristics of Sn–57.6Bi–0.4Ag alloys doped with metal-organic compounds. Electron. Mater. Lett. 10, 473–478 (2014)
C.-B. Lee, S.-B. Jung, Y.-E. Shin, C.-C. Shur, The effect of Bi concentration on wettability of Cu substrate by Sn–Bi solders. Mater. Trans. 42, 751–755 (2001)
X. Chen, F. Xue, J. Zhou, S. Liu, G. Qian, Microstructure, thermal and wetting properties of Sn–Bi–Zn lead-free solder. J. Electron. Mater. 42, 2708–2715 (2013)
C. Zhang, S. Liu, G. Qian, J. Zhou, F. Xue, Effect of Sb content on properties of Sn–Bi solders. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 24, 184–191 (2014)
P. Sebo, P. Svec, D. Janickovic, E. Illekova, M. Zemankova, Y. Plevachuk, V. Sidorov, P. Svec, The influence of silver content on structure and properties of Sn–Bi–Ag solder and Cu/solder/Cu joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 571, 184–192 (2013)
Z.M. Lai, D. Ye, Microstructure and properties of Sn–10Bi–xCu solder alloy/joint. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 3702–3711 (2016)
A.K. Gain, L.C. Zhang, Growth mechanism of intermetallic compound and mechanical properties of nickel (Ni) nanoparticle doped low melting temperature tin–bismuth (Sn–Bi) solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 781–794 (2016)
S.A. Belyakov, C.M. Gourlay, Recommended values for the β-Sn solidus line in Sn–Bi alloys. Thermochim. Acta 654, 65–69 (2017)
F. Wang, Y. Huang, Z. Zhang, C. Yan, Interfacial reaction and mechanical properties of Sn–Bi solder joints. Materials 10(8), 920 (2017)
Z.M. Lai, D. Ye, Microstructure and fracture behavior of non eutectic Sn–Bi solder alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 3182–3192 (2016)
O. Mokhtari, H. Nishikawa, Correlation between microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn–Bi–X solders. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 651, 831–839 (2016)
Q. Li, N. Ma, Y. Lei, J. Lin, H. Fu, J. Gu, Characterization of low-melting-point Sn–Bi–In lead-free solders. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 5800–5810 (2016)
T.-H. Chuang, H.-F. Wu, Effects of Ce addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn–58Bi solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 40, 71–77 (2011)
J. Shen, C. Wu, S. Li, Effects of rare earth additions on the microstructural evolution and microhardness of Sn30Bi0.5Cu and Sn35Bi1Ag solder alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23, 156–163 (2012)
J. Shen, Y.Y. Pu, H.G. Yin, D.J. Luo, J. Chen, Effects of minor Cu and Zn additions on the thermal, microstructure and tensile properties of Sn–Bi-based solder alloys. J. Alloy Compd 614, 63–70 (2014)
X.J. Wang, Y.L. Wang, F. Wang, N. Liu, J.X. Wang, Effects of Zn, Zn–Al and Zn–P additions on the tensile properties of Sn–Bi solder. Acta Metall. Sin. Engl. Lett. 27, 1159–1164 (2014)
Y. Li, K.M. Luo, A.B.Y. Lim, Z. Chen, F.S. Wu, Y.C. Chan, Improving the mechanical performance of Sn57.6Bi0.4Ag solder joints on Au/Ni/Cu pads during aging and electromigration through the addition of tungsten (W) nanoparticle reinforcement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 669, 291–303 (2016)
D.L. Ma, P. Wu, Improved microstructure and mechanical properties for Sn58Bi0.7Zn solder joint by addition of graphene nanosheets. J. Alloy Compd 671, 127–136 (2016)
Y. Ma, X. Li, W. Zhou, L. Yang, P. Wu, Reinforcement of graphene nanosheets on the microstructure and properties of Sn58Bi lead-free solder. Mater. Des. 113, 264–272 (2017)
P. He, X.C. Lu, T.S. Lin, H.X. Li, J. An, X. Ma, J.C. Feng, Y. Zhang, Q. Li, Y.Y. Qian, Improvement of mechanical properties of Sn–58Bi alloy with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 22, S692–S696 (2012)
S. Zhou, O. Mokhtari, M.G. Rafique, V.C. Shunmugasamy, B. Mansoor, H. Nishikawa, Improvement in the mechanical properties of eutectic Sn58Bi alloy by 0.5 and 1 wt% Zn addition before and after thermal aging. J. Alloy Compd 765, 1243–1252 (2018)
Y.C. Huang, W. Gierlotka, S.W. Chen, Sn–Bi–Fe thermodynamic modeling and Sn–Bi/Fe interfacial reactions. Intermetallics 18, 984–991 (2010)
M. Hirman, K. Rendl, F. Steiner, V. Wirth, in Influence of Reflow Soldering Profiles on Creation of IMC at the Interface of SnBi/Cu. 37th International Spring Seminar on Electronics Technology, 2014, pp. 147–151
T.Y. Kang, Y.Y. Xiu, L. Hui, J.J. Wang, W.P. Tong, C.Z. Liu, Effect of bismuth on intermetallic compound growth in lead free solder/Cu microelectronic interconnect. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 27, 741–745 (2011)
F. Wang, H. Chen, Y. Huang, C. Yan, Interfacial behavior and joint strength of Sn–Bi solder with solid solution compositions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 11409–11420 (2018)
T. Laurila, V. Vuorinen, J.K. Kivilahti, Interfacial reactions between lead-free solders and common base materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 49, 1–60 (2005)
X. Hu, Y. Li, Z. Min, Interfacial reaction and growth behavior of IMCs layer between Sn–58Bi solders and a Cu substrate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 2027–2034 (2013)
T.Y. Kang, Y.Y. Xiu, C.Z. Liu, L. Hui, J.J. Wang, W.P. Tong, Bismuth segregation enhances intermetallic compound growth in SnBi/Cu microelectronic interconnect. J. Alloy Compd 509, 1785–1789 (2011)
H.F. Zou, Q.K. Zhang, Z.F. Zhang, Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of SnBi/Cu joints by alloying Cu substrate. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 532, 167–177 (2012)
C.Z. Liu, W. Zhang, Bismuth redistribution induced by intermetallic compound growth in SnBi/Cu microelectronic interconnect. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 149–153 (2009)
P.J. Shang, Z.Q. Liu, D.X. Li, J.K. Shang, Bi-induced voids at the Cu3Sn/Cu interface in eutectic SnBi/Cu solder joints. Scr. Mater. 58, 409–412 (2008)
S.-K. Lin, T.L. Nguyen, S.-C. Wu, Y.-H. Wang, Effective suppression of interfacial intermetallic compound growth between Sn–58 wt.% Bi solders and Cu substrates by minor Ga addition. J. Alloy Compd 586, 319–327 (2014)
C.H. Chen, B.H. Lee, H.C. Chen, C.M. Wang, A.T. Wu, Interfacial reactions of low-melting Sn–Bi–Ga solder alloy on Cu substrate. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 197–202 (2016)
Y.-C. Huang, S.-W. Chen, Effects of Co alloying and size on solidification and interfacial reactions in Sn–57 wt.% Bi–(Co)/Cu couples. J. Electron. Mater. 40, 62–70 (2011)
O. Mokhtari, H. Nishikawa, Effects of In and Ni addition on microstructure of Sn–58Bi solder joint. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 4158–4170 (2014)
R. Xu, Y. Liu, H. Zhang, Z. Li, F. Sun, G. Zhang, Evolution of the microstructure of Sn58Bi solder paste with Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu addition during isothermal aging. J. Electron. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-06865-1
W.R. Myung, M.K. Ko, Y. Kim, S.B. Jung, Effects of Ag content on the reliability of LED package component with Sn–Bi–Ag solder. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 8707–8713 (2015)
Z.-M. Guan, G.-X. Liu, T. Liu, Kinetics of interface reaction in 40Sn–Bi/Cu and 40Sn–Bi–2Ag/Cu systems during aging in solid state. IEEE Trans. Adv. Packag. 23, 737–742 (2000)
J. Shen, C.F. Peng, M.L. Zhao, C.P. Wu, Microstructural evolutions of the Ag nano-particle reinforced SnBiCu–xAg/Cu solder joints during liquid aging. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 23, 1409–1414 (2012)
O. Mokhtari, S. Zhou, Y.C. Chan, H. Nishikawa, Effect of Zn addition on interfacial reactions between Sn–Bi solder and Cu substrate. Mater. Trans. 57, 1272–1276 (2016)
Y.-H. Ko, J.-D. Lee, T. Yoon, C.-W. Lee, T.-S. Kim, Controlling interfacial reactions and intermetallic compound growth at the interface of a lead-free solder joint with layer-by-layer transferred graphene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 5679–5686 (2016)
L. Gao, J. Wang, T. Lin, P. He, F. Lu, in Improvement of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Sn–58Bi Alloy with La 2 O 3. 14th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology, 2013, pp. 193–195
K. Suganuma, T. Sakai, K.-S. Kim, Y. Takagi, J. Sugimoto, M. Ueshima, Thermal and mechanical stability of soldering QFP with Sn–Bi–Ag lead-free alloy. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 25(4), 257–261 (2002)
J. Wang, H.S. Liu, L.B. Liu, Z.P. Jin, Interfacial reaction between Sn–Bi alloy and Ni substrate. J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1842–1847 (2006)
S.-M. Lee, J.-W. Yoon, S.-B. Jung, Interfacial reaction and mechanical properties between low melting temperature Sn–58Bi solder and various surface finishes during reflow reactions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 1649–1660 (2015)
K.P.L. Pun, M.N. Islam, J. Rotanson, C.-W. Cheung, A.H.S. Chan, Enhancement of Sn–Bi–Ag solder Joints with ENEPIG surface finish for low-temperature interconnection. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 5191–5202 (2018)
G.P. Vassilev, K.I. Lilova, J.C. Gachon, Phase diagram investigations of the Ni–Sn–Bi system. J. Alloy Compd 469, 264–269 (2009)
Z. Zhang, X. Hu, X. Jiang, Y. Li, Influences of mono-Ni(P) and dual-Cu/Ni(P) plating on the interfacial microstructure evolution of solder joints. Metall. Mater. Trans. A (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4983-7
C.N. Chiu, C.H. Wang, S.W. Chen, Interfacial reactions in the Sn–Bi/Te couples. J. Electron. Mater. 37, 40–44 (2008)
Y.W. Yen, W.K. Liou, C.M. Chen, C.K. Lin, M.K. Huang, Interfacial reactions in the Sn–xBi/Au couples. Mater. Chem. Phys. 128, 233–237 (2011)
F. Gao, C. Wang, X. Liu, Y. Takaku, I. Ohnuma, K. Ishida, Thermodynamic assessment of phase equilibria in the Sn–Au–Bi system with key experimental verification. J. Mater. Res. 25(3), 576–586 (2010)
F. Wang, L. Zhou, X. Wang, P. He, Microstructural evolution and joint strength of Sn–58Bi/Cu joints through minor Zn alloying substrate during isothermal aging. J. Alloy Compd 688, 639–648 (2016)
Q.K. Zhang, H.F. Zou, Z.F. Zhang, Improving tensile and fatigue properties of Sn–58Bi/Cu solder joints through alloying substrate. J. Mater. Res. 25, 303–314 (2010)
Q.K. Zhang, H.F. Zou, Z.F. Zhang, Influences of substrate alloying and reflow temperature on Bi segregation behaviors at Sn–Bi/Cu interface. J. Electron. Mater. 40(11), 2320–2328 (2011)
X. Chen, J. Zhou, F. Xue, Y. Yao, Mechanical deformation behavior and mechanism of Sn–58Bi solder alloys under different temperatures and strain rates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 662, 251–257 (2016)
I. Abdullah, M.N. Zulkifli, A. Jalar, R. Ismail, Deformation behaviour of Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu (SAC305) solder wire under varied tensile strain rates. Solder. Surf. Mt Technol. 29, 110–117 (2017)
D.L. Ma, P. Wu, Effects of Zn addition on mechanical properties of eutectic Sn–58Bi solder during liquid-state aging. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 25(4), 1225–1233 (2015)
M.M. Billah, Q. Chen, Strength of MWCNT-reinforced 70Sn–30Bi solder alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 98–103 (2016)
W.B. Zhu, Y. Ma, X.Z. Li, W. Zhou, P. Wu, Effects of Al2O3 nanoparticles on the microstructure and properties of Sn58Bi solder alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 7575–7585 (2018)
X.Z. Li, Y. Ma, W. Zhou, P. Wu, Effects of nanoscale Cu6Sn5 particles addition on microstructure and properties of SnBi solder alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 684, 328–334 (2017)
Q.K. Zhang, Z.F. Zhang, In situ observations on shear and creep–fatigue fracture behaviors of SnBi/Cu solder joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 2686–2693 (2011)
F. Wang, D. Li, Z. Zhang, M. Wu, C. Yan, Improvement on interfacial structure and properties of Sn–58Bi/Cu joint using Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu solder as barrier. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 19051–19060 (2017)
H.Y. Sun, Q.Q. Li, Y.C. Chan, A study of Ag additive methods by comparing mechanical properties between Sn57.6Bi0.4Ag and 0.4 wt% nano-Ag-doped Sn58Bi BGA solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, 4380–4390 (2014)
J. Shen, Y.Y. Pu, H.G. Yin, Q. Tang, Effects of Cu, Zn on the wettability and shear mechanical properties of Sn–Bi-based lead-free solders. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 532–541 (2015)
W.-R. Myung, Y. Kim, S.-B. Jung, Mechanical property of the epoxy-contained Sn–58Bi solder with OSP surface finish. J. Alloy Compd 615, S411–S417 (2014)
R. Mahmudi, A.R. Geranmayeh, S.R. Mahmoodi, A. Khalatbari, Room-temperature indentation creep of lead-free Sn–Bi solder alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 18, 1071–1078 (2007)
L. Shen, P. Septiwerdani, Z. Chen, Elastic modulus, hardness and creep performance of SnBi alloys using nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 558, 253–258 (2012)
L. Shen, P. Lu, S. Wang, Z. Chen, Creep behaviour of eutectic SnBi alloy and its constituent phases using nanoindentation technique. J. Alloys Compd 574, 98–103 (2013)
L. Shen, Y. Wu, S. Wang, Z. Chen, Creep behavior of Sn–Bi solder alloys at elevated temperatures studied by nanoindentation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 4114–4124 (2017)
L. Shen, Z.Y. Tan, Z. Chen, Nanoindentation study on the creep resistance of SnBi solder alloy with reactive nano-metallic fillers. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 561, 232–238 (2013)
R. Mahmudi, A.R. Geranmayeh, M. Salehi, H. Pirayesh, Impression creep of the rare-earth doped Sn–2% Bi lead-free solder alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21, 262–269 (2010)
R.M. Shalaby, Effect of silver and indium addition on mechanical properties and indentation creep behavior of rapidly solidified Bi–Sn based lead-free solder alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 560, 86–95 (2013)
H.-W. Miao, J.-G. Duh, B.-S. Chiou, Thermal cycling test in Sn–Bi and Sn–Bi–Cu solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 11, 609–618 (2000)
T. Akamatsu, Y. Yamagishi, K. Imamura, O. Yamaguchi, M. Minamizawa, in Solder Joint Reliability of BGA Package with Sn–Bi System Solder Balls. Proceedings of SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering, vol. 4587, 2001, pp. 547–552
M. Mostofizadeh, J. Pippola, L. Frisk, Shear strength of eutectic Sn–Bi lead-free solders after corrosion testing and thermal aging. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 1335–1346 (2014)
S.-M. Lee, J.-W. Yoon, S.-B. Jung, Board level drop reliability of epoxy-containing Sn–58 mass% Bi solder joints with various surface finishes. Mater. Trans. 57, 466–471 (2016)
W.-R. Myung, Y. Kim, S.-B. Jung, Evaluation of the bondability of the epoxy-enhanced Sn–58Bi solder with ENIG and ENEPIG surface finishes. J. Electron. Mater. 44, 4637–4645 (2015)
Y.C. Chan, D. Yang, Failure mechanisms of solder interconnects under current stressing in advanced electronic packages. Prog. Mater. Sci. 55, 428–475 (2010)
X. Gu, Y.C. Chan, Electromigration in line-type Cu/Sn–Bi/Cu solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 37, 1721–1726 (2008)
Q.L. Yang, J.K. Shang, Interfacial segregation of Bi during current stressing of Sn–Bi/Cu solder interconnect. J. Electron. Mater. 34, 1363–1367 (2005)
F. Wang, L. Liu, D. Li, M. Wu, Electromigration behaviors in Sn–58Bi solder joints under different current densities and temperatures. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 21157–21169 (2018)
D.L. Ma, P. Wu, Effects of coupled stressing and solid-state aging on the mechanical properties of Sn–58Bi–0.7Zn solder joint. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26(8), 6285–6292 (2015)
H. He, G. Xu, F. Guo, Effect of small amount of rare earth addition on electromigration in eutectic SnBi solder reaction couple. J. Mater. Sci. 44, 2089–2096 (2009)
T.W. Hu, Y. Li, Y.C. Chan, F.S. Wu, Effect of nano Al2O3 particles doping on electromigration and mechanical properties of Sn–58Bi solder joints. Microelectron. Reliab. 55, 1226–1233 (2015)
L. Yang, J. Ge, Y. Zhang, J. Dai, Y. Jing, Electromigration reliability for Al2O3-reinforced Cu/Sn–58Bi/Cu composite solder joints. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 3004–3012 (2017)
S. Ismathullakhan, H.Y. Lau, Y.C. Chan, Enhanced electromigration reliability via Ag nanoparticles modified eutectic Sn–58Bi solder joint. Microsyst. Technol. 19, 1069–1080 (2013)
D.L. Ma, P. Wu, Effects of coupled stressing and solid-state aging on the mechanical properties of graphene nanosheets reinforced Sn–58Bi–0.7Zn solder joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 651, 499–506 (2016)
G. Xu, F. Guo, X. Wang, Z. Xia, Y. Lei, Y. Shi, X. Li, Retarding the electromigration effects to the eutectic SnBi solder joints by micro-sized Ni-particles reinforcement approach. J. Alloy Compd 509, 878–884 (2011)
X. Zhao, M. Saka, M. Muraoka, M. Yamashita, H. Hokazono, Electromigration behaviors and effects of addition elements on the formation of a Bi-rich layer in Sn58Bi-based solders. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 4179–4185 (2014)
F. Wang, L. Zhou, Z. Zhang, J. Wang, X. Wang, M. Wu, Effect of Sn–Ag–Cu on the improvement of electromigration behavior in Sn–58Bi solder joint. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 6204–6213 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51875269) and the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant Nos. SJCX18_0760 and KYCX17_1835).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Chen, H., Huang, Y. et al. Recent progress on the development of Sn–Bi based low-temperature Pb-free solders. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 3222–3243 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00701-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00701-w