Abstract
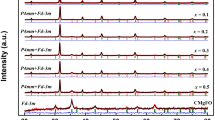
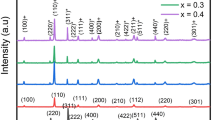
Different compositions of the composite lead-free multiferroic magnetoelectric systems are fabricated by employing piezoelectric Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 (BCZT) and magnetostrictive CoFe2O4 (CFO) by varying the CFO weight fraction. The magnetic, dielectric, ferroelectric and magnetoelectric (ME) properties of the system are analyzed and found to be varying with the ferrite concentration. Even though the composite systems exhibit high magnetocapacitance (MC) properties (~ 35%), the possible stray contributions from magnetoresistance and magnetostriction make it unreliable for the quantitative determination of ME coupling coefficient (MECC). Therefore, a dynamic method is chosen for the measurement of magnetoelectric coupling. All the compositions have shown fairly good ME coupling. It is found that the ME coupling increases with ferrite fraction and the highest ME coupling of 14.8 mV/(cm Oe) is observed for 0.6BCZT–0.4CFO composite. It is also observed that the ME voltage increases linearly with the ac modulating field with a voltage generation of 1.25 V/cm (for x = 0.4) for a small ac modulating field of 100 Oe. This high sensitivity and linear response of ME coupling to the ac magnetic fields offer the possibility of employing these particulate composites for a wide range of applications from magnetic field sensors to energy harvesters.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Taylor, Y. Li, X. Yang et al., One-dimensional metal oxide nanotubes, nanowires, nanoribbons, and nanorods: synthesis, characterizations, properties and applications. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408436.2011.606512
Y. Zhu, J.W. Zu, A magnetoelectric generator for energy harvesting from the vibration of magnetic levitation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 48, 3344–3347 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2012.2199289
C.S.C. Lekha, A.S. Kumar, S. Vivek et al., High voltage generation from lead-free magnetoelectric coaxial nanotube arrays and their applications in nano energy harvesters. Nanotechnology 28, 055402 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/28/5/055402
J. Reermann, P. Durdaut, S. Salzer et al., Evaluation of magnetoelectric sensor systems for cardiological applications. Measurement 116, 230–238 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.09.047
R. Jahns, H. Greve, E. Woltermann et al., Sensitivity enhancement of magnetoelectric sensors through frequency-conversion. Sens. Actuators A 183, 16–21 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNA.2012.05.049
W. Saenrang, B.A. Davidson, F. Maccherozzi et al., Deterministic and robust room-temperature exchange coupling in monodomain multiferroic BiFeO3 heterostructures. Nat. Commun. 8, 1583 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01581-6
M. Bibes, A. Barthélémy, Towards a magnetoelectric memory. Nat. Mater. 7, 425–426 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2189
Y. Wang, J. Hu, Y. Lin, C.-W. Nan, Multiferroic magnetoelectric composite nanostructures. NPG Asia Mater 2, 61–68 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/asiamat.2010.32
Y. Zhang, Z. Li, C. Deng et al., Demonstration of magnetoelectric read head of multiferroic heterostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 152510 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2912032
N. Kumar, A. Shukla, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, electrical and magnetic characteristics of Ni/Ti modified BiFeO3 lead free multiferroic material. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 28, 6673–6684 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6359-y
N. Kumar, A. Shukla, N. Kumar, R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of eco-friendly complex multiferroic material: Bi(Co0.35Ti0.35Fe0.30)O3. Ceram. Int. 45, 822–831 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CERAMINT.2018.09.249
D. Khomskii, Trend: classifying multiferroics: Mechanisms and effects. Physics (College Park Md) 2, 20 (2009)
W. Eerenstein, N.D. Mathur, J.F. Scott, Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 442, 759–765 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05023
C.-W. Nan, M.I. Bichurin, S. Dong et al., Multiferroic magnetoelectric composites: historical perspective, status, and future directions. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 031101 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2836410
J.G. Wan, X.W. Wang, Y.J. Wu et al., Magnetoelectric CoFe2O4–Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 composite thin films derived by a sol-gel process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 122501 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1889237
A.J. Gualdi, F.L. Zabotto, D. Garcia et al., Understanding the dynamic magnetization process for the magnetoelectric effect in multiferroic composites. J. Appl. Phys. 119, 124110 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4944889
L.K. Pradhan, R. Pandey, R. Kumar, M. Kar, Lattice strain induced multiferroicity in PZT-CFO particulate composite. J. Appl. Phys. 123, 074101 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5008607
H. Yang, G. Zhang, Y. Lin, Enhanced magnetoelectric properties of the laminated BaTiO3/CoFe2O4 composites. J. Alloys Compd. 644, 390–397 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2015.05.020
B. Sarkar, B. Dalal, V. Dev Ashok et al., Magnetic properties of mixed spinel BaTiO3-NiFe2O4 composites. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 123908 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4869782
A.S. Gaikwad, S.E. Shirsath, S.R. Wadgane et al., Magneto-electric coupling and improved dielectric constant of BaTiO3 and Fe-rich (Co0.7Fe2.3O4) ferrite nano-composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 465, 508–514 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMMM.2018.06.036
W. Liu, X. Ren, Large piezoelectric effect in Pb-free ceramics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 257602 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.257602
K.K. Mohaideen, P.A. Joy (2012) High magnetostriction and coupling coefficient for sintered cobalt ferrite derived from superparamagnetic nanoparticles High magnetostriction and coupling coefficient for sintered cobalt ferrite derived from superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4745922
F. Yan, G. Chen, L. Lu et al., Local probing of magnetoelectric coupling and magnetoelastic control of switching in BiFeO3-CoFe2 O4 thin-film nanocomposite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 042906 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4816793
M.M. Selvi, P. Manimuthu, K.S. Kumar, C. Venkateswaran, Magnetodielectric properties of CoFe2O4–BaTiO3 core–shell nanocomposite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 369, 155–161 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.06.039
C.G. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audiofrequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 121–124 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.83.121
G. Catalan, Magnetocapacitance without magnetoelectric coupling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 102902 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2177543
A.J. Gualdi, F.L. Zabotto, D. Garcia, A.J.A. de Oliveira, Stress magnetization model for magnetostriction in multiferroic composite. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 053913 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4816785
S. Ito, K. Aso, Y. Makino, S. Uedaira, Magnetostriction and magnetization of iron-based amorphous alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 37, 665–666 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.92029
A. Muhammad, R. Sato-Turtelli, M. Kriegisch et al., Large enhancement of magnetostriction due to compaction hydrostatic pressure and magnetic annealing in CoFe2O4. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 013918 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3675489
R.M. Bozorth, E.F. Tilden, A.J. Williams, Anisotropy and magnetostriction of some ferrites. Phys. Rev. 99, 1788–1798 (1955). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.99.1788
C.S.C. Lekha, A.S. Kumar, S. Vivek et al., Room temperature magnetoelectric properties of lead-free alkaline niobate based particulate composites. Ceram. Int. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CERAMINT.2019.01.089
A.S. Kumar, C.S.C. Lekha, S. Vivek et al., Multiferroic and magnetoelectric properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3–CoFe2O4 core–shell nanocomposite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 418, 294–299 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.02.065
J. Paul Praveen, V.R. Monaji, E. Chandrakala et al., Enhanced magnetoelectric coupling in Ti and Ce substituted lead free CFO-BCZT laminate composites. J. Alloys Compd. 750, 392–400 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2018.04.026
Y. Wang, Y. Pu, Y. Shi, Y. Cui, Ferroelectric, magnetic, magnetoelectric properties of the Ba0.9Ca0.1Ti0.9Zr0.1O3/CoFe2O4 laminated composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 11125–11131 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6899-1
Acknowledgements
ASK, CSC, VS, and SSN acknowledge Central University of Kerala for financial support. ASK wish to acknowledge University Grants Commission, India for the Junior and Senior Research Fellowship (F.17–131/2012(SA-1) and CSC and SSN wish to acknowledge DST, India for the financial support in WOS-A (SR/WOS-A/PS-14/2014) and YSS/2014/000431. SSN acknowledge DBT, India for the financial support through the project 6292P52/RGCB/PMD/DBT/RPKT/2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors certify that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A.S., Lekha, C.S.C., Vivek, S. et al. Effect of CoFe2O4 weight fraction on multiferroic and magnetoelectric properties of (1 − x)Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3 − xCoFe2O4 particulate composites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 8239–8248 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01140-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01140-3