Abstract
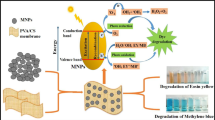
The present study reveals the laser ablation synthesis of zeolite nanorod-based membranes for the first time as an efficient and selective adsorbent material toward cationic azo dyes. Zeolitenanrods were prepared by laser after that incorporated into Poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) matrix with different amounts (2, 5, 10, and 20 wt.%) by a simple and cost-effective process. The samples were characterized using XRD, HRTEM, ATR-FTIR, and FESEM. The loading of nanozeolite was presented by XRD and ATR-FTIR confirming the interaction between PVDF and nanozeolite. HRTEM revealed that the prepared nanozeolite has a rod shape with a diameter of 8–20 nm. The adsorption efficiency of the synthesized nanocomposite membranes was evaluated by monitoring the removal of three model dyes, namely, methylene blue (MB), crystal violet (CV), and methyl orange (MO). The results proved that the nanozeolite/PVDF membranes have high adsorption affinity toward cationic dyes and almost zero affinity toward anionic dyes. Additionally, the incorporation of nanozeolite has a pronounced effect on the adsorption performance of the PVDF membrane. The decolorization for MB using the composite membrane was 96.1%, whereas for pure PVDF membrane was only 30.3%. Moreover, the CV removal percentage increased from 40% to 95.2% after sensitization with nanozeolite. Finally, the impact of changing nanozeolite content in the modified membrane, contact time, initial dye concentration, and adsorbent dose on the adsorption performance of the modified membranes was studied.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
R. Saxena, M. Saxena, A. Lochab, Recent progress in nanomaterials for adsorptive removal of organic contaminants from wastewater. Chem. Select 5(1), 335–353 (2020)
H. Ali, Ternary system from mesoporous CdS–ZnS modified with polyaniline for removal of cationic and anionic dyes. Res. Chem. Intermed. 46(1), 571–592 (2020)
M. Adel, M.A. Ahmed, A.A. Mohamed, Effective removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using reduced graphene oxide functionalized with manganese ferrite nanoparticles. Composites Commun. 22, 100450 (2020)
J. Cheng, C. Zhan, J. Wu, Z. Cui, J. Si, Q. Wang, X. Peng, L.S. Turng, Highly efficient removal of methylene blue dye from an aqueous solution using cellulose acetate nanofibrous membranes modified by polydopamine. ACS Omega 5(10), 5389–5400 (2020)
M.A. Ahmed, Z.M. Abou-Gamra, Mesoporous MgO nanoparticles as a potential sorbent for removal of fast orange and bromophenol blue dyes. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 1(1), 1–11 (2016)
M.N. Rashed, Adsorption technique for the removal of organic pollutants from water and wastewater, in Organic pollutants-monitoring risk and treatment. (Books on demand publisher, Norderstedt, 2013), pp. 167–194
C. Zheng, L. Zhao, X. Zhou, Z. Fu, A. Li, Treatment technologies for organic wastewater. Water Treatment 11, 250–286 (2013)
M. Adel, M.A. Ahmed, A.A. Mohamed, Synthesis and characterization of magnetically separable and recyclable crumbled MgFe2O4/reduced graphene oxide nanoparticles for removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 149, 109 (2021)
D. Sud, G. Mahajan, M.P. Kaur, Agricultural waste material as potential adsorbent for sequestering heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions–a review. Biores. Technol. 99(14), 6017–6027 (2008)
N. Pandey, S.K. Shukla, N.B. Singh, Water purification by polymer nanocomposites: an overview. Nanocomposites 3(2), 47–66 (2017)
A. Lee, J.W. Elam, S.B. Darling, Membrane materials for water purification: design, development, and application. Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. 2(1), 17–42 (2016)
M.R. Abukhadra, A.S. Mohamed, Adsorption removal of safranin dye contaminants from water using various types of natural zeolite. SILICON 11(3), 1635–1647 (2019)
S. Wang, H. Li, L. Xu, Application of zeolite MCM-22 for basic dye removal from wastewater. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 295(1), 71–78 (2006)
W. Chunfeng, L. Jiansheng, W. Lianjun, S. Xiuyun, J. Huang, Adsorption of dye from wastewater by zeolites synthesized from fly ash: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 17(3), 513–521 (2009)
G. Amin, D. Đorđević, S. Konstantinović, I. Jordanov, The removal of the textile basic dye from the water solution by using natural zeolite. Adv. Technol. 6(2), 67–71 (2017)
S. Radoor, J. Karayil, J. Parameswaranpillai, S. Siengchin, Removal of anionic dye Congo red from aqueous environment using polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate/ZSM-5 zeolite membrane. Sci. Rep. 10(1), 1–15 (2020)
S. Alyarnezhad, T. Marino, J.B. Parsa, F. Galiano, C. Ursino, H. Garcìa, M. Puche, A. Figoli, Polyvinylidene fluoride-graphene oxide membranes for dye removal under visible light irradiation. Polymers 12(7), 1509 (2020)
X. Tan, D. Rodrigue, A review on porous polymeric membrane preparation. Part I: production techniques with polysulfone and poly (vinylidene fluoride). Polymers 11(7), 1160 (2019)
D.H. Kang, H.W. Kang, Surface energy characteristics of Zeolite embedded PVDF nanofiber films with electrospinning process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 387, 82–88 (2016)
T. He, W. Zhou, A. Bahi, H. Yang, F. Ko, High permeability of ultrafiltration membranes based on electrospun PVDF modified by nanosized zeolite hybrid membrane scaffolds under low pressure. Chem. Eng. J. 252, 327–336 (2014)
S. Janakiraman, A. Surendran, S. Ghosh, S. Anandhan, A. Venimadhav, Electroactive poly (vinylidene fluoride) fluoride separator for sodium ion battery with high coulombic efficiency. Solid State Ionics 292, 130–135 (2016)
A.M. Abdelghany, A.A. Menazea, M.A. Abd-El-Maksoud, T.K. Khatab, Pulsed laser ablated zeolite nanoparticles: A novel nano-catalyst for the synthesis of 1, 8-dioxo-octahydroxanthene and N-aryl-1, 8-dioxodecahydroacridine with molecular docking validation. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 34(2), e5250 (2020)
R. Belaabed, S. Elabed, A. Addaou, A. Laajab, M.A. Rodríguez, A. Lahsini, Synthesis of LTA zeolite for bacterial adhesion. boletín de la sociedad española de cerámica y vidrio 55(4), 152–158 (2016)
F. Zamani, M. Rezapour, S. Kianpour, Immobilization of L-lysine on zeolite 4A as an organic-inorganic composite basic catalyst for synthesis of α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds under mild conditions. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc 34(8), 2367 (2013)
H. Thakkar, S. Eastman, A. Hajari, A.A. Rownaghi, J.C. Knox, F. Rezaei, 3D-printed zeolite monoliths for CO2 removal from enclosed environments. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(41), 27753–27761 (2016)
A.L. Patterson, The Scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 56(10), 978 (1939)
T.S. Tverdokhlebova, L.S. Antipina, V.L. Kudryavtseva, K.S. Stankevich, I.M. Kolesnik, E.A. Senokosova, E.A. Velikanova, L.V. Antonova, D.V. Vasilchenko, T.T. Dambaev, E.V. Plotnikov, V.M. Bouznik, E.N. Bolbasov, Composite ferroelectric membranes based on vinylidene fluoride-tetrafluoroethylene copolymer and polyvinylpyrrolidone for wound healing. Membranes 11(1), 21 (2021)
M.J. Tommalieh, A.M. Ismail, N.S. Awwad, H.A. Ibrahium, M.A. Youssef, A.A. Menazea, Investigation of electrical conductivity of gold nanoparticles scattered in polyvinylidene fluoride/polyvinyl chloride via laser ablation for electrical applications. J. Electron. Mater. 49(12), 7603–7608 (2020)
A.A. Menazea, A.M. Ismail, I.S. Elashmawi, The role of Li4Ti5O12 nanoparticles on enhancement the performance of PVDF/PVK blend for lithium-ion batteries. J. Market. Res. 9(3), 5689–5698 (2020)
A.M. Ismail, M.H. El-Newehy, M.E. El-Naggar, A.M. Moydeen, A.A. Menazea, Enhancment the electrical conductivity of the synthesized polyvinylidene fluoride/polyvinyl chloride composite doped with palladium nanoparticles via laser ablation. J. Market. Res. 9(5), 11178–11188 (2020)
Z. Wu, J. Xie, H. Liu, T. Chen, P. Cheng, C. Wang, D. Kong, Preparation, characterization, and performance of 4A zeolite based on opal waste rock for removal of ammonium ion. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 36(9–10), 1700–1715 (2018)
H. Chen, H. Yang, Y. Xi, Highly ordered and hexagonal mesoporous silica materials with large specific surface from natural rectorite mineral. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 279, 53–60 (2019)
P. Thakur, A. Kool, B. Bagchi, N.A. Hoque, S. Das, P. Nandy, In situ synthesis of Ni (OH) 2 nanobelt modified electroactive poly (vinylidene fluoride) thin films: remarkable improvement in dielectric properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(19), 13082–13091 (2015)
M. Shahabuddin, V. Gupta, K. Dev, A.A. Basfar, Physico-chemical modification induced by 70 MeV carbon ions in alpha phased polyvinylidene fluoride (α-PVDF) polymer. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 52, 131–136 (2014)
A. Badawi, Engineering the optical properties of PVA/PVP polymeric blend in situ using tin sulfide for optoelectronics. Appl. Phys. A 126, 1–12 (2020)
T.S. Soliman, S.A. Vshivkov, Effect of Fe nanoparticles on the structure and optical properties of polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposite films. J. Non Cryst. Solids 519, 119452 (2019)
N.F. Mott, E.A. Davis, Electronic Processes in Non-Crystalline Materials, 2nd edn. (Clarendon, 1979)
R. Sabarish, G. Unnikrishnan, Polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethyl cellulose/ZSM-5 zeolite biocomposite membranes for dye adsorption applications. Carbohyd. Polym. 199, 129–140 (2018)
G.V. Brião, S.L. Jahn, E.L. Foletto, G.L. Dotto, Highly efficient and reusable mesoporous zeolite synthetized from a biopolymer for cationic dyes adsorption. Colloids Surf. A 556, 43–50 (2018)
A.A. Essawy, S.M. Sayyah, A.M. El-Nggar, Ultrasonic-mediated synthesis and characterization of TiO2-loaded chitosan-grafted-polymethylaniline nanoparticles of potent efficiency in dye uptake and sunlight driven self-cleaning applications. RSC Adv. 6(3), 2279–2294 (2016)
V.K. Gupta, D. Pathania, N.C. Kothiyal, G. Sharma, Polyaniline zirconium (IV) silicophosphate nanocomposite for remediation of methylene blue dye from waste water. J. Mol. Liq. 190, 139–145 (2014)
F. Piri, A. Mollahosseini, M.M. Hosseini, Enhanced adsorption of dyes on microwave-assisted synthesized magnetic zeolite-hydroxyapatite nanocomposite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 7(5), 103338 (2019)
V. Sharma, P. Rekha, P. Mohanty, Nanoporous hypercrosslinked polyaniline: an efficient adsorbent for the adsorptive removal of cationic and anionic dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 222, 1091–1100 (2016)
A.H. Jawad, A.S. Abdulhameed, A. Reghioua, Z.M. Yaseen, Zwitterion composite chitosan-epichlorohydrin/zeolite for adsorption of methylene blue and reactive red 120 dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 163, 756–765 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ismail, A.M., Menazea, A.A. & Ali, H. Selective adsorption of cationic azo dyes onto zeolite nanorod-based membranes prepared via laser ablation. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 19352–19367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06453-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06453-w