Abstract
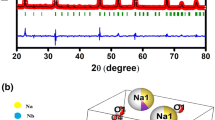
Polycrystalline lead free 0.15(K0.5Bi0.5TiO3)–0.85(NaNbO3) ceramic is synthesized using conventional solid state reaction technique. Structural, dielectric, optical and impedance properties of the sample are investigated. X-ray diffraction (XRD) study reveals K0.5B0.5TiO3 (KBT) diffusing into the NaNbO3 (NN) lattices to form a new perovskite-type solid solution with orthorhombic structure (space group Pmc2 1 ) at room temperature. Addition of small amount of KBT transforms NN ceramic from anti-ferroelectric to ferroelectric material. The XRD data has been refined using Rietveld refinement technique. FTIR spectra reflect an appreciable change in its vibrational phonon modes of the sample. The optical band gap is estimated to be 3.02 eV from the diffused absorbance spectra, which is useful in photo catalytic applications. Different vibrational modes in the frequency range of 130–900 cm−1 is observed from the Raman spectrum. FESEM micrograph reveals the homogeneous grains and well-defined grain boundaries with some few pores. Dielectric and complex impedance spectroscopic studies are carried out in a wide range of frequency (i.e., 103–106 Hz) and temperature (30–475 °C). The presence of ferroelectric properties is confirmed from P–E loop. A strong correlation between its microstructure and electrical parameters is established from the study of the electrical properties of the material. The ac conductivity spectrum obeys Jonscher’s power law. Negative temperature coefficient of resistance behavior of the material is inferred from temperature dependence of dc conductivity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Fu, H. Taniguchi, M. Itoh, S. Koshihara, N. Yamamoto, S. Mori, Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 207601 (2009)
M.D. Maeder, D. Damjanovic, N. Setter, J. Electroceram. 13, 385 (2004)
O. Raymond, R. Font, J. Portelles, J.M. Siqueiros, J. Appl. Phys. 109, 094106 (2011)
N. Wakiya, N. Ishizawa, K. Shinozaki, N. Mizutani, Mater. Res. Bull. 30, 1121 (1995)
B.K. Barick, K.K. Mishra, A.K. Arora, R.N.P. Choudhary, D.K. Pradhan, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 44, 355402 (2011)
X. Lu, J. Xu, L. Yang, C. Zhou, Y.Y. Zhao, C. Yuan, Q. Li, G. Chen, H. Wang, J. Materiomics, 2, 87
P.V.B. Rao, E.V. Ramana, T.B. Sankaram, J. Alloys Comp. 467, 293 (2009)
G.A. Babu, R. Subhramanyam, I. Bhaumik, S. Ganeshmoorthy, P. Ramasamy, P.K. Gupta, Mat. Res. Bull. 53, 136 (2014)
T. Karthik, S. Asthana, Mater. Lett 190, 273 (2017)
H. Xie, D. Li Jin, X. Shen, G. Wang, Shen, J. Cryst. Growth 311, 3626 (2009)
X.H. Hao, J. Adv. Dielectr. 3, 1330001 (2013)
S.K. Mishra, N. Choudhury, S.L. Chaplot, P.S.R. Krishna, R. Mittal, Phys. Rev. B 76, 024110 (2007)
S. Lanfredi, M.H. Lente, J.A. Eiras, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 27
M.T. Benlahrache, N. Benhamla, S. Achour, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 241, 493 (2004)
H. Wu, A. Navrotsky, Y. Su, M.L. Balmer, Chem. Mater. 17,1880 (2005)
A. Aydi, H. Khemakhem, C. Boudaya, R.V. Mühll, Solid State Sci. 6, 333, (2004)
C. Chaker, W.E. Gharbi, N. Abdelmoula, H. Khemakhem, A. Simon, M. Maglione, J. Alloys Compd. 481, 305 (2009)
D. Lin, K.W. Kwok, J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 21, 1060 (2010)
J. Rodriguez-Carvajal, Phys. B 192, 55 (1993)
A. Monshi, M.R. Foroughi, M.R. Monshi, World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 2, 154 (2012)
R.L. Frost, J. Yang, Z. Ding, Chin. Sci. Bull. 48, 1844 (2003)
M. Zheng-Zheng, L. Jian-Qing, T. Z-Ming, Q. Yang, Y. Song-Liu, Chin. Phys. B 21, 107503 (2012)
B.N. Parid.a, R.K. Parida, A. Panda, J. Alloys Comp. 696, 338 (2017)
M.F. Mostafa, S.S. Ata-Allah, A.A.A. Youssef, H.S. Refai, J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 320, 344 (2008)
S. Coste, A. Lecomte, P. Thomas, T. Merle-Mejean, J.C. Champarnaud-Mesjard, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 41, 79 (2007)
E.A. Perianu, I.A. Gorodea, F. Gheorghiu, A.V. Sandu, A.C. Ianculescu, I. Sandu, A.R. Iordan, M.N. Palamaru, Rev. Chim. 62(1), 17 (2011)
Peak Fit Software. http://www.sigmaplot.co.uk/products/peakfit/peakfit.php
Y. Hou, M. Zhu, L. Hou, J. Liu, J. Tang, H. Wang, H. Yan. J. Cryst. Growth 273, 500 (2005)
D. Chao-Ling, Z. Shan-Tao, L.M. Hui, G. Zheng-Bin, C. Guang-Xu, W. Jia, C. Yan-Feng, Chin. Phys. 4, 0854 (2006)
M. Karpierz, J. Suchanicz, K. Konieczny, D. Sitko, P. Marchet, U. Lehuczuk, Ph. Transit. 88, 662 (2015)
R.M. Pittman. A.T. Bell, J. Phys. Chem. 97, 12178 (1993)
H. Idink, V. Srikanth, W.B. White, E.C. Subbarao, J. Appl. Phys. 76, 1819 (1994)
J.C. Anderson, Dielectrics (Chapman & Hall, London, 1964)
P.R. Das, B. Pati, B.C. Sutar, R.N.P. Choudhary, Adv. Mater. Lett. 3(1), 8 (2012)
S.K. Pradhan, S.N. Das, S. Halder, S. Bhuyan, R.N.P. Choudhary, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 9627 (2017)
C.S. Devi, M. Buchi Suresh, G.S. Kumar, G. Prasad, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 228, 38 (2018)
C.G. Koops, Phys. Rev. 83, 121 (1951)
P. Gupta, R. Padhee, P.K. Mohapatra, R.N.P. Choudhary, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 17344 (2017)
D.C. Sinclair, A.R. West, J. Appl. Phys. 66, 3850 (1989)
G.G. Roberts, B. Holcroft, Thin Solid Films 180, 211 (1989)
S.N. Das, A. Pattanaik, S. Kadambini, S. Pradhan, S. Bhuyan, R.N.P. Choudhary, J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 27, 10099 (2016)
R.N.P. Choudhary, D.K. Pradhan, C.M. Tirado, G.E. Bonilla, R.S. Katiyar, J. Mater. Sci. 42, 7423 (2007)
D.K. Pradhan, B. Behera, P.R. Das, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 23, 779 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohanty, S.K., Behera, B., Pati, B. et al. Electrical and optical properties of lead-free 0.15(K0.5Bi0.5TiO3)–0.85(NaNbO3) solid solution. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 12269–12277 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9340-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-9340-5