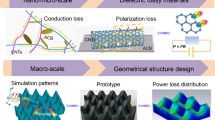
Abstract
The electromagnetic simulation can be used to design the macroscopic absorbing structure of the microwave absorbing material. Research indicates that the macrostructure can adjust the impedance matching and electromagnetic properties of the materials, thereby improving the absorption performance. Among them, the honeycomb structure is often used in actual products due to its good absorption characteristics and mechanical properties. Therefore, in this work, the absorption performance of the carbon microsphere material was improved through the honeycomb structure design. The carbon microsphere material is firstly prepared by sintering phenolic resin, which has the advantages of convenient synthesis, high yield, and a narrow absorption bandwidth of 4.4 GHz. Then, through the high frequency structure simulator (HFSS) electromagnetic simulation, the honeycomb structure based on the carbon microspheres was macroscopically designed, achieving a larger 8.3 GHz absorption frequency bandwidth. This research completed the combination of electromagnetic simulation and honeycomb structure, improved the absorption bandwidth of carbon microspheres, and opened up a new way for the further improvement and practical application for traditional absorption materials.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S. Cao, W.L. Song, Z.L. Hou, B. Wen, J. Yuan, The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/silica composites. Carbon 48, 788–796 (2010)
W.L. Song, M.S. Cao, Z.L. Hou, X.Y. Fang, X.L. Shi, J. Yuan, High dielectric loss and its monotonic dependence of conducting-dominated multiwalled carbon nanotubes/silica nanocomposite on temperature ranging from 373 to 873 K in X-band. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 233110 (2009)
H.L. Lv, Z.H. Yang, S.J. Ong, C. Wei, H.B. Liao, S.B. Xi, Y.H. Du, G.B. Ji, Z.C.J. Xu, A flexible microwave shield with tunable frequency-transmission and electromagnetic compatibility. Adv. Funct. Mater. 4, 1900163 (2019)
Y. Feng, D. Li, Y. Bai, A. Hua, D.S. Pan, Y. Li, Y. Wang, J. He, Z.H. Wang, Y.J. Zhang, W. Liu, Z.D. Zhang, The effect of core–shell structure on microwave absorption properties of graphite-coated magnetic nanocapsules. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 1429–1435 (2019)
X. Chen, X. Jia, Z. Wu, Z.X. Tang, Y.X. Zeng, X.J. Wang, X.Q. Fu, Y.H. Zou, A Graphite-based metamaterial microwave absorber. IEEE Antenn. Wirele. Propagation Lett. 18, 1016–1020 (2019)
C.P.L. Rubinger, M.E. Leyva, GHz permittivity of carbon black and polyaniline with styrene–butadiene–styrene composites. Polym. Bull. 76, 615–626 (2019)
B.M. Chen, B. Li, Y. Gao, T.C. Ling, Z.Y. Lu, Z.J. Li, Investigation on electrically conductive aggregates produced by incorporating carbon fiber and carbon black. Constr. Build Mater. 144, 106–114 (2017)
F. Ye, Q. Song, Z.C. Zhang, W. Li, S.Y. Zhang, X.Y. Yin, Y.Z. Zhou, H.W. Tao, Y.S. Liu, L.F. Cheng, L.T. Zhang, H.J. Li, Direct growth of edge-rich graphene with tunable dielectric properties in porous Si3N4 ceramic for broadband high performance microwave absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28, 1707205 (2018)
W. Zhou, R.M. Yin, L. Long, H. Luo, W.D. Hu, Y.H. Ding, Y. Li, Enhanced high-temperature dielectric properties and microwave absorption of SiC nanofibers modified Si3N4 ceramics within the gigahertz range. Ceram. Int. 44, 12301–12307 (2018)
S. Dong, W.Z. Zhang, P. Hu, Y.M. Zhang, J.C. Han, X.G. Luo, Nitrogen content dependent microwave absorption property of nitrogen-doped SiC materials annealed in N2: opposing trends for microparticles and nanowires. J. Alloy. Compd. 758, 256–267 (2018)
X.L. Ye, Z.F. Chen, M. Li, T. Wang, C. Wu, J.X. Zhang, Q.B. Zhou, H.Z. Liu, S. Cui, Microstructure and microwave absorption performance variation of SiC/C foam at different elevated-temperature heat treatment . ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 18395–18404 (2019)
X.L. Wang, X. Huang, Z.R. Chen, X.P. Liao, C. Liu, B. Shi, Ferromagnetic hierarchical carbon nanofiber bundles derived from natural collagen fibers: truly lightweight and high-performance microwave absorption materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 10146–10153 (2015)
N. Zhao, W. Wang, X. Lei, Synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of Fe3N nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 28, 15701–15707 (2017)
Q.H. Liu, Q. Cao, H. Bi, C.Y. Liang, K.P. Yuan, W. She, Y.J. Yang, R.C. Che, CoNi@SiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 28, 486–490 (2016)
X.L. Wang, Q.Y. Geng, G.M. Shi, G. Xu, J. Yu, Y.Y. Guan, Y.J. Zhang, D. Li, One-pot solvothermal synthesis of Fe/Fe3O4 composites with broadband microwave absorption. J. Alloy Compd. 803, 818–825 (2019)
Z.R. Jia, D. Lan, K.J. Lin, M. Qin, K.C. Kou, G.L. Wu, H.J. Wu, Progress in low-frequency microwave absorbing materials. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 29, 17122–17136 (2018)
S. Jeon, J. Kim, K.H. Kim, Microwave absorption properties of graphene oxide capsulated carbonyl iron particles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 475, 1065–1069 (2019)
L.H. He, Y. Zhao, L.Y. Xing, P.G. Liu, Z.Y. Wang, Y.W. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y.C. Du, Preparation of reduced graphene oxide coated flaky carbonyl iron composites and their excellent microwave absorption properties. RSC Adv. 8, 2971–2977 (2018)
P.B. Liu, S. Gao, Y. Wang, Y. Huang, W.J. He, W.H. Huang, J.H. Luo, Carbon nanocages with N-doped carbon inner shell and Co/N-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem. Eng. J. 381, 122653 (2020)
P.B. Liu, S. Gao, Y. Wang, F.T. Zhou, Y. Huang, W.H. Huang, N.H. Chang, Core-shell Ni@C encapsulated by N-doped carbon derived from nickel-organic polymer coordination composites with enhanced microwave absorption. Carbon 170, 503–516 (2020)
P.B. Liu, S. Gao, Y. Wang, F.T. Zhou, Y. Huang, J.H. Luo, Metal-organic polymer coordination materials derived Co/N-doped porous carbon composites for frequency-selective microwave absorption. Compos. Part B 202, 108406 (2020)
H.J. Wu, Z.H. Zhao, G.L. Wu, Facile synthesis of FeCo layered double oxide/raspberry-like carbon microspheres with hierarchical structure for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 566, 21–32 (2020)
X.H. Li, J. Feng, Y.P. Du, J.T. Bai, H.M. Fan, H.L. Zhang, Y. Peng, F.S. Li, One-pot synthesis of CoFe2O4/graphene oxide hybrids and their conversion into FeCo/Graphene hybrids for lightweight and highly efficient microwave absorber. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 5535–5546 (2015)
Y.C. Du, W.W. Liu, R. Qiang, Y. Wang, X.J. Han, J. Ma, P. Xu, Shell thickness-dependent microwave absorption of coreshell Fe3O4 composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 12997–13006 (2014)
L. Wang, Y. Huang, X. Sun, H.J. Huang, P.B. Liu, M. Zong, Y. Wang, Synthesis and microwave absorption enhancement of Graphene@Fe3O4@SiO2@NiO nanosheet hierarchical structures. Nanoscale 6, 3157–3164 (2014)
Y. Ding, L. Zhang, Q.L. Liao, G.J. Zhang, S. Liu, Y. Zhang, Electromagnetic wave absorption in reduced graphene oxide functionalized with Fe3O4/Fe nanorings. Nano Res. 9, 2018–2025 (2016)
X.J. Fan, H.Q. Zhou, X. Guo, WC nanocrystals grown on vertically aligned carbon nanotubes: an efficient and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Nano 9, 5125–5134 (2015)
G.L. Wu, Y.H. Cheng, Y.Y. Ren, Y.Q. Wang, Z.D. Wang, H.J. Wu, Synthesis and characterization of γ-Fe2O3@C nanorod carbon sphere composite and its application as microwave absorbing material. J. Alloys Compd. 652, 346–350 (2015)
M. Wu, A.K. De, X.S. Qi, R. Xie, S.J. Qin, C.Y. Deng, G.L. Wu, W. Zhong, Optimization, selective and efficient production of CNTs/CoxFe3-xO4 core/shell nanocomposites as outstanding microwave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. C 8, 11936–11949 (2020)
R. Wang, E.Q. Yang, X.S. Qi, R. Xie, S.J. Qin, C.Y. Deng, W. Zhong, Constructing and optimizing core@shell structure CNTs@MoS2 nanocomposites as outstanding microwave absorbers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 516, 146–159 (2020)
X. Li, L.M. Yu, W.K. Zhao, Y.Y. Shi, L.J. Yu, Y.B. Dong, Y.F. Zhu, Y.Q. Fu, X.D. Liu, F.Y. Fu, Prism-shaped hollow carbon decorated with polyaniline for microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 379, 122393 (2020)
D.P. Sun, Q. Zou, Y.P. Wang, Y.J. Wang, W. Jiang, F.S. Li, Controllable synthesis of porous Fe3O4@ZnO sphere decorated graphene for extraordinary electromagnetic wave absorption. Nanoscale 6, 6557–6562 (2014)
J.L. Liu, H.S. Liang, H.J. Wu, Hierarchical flower-like Fe3O4/MoS2 composites for selective broadband electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Compos. Part A 130, 105760 (2020)
H. Wang, Y.Y. Dai, D.Y. Geng, S. Ma, D. Li, J. An, J. He, W. Liu, Z.D. Zhang, CoxNi100-x nanoparticles encapsulated by curved graphite layers: controlled in situ metal-catalytic preparation and broadband microwave absorption. Nanoscale 7, 17312–17319 (2015)
Y.Y. Shi, L.J. Yu, K. Li, S.Z. Li, Y.B. Dong, Y.F. Zhu, Y.Q. Fu, F.B. Meng, Well-matched impedance of polypyrrole-loaded cotton non-woven fabric/polydimethylsiloxane composite for extraordinary microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 197, 108246 (2020)
M. Qin, H.S. Liang, X.R. Zhao, H.J. Wu, Filter paper templated one-dimensional NiO/NiCo2O4 microrod with wideband electromagnetic wave absorption capacity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 566, 347–356 (2020)
L. Liu, C.Z. Fan, N.B. Zhu, Z.Y. Zhao, R.P. Liu, Effective electromagnetic properties of honeycomb substrate coated with dielectric or magnetic layer. Appl. Phys. A 116, 901–905 (2014)
W.H. Choi, C.G. Kim, Broadband microwave-absorbing honeycomb structure with novel design concept. Compos. Part B 83, 14–20 (2015)
X. Li, Y.F. Zhu, X.Q. Liu, B.B. Xu, Q.Q. Ni, A broadband and tunable microwave absorption technology enabled by VGCFs/PDMS-EP shape memory composites. Compos. Struct. 238, 111954 (2020)
Y. Cheng, J.Z.Y. Seow, H.Q. Zhao, Z.C.J. Xu, G.B. Ji, A flexible and lightweight biomass-reinforced microwave absorber. Nano-Micro Lett. 12, 125 (2020)
X.H. Liang, Z.M. Man, B. Quan, J. Zheng, W.H. Gu, Z. Zhang, G.B. Ji, The environment-stable CoxNiy encapsulation in stacked porous carbon nanosheets for enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett. 12, 102 (2020)
Y. Wang, X. Gao, X.M. Wu, W.Z. Zhang, C.Y. Luo, P.B. Liu, Facile design of 3D hierarchical NiFe2O4/N-GN/ZnO composite as a high performance electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 375, 121942 (2019)
Y.C. Sun, D.P. Li, Y. Yang, L.S. Fan, S. Wu, P. Wang, Y. Song, Achieving rough sphere-shaped ZnS with superior attenuation electromagnetic absorption performance. RSC Adv. 7, 3907–3913 (2017)
X.M. Zhang, G.B. Ji, W. Liu, B. Quan, X.H. Liang, C.M. Shang, Y. Cheng, Y.W. Du, Thermal conversion of Fe3O4@metal-organic framework: a new method for efficient Fe-Co/nanoporous carbon microwave absorbing material. Nanoscale 7, 12932–12942 (2015)
W. Feng, Y. Wang, J. Chen, L. Wang, L. Guo, J. Ouyang, D. Jia, Y. Zhou, Reduced graphene oxide decorated with in-situ growing ZnO nanocrystals: facile synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties. Carbon 108, 52–60 (2016)
L. Lin, H.L. Xing, R.W. Shu, L. Wang, X.L. Ji, D.X. Tan, Y. Gan, Preparation and microwave absorption properties of multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with Ni-doped SnO2 nanocrystals. RSC Adv. 5, 94539–94550 (2015)
H.L. Lv, Y.H. Guo, G.L. Wu, G.B. Ji, Y. Zhao, Z.C.J. Xu, Interface polarization strategy to solve electromagnetic wave interference issue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 5660–5668 (2017)
X.Q. Cui, X.H. Liang, J.B. Chen, W.H. Gu, G.B. Ji, Y.W. Du, Customized unique core-shell Fe2N@N-doped carbon with tunable void space for microwave response. Carbon 156, 49–57 (2020)
Acknowledgements
Financial supports from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 51971111) and the Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Bionic Functional Materials are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, N., Gu, W., Zhao, Y. et al. The enhanced microwave broadband absorbing ability of carbon microspheres via electromagnetic simulating honeycomb design. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 25809–25819 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04780-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04780-y