Abstract
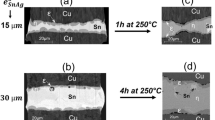
In this work, we study the Transient Liquid Phase Bonding (TLPB) for flip chip interconnexion using copper pillar and SnAg solder alloy technologies. Cu and SnAg bumps with a size of 90 × 90 µm2 were deposited using electroplating process with a thickness of 20 µm and 15–30 µm, respectively. Two types of Cu were deposited: with or without additives. Before the TLPB process, soldering experiments with or without pre-reflow were carried out at 250 °C in order to insure a good filling of the joint. Afterwards, isothermal holdings up to 4 h were performed in the temperature range between 250 and 350 °C under air atmosphere. Two main aspects of Cu/SnAg system are studied and analyzed: (i) the evolution of morphology, microstructure, and growth kinetics of intermetallics (IMCs) during the TLPB and especially (ii) the formation and growth of gas bubbles within the liquid solder during TLPB process. Destructive (scanning electron microscopy) and non-destructive (X-ray) characterizations are performed to analyze and understand the evolution of microstructure as well as the formation and evolution of cavities within the joint during the TLPB process. Non-destructive X-ray radiography with 5 µm resolution and 3D X-ray tomography analysis with 0.7 µm resolution were conducted for the same joint at different steps of its evolution between its initial state (just after the soldering process: about 3 min at 250 °C) and 4 h at 250 °C in order to follow “in situ” the evolution of volume defects inside the joint and especially the evolution of gas bubbles within the joints.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.W. Yoon, M.D. Glover, H.A. Mantooth, K. Shiozaki, Reliable and repeatable bonding technology for high temperature automotive power modules for electrified vehicles. J. Micromech. Microeng. 23(1), 015017 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/23/1/015017
K.E. Aasmundtveit, T.A. Tollefsen, T.-T. Luu, A. Duan, K. Wang, N. Hoivik, Solid–liquid interdiffusion (SLID) bonding—intermetallic bonding for high temperature applications, in 2013 European Microelectronics Packaging Conference (EMPC) (2013), pp. 1–6
N. Heuck, K. Guth, M. Thoben, A. Mueller, N. Oeschler, L. Boewer, R. Speckels, S. Krasel, A. Ciliox, Aging of new interconnect-technologies of power-modules during power-cycling, in CIPS 2014 8th International Conference on Integrated Power Electronics Systems (2014), pp. 1–6
T.-C. Huang, V. Smet, S. Kawamoto, V. Sundaram, P.M. Raj, R.R. Tummala, Modeling, design and demonstration of ultra-short and ultra-fine pitch metastable Cu–Sn interconnections with high-throughput SLID assembly, in 2015 IEEE 65th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC). (2015), pp. 1377–1384. https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTC.2015.7159777
H. Huebner, S. Penka, B. Barchmann, M. Eigner, W. Gruber, M. Nobis, S. Janka, G. Kristen, M. Schneegans, Microcontacts with sub-30 μm pitch for 3D chip-on-chip integration. Microelectron. Eng. 83(11), 2155–2162 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.200-6.09.026
A. Munding, A. Kaiser, P. Benkart, E. Kohn, A. Heittmann, H. Hubner, U. Ramacher, Scaling aspects of microjoints for 3D chip interconnects, in 2006 European Solid-State Device Research Conference (2006), pp. 262–265. https://doi.org/10.1109/ESSDER.2006.307688
R. Labie, P. Limaye, K. Lee, C. Berry, E. Beyne, I. De Wolf, Reliability testing of Cu–Sn intermetallic micro-bump interconnections for 3D-device stacking, in 3rd Electronics System Integration Technology Conference ESTC (2010), pp. 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ESTC.2010.5642925
M. Gerber, C. Beddingfield, S. O'Connor, M. Yoo, M. Lee, D. Kang, S. Park, C. Zwenger, R. Darveaux, R. Lanzone, K. Park, Next generation fine pitch Cu pillar technology—enabling next generation silicon nodes, in 2011 IEEE 61st Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC) (2011), pp. 612–618. https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTC.2011.5898576
A. Huffman, M. Lueck, C. Bower, D. Temple, Effects of assembly process parameters on the structure and thermal stability of Sn-capped Cu bump bonds, in 2007 Proceedings 57th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (2007), pp. 1589–1596. https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTC.2007.374007
R. Agarwal, W. Zhang, P. Limaye, R. Labie, B. Dimcic, A. Phommahaxay, P. Soussan, Cu/Sn microbumps interconnect for 3D TSV chip stacking, in 2010 Proceedings 60th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), (2010), pp. 858–863. https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTC.2010.5490698
W. Zhang, P. Limaye, Y. Civale, R. Labie, P. Soussan, Fine pitch Cu/Sn solid state diffusion bonding for making high yield bump interconnections and its application in 3D integration, in 3rd Electronics System Integration Technology Conference ESTC (2010), pp. 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/ESTC.2010.5643011
Y. Lv, M. Chen, M. Cai, S. Liu, A reliable Cu–Sn stack bonding technology for 3D-TSV packaging. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 29(2), 025003 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/0268-1242/29/2/025003
R.A. Gagliano, M.E. Fine, Thickening kinetics of interfacial Cu6Sn5 and Cu3Sn layers during reaction of liquid tin with solid copper. J. Electron. Mater. 32(12), 1441–1447 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-003-0113-3
M. Yang, M. Li, C. Wang, Interfacial reactions of eutectic Sn3.5Ag and pure tin solders with Cu substrates during liquid-state soldering. Intermetallics 25, 86–94 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2012.02.023
O. Liashenko, A.M. Gusak, F. Hodaj, Phase growth competition in solid/liquid reactions between copper or Cu3Sn compound and liquid tin-based solder. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25(10), 4664–4672 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2221-7
I. Panchenko, K. Croes, I. De Wolf, J. De Messemaeker, E. Beyne, K.-J. Wolter, Degradation of Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compound by pore formation in solid–liquid interdiffusion Cu/Sn microbump interconnects. Microelectron. Eng. 117, 26–34 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2013.12.003
C. Chen, D. Yu, K.N. Chen, Vertical interconnects of microbumps in 3D integration. MRS Bull. 40, 257–263 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2015.29
J. Meyer, I. Panchenko, L. Wambera, S. Bickel, W. Wahrmund, M.J. Wolf, Accelerated SLID bonding for fine-pitch interconnects with porous microstructure, in 2017 IEEE 67th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC) (2017), pp. 405–410. https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTC.2017.231
D.T. Chu, Y.C. Chu, J.A. Lin, Y.T. Chen, C.C. Wang, Y.F. Song, C.C. Chiang, C. Chen, Growth competition between layer-type and porous-type Cu3Sn in microbumps. Microelectron. Reliab. 79, 32–37 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2017.10.001
J.F. Li, P.A. Agyakwa, C.M. Johnson, Interfacial reaction in Cu/Sn/Cu system during the transient liquid phase soldering process. Acta Mater. 59(3), 1198–1211 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.10.053
J.S. Kang, R.A. Gagliano, G. Ghosh, M.E. Fine, Isothermal solidification of Cu/Sn diffusion couples to form thin-solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 31(11), 1238–1243 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-002-0015-9
C. Flötgen, M. Pawlak, E. Pabo, H.J. van de Wiel, G.R. Hayes, V. Dragoi, Wafer bonding using Cu–Sn intermetallic bonding layers. Microsyst. Technol. 20(4), 653–662 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-2002-x
F. Brem, C. Liu, D. Raik, Influence of Cu joining partner in transient liquid phase bonding, in 2012 4th Electronic System-Integration Technology Conference (2012), pp. 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ESTC.2012.6542135
I. Panchenko, J. Grafe, M. Mueller, K.-J. Wolter, Microstructure investigation of Cu/SnAg solid-liquid interdiffusion interconnects by Electron Backscatter Diffraction, in 2013 IEEE 15th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference (EPTC 2013) (2013), pp. 318–323. https://doi.org/10.1109/EPTC.2013.6745735
T.-T. Luu, A.N.I. Duan, K.E. Aasmundtveit, N. Hoivik, Optimized Cu–Sn wafer-level bonding using intermetallic phase characterization. J. Electron. Mater. 42, 3582–3592 (2013)
E.M. Barik, C. Gillot, F. Hodaj, Optimization of soldering experiments for power devices interconnection and packaging, in 2020 IEEE 8th Electronics System-Integration Technology Conference (ESTC) (2020), pp. 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/ESTC48849.2020.9229817
M.S. Park, M.K. Stephenson, C. Shannon, Experimental and computational study of the morphological evolution of intermetallic compound (Cu6Sn5) layers at the Cu/Sn interface under isothermal soldering conditions. Acta Mater. 60(13–14), 5125–5134 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2012.06.008
J. Bertheau, Etude et caractérisation d’interconnexions intermétalliques à partir de plot de cuivre et d’alliage SnAgCu pour l’empilement tridimentionnel de composants actifs, Phd Theisis, Grenoble University, France (2014)
O. Liashenko, Mouillage, germination et croissance lors du brasage en électronique, Phd Theisis, Grenoble University, France (2015)
A.M. Gusak, K.N. Tu, Kinetic theory of flux-driven ripening. Phys. Rev. B 66(11), 115403 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.66.115403
I. Panchenko, J. Grafe, M. Mueller, K.-J. Wolter, Effects of bonding pressure on quality of SLID interconnects, in 2012 4th Electronic System-Integration Technology Conference (2012), pp. 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/ESTC.2012.6542097
J. Bertheau, F. Hodaj, N. Hotellier, J. Charbonnier, Effect of intermetallic compound thickness on shear strength of 25 μm diameter Cu-pillars. Intermetallics 51, 37–47 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2014.02.012
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barik, E.M., Gillot, C. & Hodaj, F. Bubble formation and growth during Transient Liquid Phase Bonding in Cu/SnAg system for microelectronic packaging. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 2360–2374 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07435-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07435-8