Abstract
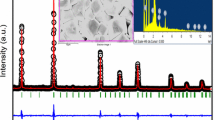
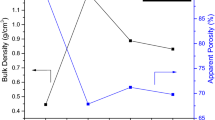
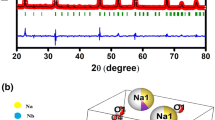
A new polycrystalline lead-free 0.05(K0.5Bi0.5TiO3)–0.95(NaNbO3) (KBT–NN) composites ceramics have been prepared by solid-state reaction method and their structural, optical, dielectric, ferroelectric and impedance properties are investigated. X-ray diffraction and Rietveld refinement data reveal that this composites ceramics possesses a perovskite-type orthorhombic structure after the diffusion of K0.5Bi0.5TiO3 into the NaNbO3. An appreciable change in its vibrational phonon modes of KBT on addition of NaNbO3 is exhibited in the material as observed from Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) spectrum. The optical band gap energy of the sample is determined from the diffused absorbance spectra to be 3.2 eV, which may be useful in photo-catalytic application. In the frequency range of 130–900 cm−1, different vibrational modes are observed from Raman spectrum. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) images reveal a well-defined and homogeneous morphology. Polarization vs. electric field study confirms the ferroelectricity. Dielectric and complex impedance spectroscopic studies are performed over a wide range of frequency (i.e., 103–106 Hz) and temperature (30°–500 °C) and it is found that Jonscher’s power law is well applicable to the alternating current (ac) conductivity spectrum. The direct current (dc) conductivity of the material, which depends upon temperature, exhibits the decrease resistance with increase of temperature similar to that of semiconductors. The dc conductivity confirms that the conduction mechanism is influenced by oxygen vacancies.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Wang, H. Du, X. Shi, Dielectric and ferroelectric properties of (1-x)Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3-xSrTiO3 lead-free piezoceramics system. J. Phys. 152, 012065 (2009)
B. Parija, S.K. Rout, L.S. Cavalcante, A.Z. Simões, S. Panigrahi, E. Longo, N.C. Batista, Structure, microstructure and dielectric properties of 100–x(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3–x[SrTiO3], composites ceramics. Appl. Phys. A 109, 715 (2012)
M. Rawat, K.L. Yadav, Dielectric, ferroelectric and magnetoelectric response in Ba0.92(Bi0.5Na0.5)0.08TiO3–Ni0.65Zn0.35Fe2O4 composite ceramics. Smart Mater. Struct. 23, 085032 (2014)
D. White, X. Zhao, M.F. Bresser, X. Tan, Structure and properties of (1–x)Pb(Mg1/2W1/2)O3–xPb(Zr0.5Ti0.5)O3 solid solution ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 43, 5258 (2008)
M.D. Maeder, D. Damjanovic, N. Setter, Lead free piezoelectric materials. J. Electroceram. 13, 385 (2004)
R. Selvamani, G. Singh, V. Sathe, V.S. Tiwari, P.K. Gupta, Dielectric, structural and Raman studies on (Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3)(1–x)(BiCrO3)x ceramic. J. Phys. 23, 55901 (2011)
C.F. Buhrer, Some properties of bismuth perovskites. J. Chem. Phys. 36, 798 (1962)
B.K. Barick, K.K. Mishra, A.K. Arora, R.N.P. Choudhary, D.K. Pradhan, Impedance and Raman spectroscopic studies of (Na0.5Bi0.5)TiO3. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 44, 355402 (2011)
X. Lu, J. Xu, L. Yang, C. Zhou, Y.Y. Zhao, C. Yuan, Q. Li, G. Chen, H. Wang, Energy storage properties of (Bi0.5Na0.5)0.93Ba0.07TiO3 lead-free ceramics modified by La and Zr co-doping. J. Materiomics 2, 87 (2016)
Y. Hiruma, R. Aoyagi, H. Nagata, T. Takenaka, Ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of (Bi1/2K1/2)TiO3 ceramics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 44, 5040 (2005)
J. Guo, M. Zhu, L. Li, M. Zheng, Y. Hou, Relaxor to ferroelectric crossover in KBT ceramics by prolonged annealing. J. Alloys. Compd. 703, 448 (2017)
Y. Hou, M. Zhu, L. Hou, J. Liu, J. Tang, H. Wang, H. Yan, Synthesis and characterization of lead-free K0.5Bi0.5TiO3 ferroelectrics by sol–gel technique. J. Cryst. Growth 273, 500 (2005)
W.L. Li, W.P. Cao, D. Xu, W. Wang, W.D. Fei, Phase structure and piezoelectric properties of NBT–KBT–BT ceramics prepared by sol–gel flame synthetic approach. J. Alloys. Compd. 613, 181 (2014)
G.A. Babu, R. Subhramanyam, I. Bhaumik, S. Ganeshmoorthy, P. Ramasamy, P.K. gupta, Growth and characterization of undoped and Mn doped lead-free piezoelectric NBT–KBT single crystals. Mat. Res. Bull. 53, 136 (2014)
T. Karthik, S. Asthana, Enhanced mechanical and ferroelectric properties through grain size refinement in site specific substituted lead free Na0.5–xKxBi0.5TiO3 (x = 0–0.10) ceramics. Mater. Lett. 190, 273 (2017)
H. Xie, D. Li Jin, X. Shen, Wang, G. Shen, Morphotropic phase boundary, segregation effect and crystal growth in the NBT-KBT system. J. Cryst. Growth 311, 3626 (2009)
X.H. Hao, A review on the dielectric materials for high-energy storage application. J. Adv. Dielectr. 3, 1330001 (2013)
B. Jaffe, W.R. Cook, H. Jaffe, Piezoelectric Ceramics, (Academic Press, London, 1971), p. 190
S. Lanfredi, M.H. Lente, J.A. Eiras, Phase transition at low temperature in NaNbO3 ceramic. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 2731 (2002)
S. Tripathi, D. Pandey, S.K. Mirshra, P.S.R. Krishna, Morphotropic phase-boundary-like characteristic in a lead-free and non-ferroelectric (1-x)NaNbO3-xCaTiO3system. Phys. Rev. B 77, 052104 (2008)
T. Zeng, K.W. Kwok, H.L.W. Chan, Ferroelectric and Piezoelectric properties of Na1 – xBaxNb1–xTixO3 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 89, 2828 (2006)
M.T. Benlahrache, N. Benhamla, S. Achour, Dielectric properties of BaTiO3–NaNbO3 composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 1493 (2004)
H. Wu, A. Navrotsky, Y. Su, M.L. Balmer, Perovskite solid solutions along the NaNbO3–SrTiO3 join: phase transitions, formation enthalpies, and implications for general perovskite energetics. Chem. Mater. 17, 1880 (2005)
A. Aydi, H. Khemakhem, C. Boudaya, R. Mühll, New ferroelectric and relaxor ceramics in the mixed oxide system NaNbO3–BaSnO3,. Solid State Sci. 6, 333 (2004)
C. Chaker, W.E. Gharbi, N. Abdelmoula, H. Khemakhem, A. Simon, M. Maglione, Physical properties of the new ceramics in the mixed oxide system Na1–xLixNb1–xSbxO3,. J. Alloys Compd. 481, 305 (2009)
D. Lin, K.W. Kwok, Ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of new NaNbO3–Bi0.5K0.5TiO3 lead-free ceramics. J. Mater.Sci. 21, 1060 (2010)
J.R. Macdonald, Impedance Spectroscopy Emphasizing Solid Materials and Systems (Chapter-4) (Wiley, New York, 1987)
A.P. Barranco, M.P.G. Amador, A. Huanosta, R. Valenzuela, Phase transitions in ferrimagnetic and ferroelectric ceramics by Ac measurements Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 2039 (1998)
H.M. Rietveld, A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 22, 65–71 (1969)
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray diffraction (Addison-Wesley Publishing co. Inc., Reading, 1978
Y. Hou, M. Zhu, L. Hou, J. Liu, J. Tang, H. Wang, H. andYan, Synthesis and characterization of lead-free K0.5Bi0.5TiO3 ferroelectrics by sol–gel technique. J. Cryst. Growth 273, 500 (2005)
Z.S. D-Ling, L.M. Tao, G.Z. Hui, C.G. Bin, W. Xu, C. Jia, Y. Feng, Raman spectroscopic study of ceramic Sr2Bi4Ti5O18. Chin. Phys. 15, 0854 (2006)
M. Rusty. Pittman, T. Alexies, Bell, Raman studies of the structure of niobium oxide/titanium oxide (Nb2O5.TiO2). J.Phys. Chem. 97, 12178 (1993)
M.F. Mostafa, S.S. Ata-Allah, A.A.A. Youssef, H.S. Refai, Electric and AC magnetic investigation of the manganites La0.7Ca0.3Mn0.96In0.04xAl(1–x)0.04O3; (0.0≤x≤1.0). J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 320, 344 (2008)
S. Coste, A. Lecomte, P. Thomas, T. Merle-Mejean, J.C. Champarnaud-Mesjard, Sol-gel synthesis of TeO2-based materials using citric acid as hydrolysis modifier. J.Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 41, 79 (2007)
E.A. Perianu, I.A. Gorodea, F. Gheorghiu, A.V. Sandu, A.C. Ianculescu, I. Sandu, A.R. Iordan, M.N. Palamaru, Rev. Chim. 62, 17 (2011)
R.L. Frost, J. Yang, Z. Ding, Raman and FTIR spectroscopy of natural oxalates: implications for the evidence of life on Mars. Chin. Sci. Bull. 48, 1844 (2003)
B.N. Parida, R.K. Parida, A. Panda, Multi-ferroic and optical spectroscopy properties of (Bi0.5Sr0.5) (Fe0.5Ti0.5) O3 solid solution. J. Alloys Compd. 696, 338–344 (2017)
M. Zheng-Zheng, L. Jian-Qing, T. Z-Ming, Q. Yang, Y. Song-Liu, Improved multiferroic properties of La-doped 0.6BiFeO3–0.4SrTiO3 solid solution ceramics. Chin. Phys. B 21, 107503 (2012)
V. Provenzano, L.P. Boesch, V. Volterra, C.T. Moynihan, P.B. Macedo, Electrical relaxation in Na2O·3SiO2 glass. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 55, 492 (1972)
H. Jain, C.H. Hsieh, ‘Window’ effect in the analysis of frequency dependence of ionic conductivity. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 172, 1408 (1994)
C.K. Suman, K. Prasad, R.N.P. Choudhary, Complex impedance studies on tungsten-bronze electroceramic: Pb2Bi3LaTi5O18. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 369 (2006)
S. Chatterjee, P.K. Mahapatra, R.N.P. Choudhary, A.K. Thakur, Complex impedance studies of sodium pyrotungstate – Na2W2O7. Phys. Status Sol. 201, 588 (2004)
P.R. Das, B. Pati, B.C. Sutar, R.N.P. Choudhary, Electrical properties of complex tungsten bronze ferroelectrics; Na2Pb2R2W2Ti4V4O30 (R = Gd, Eu). Adv. Mater. Lett. 3, 8 (2012)
A. Feteira, Negative temperature coefficient Resistance (NTCR) ceramic thermistors: an industrial perspective. J. Am.Ceram. Soc. 92, 967 (2009)
R. Sagar, P. Hudge, S. Madolappa, A.C. Kumbharkhane, R.L. Raibagkar, Electrical properties and microwave dielectric behavior of holmium substituted barium zirconium titanate ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 537, 197 (2012)
D.C. Sinclair, A.R. West, Impedance and modulus spectroscopy of semiconducting BaTiO3 showing positive temperature coefficient of resistance. J. Appl. Phys. 66, 3850 (1989)
Z. Imran, M.A. Rafiq, K. Rasool, S.S. Batool, M.M. Hasan, Temperature dependent transport and dielectric properties of cadmium titanate nanofiber mats. AIP Adv. 3, 032146 (2013)
S.M. Pilgrim, A.E. Sutherland, S.R. Winzer, Diffuseness as a useful parameter for relaxor ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73, 3122 (1990)
P.S. Das, P.K. Chakraborty, B. Behera, R.N.P. Choudhary, Electrical properties of Li2BiV5O15 ceramics. Physica B 395, 98 (2007)
I.M. Hodge, M.D. Ingram, A.R. West, A new method for analysing the a.c. behaviour of polycrystalline solid electrolytes. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 58, 429 (1975)
J.R. Macdonald, Note on the parameterization of the constant-phase admittance element. Solid State Ionics 13, 147 (1984)
Acknowledgements
One of the authors H.S.Mohanty acknowledges the financial support from CSIR, India for the SRF fellowship. First author S.K. Mohanty acknowledge the help of Dr. P.K. Sahoo for extending experimental facilities in NISER, Bhubaneswar and UGC for sanctioning Study Leave under FDP programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohanty, S.K., Mohanty, H.S., Behera, B. et al. Influence of NaNbO3 on the structural, optical and dielectric properties of 0.05(K0.5Bi0.5TiO3)–0.95(NaNbO3) composites ceramics. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 5833–5844 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00881-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00881-5