Abstract
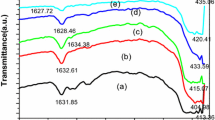
In the present work, pure and Pr doped CeO2 nanoparticles in the form of Ce1−xPrxO2 (x = 0, 0.05, 0.10, 0.15 and 0.20) were synthesized by citrate–nitrate auto combustion method. The combustion derived products were annealed at 700 °C and characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), ultraviolet-diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-DRS), Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), Fourier Transform-Raman Spectroscopy (FT-Raman), photoluminescence analysis (PL) and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) studies. XRD studies revealed that all the samples exhibited single phase cubic fluorite structure. SEM images displayed that pure and Pr doped CeO2 nanoparticles had irregular flaky shape with few agglomerations. TEM results show the proper formation of cubic fluorite structure of nanoparticles. UV-DRS spectroscopy results showed the red shifting in the absorption band edge with increased Pr concentration. The vibrational band assignment of pure and Pr doped CeO2 nanoparticles were analyzed by FT-IR spectroscopy. FT-Raman studies revealed increased defect concentration for the doped samples compared with pure CeO2. PL intensities of doped CeO2 nanoparticles decrease compared with pure CeO2 nanoparticles due to the evolution of non-radioactive oxygen vacancies in the structure. VSM results depicted the suppression of ferromagnetic behavior on Pr doping.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Morimoto, H. Tomonaga, A. Mitani, Ultraviolet ray absorbing coatings on glass for automobiles. Thin Solid Films 351, 61–65 (1999)
S. Armini, S. De Messemaeker, C.M. Whelan, M. Mionpour, K. Maex, Composite polymer core-ceria sheet abrasive particles during oxide CMP: a defective study. J. Electrochem. Soc. 155, H653–H666 (2008)
G. RangaRao, P. Fornasiero, R. Di Monte, J. Kaspar, G. Vlaic, G. Balducci, S. Meriani, G. Gubitosa, A. Cremona, M. Grazianiy, Reduction of No over partially reduced metal-loaded CeO2-ZrO2 solid solutions. J. Catal. 162, 1–9 (1996)
P. Fornasiero, G. Balducci, R. Di Monte, J. Kaspar, V. Sergo, G. Gubitosa, A. Ferrero, M. Graziani, Modification of the redox behavior of CeO2 induced by structural doping with ZrO2. J. Catal. 164, 173–183 (1996)
Y. Zhai, S. Zhang, H. Pang, Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of CeO2 nanocrystalline using ammonium bicarbonate as precipitant. Mater. Lett. 61, 1863–1866 (2007)
P. Borker, A.V. Salker, Solar assisted photocatalytic degradation of naphthol blue black dye using Ce1−x Mn x O2. Mater. Chem. Phys. 103, 366–370 (2007)
M.A.F. Oksuzomern, G. Donmez, V. Sariboga, T.G. Altincekic, Microstructure and ionic conductivity properties of gadolinia doped ceria (GdxCe1−xO2−x/2) electrolytes for intermediate temperature SOFCs prepared by the polyol method. Ceram. Int. 39, 7305–7315 (2013)
S. Yuan-Qiang, Z. Huai-Wu, W. Qi-Ye, Z. Hao, J.Q. Xiao, Additional Y3+doping effect on ferromagnetism of Ce0.97Co0.03O2−δcompounds. Chin. Phys. Lett. 25, 1106–1109 (2008)
T. Dietl, H. Ohno, F. Matsukura, J. Cibert, D. Ferrand, Zener model description of ferromagnetism in Zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science 287, 1019–1022 (2000)
A. Tiwari, M. Bhosle, S. Ramachandran, N. Sudhakar, J. Narayan, S. Budak, A. Gupta, Ferromagnetism in Co doped CeO2: observation of a giant magnetic moment with a high Curie temperature. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 142511–142513 (2006)
L.R. Shah, B. Ali, H. Zhu, W.G. Wang, Y.Q. Song, H.W. Zhang, S.I. Shah, J.Q. Xiao, Detailed study on the role of oxygen acancies in structural, magnetic and transport behavior of magnetic insulator: Co-CeO2. J. Phys. 21, 486004–4186013 (2009)
F. Abbas, T. Jan, J. Iqbal, M. Sajjad, H. Naqvi, Fe doping induced enhancement in room temperature ferromagnetism and selective cytotoxicity of CeO2 nanoparticles. Curr. Appl. Phys. 15, 1428–1434 (2015)
E. Swatsitang, S. Phokha, S. Hunpratub, S. Maensiri, Characterization of Sm-doped CeO2 nanoparticles and their magnetic properties. Phys. B 485, 14–20 (2016)
G.R. Li, D.L. Qu, L. Arurault, Y.X. Tong, Hierarchically porous Gd3+-doped CeO2 nanostructures for the remarkable enhancement of optical and magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 1235–1241 (2009)
N. Shehata, K. Meehan, M. Hudait, N. Jain, Control of oxygen vacancies and Ce3+ concentrations in doped ceria nanoparticles via the selection of lanthanide element. J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 1173–1183 (2013)
X. Liu, S. Chen, X. Wang, Synthesis and photoluminescence of CeO2:Eu3+ phosphor powders. J. Lumin. 127, 650–654 (2007)
J.H. Cho, M. Bass, S. Babu, J.M. Dowding, W.T. Self, S. Seal, Up conversion luminescence of Yb3+-Er3+ co doped CeO2nanocrystals with imaging applications. J. Lumin. 132, 743–749 (2012)
L. Wang, F. Menga, K. Li, F. Lu, Characterization and optical properties of pole-like nano-CeO2 synthesized by a facile hydrothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 286, 269–274 (2013)
H. Guo, Green and red upconversion luminescence in CeO2:Er3+ powders produced by 785 nm laser. J. Solid State Chem. 180, 127–131 (2007)
F.A. Al-Agel, E. Al-Arfaj, A.A. Al-Ghamdi, Y. Losovyj, L.M. Bronstein, W.E. Mahmoud, A novel recipe to improve the magnetic properties of Mn doped CeO2 as a room temperature ferromagnetic diluted metal oxide. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 360, 73–79 (2014)
M.S.M. Suan, M.R. Johan, T.C. Siang, Synthesis of Y3Ba5Cu8O18 superconductor powder by auto-combustion reaction: effects of citrate–nitrate ratio. Physica C 480, 75–78 (2012)
S.R. Jain, K.C. Adiga, A new approach to thermochemical calculations of condensed fuel-oxide. Combust. Flame Vol. 40, 71–79 (1981)
G.Q. Xie, M.F. Luo, M. He, P. Fang, J.M. Ma, Y.F. Ying, Z.L. Yan, An improved method for preparation of Ce0.8Pr0.2OY solid solution with nanoparticles smaller than 10 nm. J. Nanopart. Res. 9, 471–478 (2007)
A.I.Y. Tok, S.W. Du, F.Y.C. Boey, W.K. Chong, Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of rare earth doped ceria nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 466, 223–229 (2007)
A.C. Cabral, L.S. Cavalcante, R.C. Deus, E. Longo, A.Z. Simões, F. Moura, Photoluminescence properties of praseodymium doped cerium oxide nanocrystals. Ceram. Int. 40, 4445–4453 (2014)
P. Shuk, M. Greenblatt, Hydrothermal synthesis and properties of mixed conductors based on Ce1−xPrxO2−δ solid solutions. Solid State Ionics. 116, 217–223 (1999)
K.A. Bhabu, J. Theerthagiri, J. Madhavan, T. Balu, T.R. Rajasekaran, A.K. Arof, Investigations on acceptor (Pr3+) and donor (Nb5+) doped cerium oxide for the suitability of solid oxide fuel cell electrolytes. Ionics 22, 2461–2470 (2016)
M.C. Dimri, H. Khanduri, H. Kooskora, J. Subbi, I. Heinmaa, A. Mere, J. Krustok, R. Stern, Ferromagnetism in rare earth doped cerium oxide bulk samples. Physica Status Solidi 209, 353–358 (2012)
S.A. Hassanzadeh-Tabrizia, M. Mazaheri, M. Aminzare, S.K. Sadrnezhaad, Reverse precipitation synthesis and characterization of CeO2 nanopowder. J. Alloy. Compd. 491, 499–502 (2010)
S. Colis, A. Bouaine, G. Schmerber, C. Ulhaq-Bouillet, A. Dinia, S. Choua, P. Turek, High-temperature ferromagnetism in Co-doped CeO2 synthesized by the coprecipitation technique. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 7256–7263 (2012)
P. Patsalas, S. Logothetidis, L. Sygellou, S. Kennou, Structure-dependent electronic properties of nanocrystalline cerium oxide films. Phys. Rev. B 68, 035104 (2003)
I.T. Liu, M.H. Hon, C.Y. Kuan, L.G. Teoh, Structure and optical properties of Ag/CeO2 nanocomposites. Appl. Phys. A 111, 1181–1186 (2013)
S. Patil, S. Seal, Y. Guo, A. Schulte, J. Norwood, Role of trivalent La and Nd dopants in lattice distortion and oxygen vacancy generation in cerium oxide nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 243110 (2006)
B. Choudhury, A. Choudhury, Ce3+ and oxygen vacancy mediated tuning of structural and optical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 131, 666–671 (2012)
F.A. Mir, K.M. Batoo, I. Chatterjee, G.M. Bhat, Preparation and ac electrical characterizations of Cd doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 25, 1564–1570 (2014)
R. Tholkappiyan, K. Vishista, Combustion synthesis of Mg-Er ferrite nanoparticles: cation distribution and structural, optical and magnetic properties. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 40, 631–642 (2015)
A.K. Tripathi, M.C. Mathpal, P. Kumar, M.K. Singh, M.A.G. Soler, A. Agarwal, Structural, optical and photoconductivity of Sn and Mn doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 622, 37–47 (2015)
M. Zawadzki, Preparation and characterization of ceria nanoparticles by microwave-assisted solvothermal process. J. Alloy. Compd. 454, 347–351 (2008)
T. Suzuki, I. Kosacki, H.U. Anderson, Electrical conductivity and lattice defects in nanocrystalline cerium oxide thin films. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 2007–2014 (2001)
R. Kostic, S. Askrabic, Z.D. Mitrovic, Z.V. Popovic, Low-frequency Raman scattering from CeO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 90, 679–683 (2008)
J.E. Spanier, R.D. Robinson, F. Zhang, S.W. Chan, I.P. Herman, Size-dependent properties of CeO2−y nanoparticles as studied by Raman scattering. Phys. Rev. B 64, 245407 (2001)
W.F. Zhang, Y.L. He, M.S. Zhang, Z. Yin, Q. Chen, Raman scattering study on anatase TiO2 nanocrystals. J. Phys. D 33, 912–916 (2000)
H.C. Choi, Y.M. Jung, S.B. Kim, Size effects in the Raman spectra of TiO2 nanoparticles. Vib. Spectrosc. 37, 33–38 (2005)
V.V. Pushkarev, V.I. Kovalchuk, J.L. d’Itri, Probing defect sites on the CeO2 surface with dioxygen. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 5341–5348 (2004)
A. Kumar, S. Babu, A.S. Karakoti, A. Schulte, S. Seal, Luminescence properties of europium-doped cerium oxide nanoparticles: role of vacancy and oxidation states. Langmuir 25, 10998–11007 (2009)
K.T. Suzuki, H.U. Anderson, P. Colomban, Raman scattering and lattice defects in nanocrystalline CeO2 thin films. Solid State Ion. 149, 99–105 (2002)
L. Wu, S. Dey, M. Gong, F. Liu, R.H. Castro, Surface segregation on manganese doped ceria nanoparticles and relationship with nanostability. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 30187–30196 (2014)
D. Manoharan, K. Vishista, Optical properties of nano-crystalline cerium dioxide synthesized by single step aqueous citrate-nitrate gel combustion method. Asian J. Chem. 25, 9045–9049 (2013)
K.A. Bhabu, J. Theerthagiri, J. Madhavan, T. Balu, G. Muralidharan, T.R. Rajasekaran, Cubic fluorite phase of samarium doped cerium oxide (CeO2)0.96Sm0.04 for solid oxide fuel cell electrolyte. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 1566–1577 (2015)
M.K. Chinnu, K.V. Anand, R.M. Kumar, T. Alagesan, R. Jayavel, Synthesis and enhanced electrochemical properties of Sm:CeO2 nanostructure by hydrothermal route. Mater. Lett. 113, 170–173 (2013)
F. Abbas, T. Jana, J. Iqbala, I. Ahmad, M. Sajjad, H. Naqvi, M. Malikd, Facile synthesis of ferromagnetic Ni doped CeO2nanoparticles with enhanced anticancer activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 357, 931–936 (2015)
S. Samiee, E.K. Goharshadi, Effects of different precursors on size and optical properties of ceria nanoparticles prepared by microwave-assisted method. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 1089–1095 (2012)
G. Wang, Q. Mu, T. Chen, Y. Wang, Synthesis, characterization and photoluminescence of CeO2 nanoparticles by a facile method at room temperature. J. Alloy. Compd. 493, 202–207 (2010)
S. Phoka, P. Laokul, E. Swatsitang, V. Promarak, S. Seraphin, S. Maensiria, Synthesis, structural and optical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles synthesized by a simple polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) solution route. Mater. Chem. Phys. 115, 423–428 (2009)
A.Z. Liu, J.X. Wang, C.R. He, H. Miao, Y. Zhang, W.G. Wang, Synthesis and characterization of Gd0.1Ce0.9O1.95nanopowder via an acetic-acrylic method. Ceram. Int. 39, 6229–6235 (2013)
R. Tholkappiyan, A. Nirmalesh Naveen, S. Sumithra, K. Vishista, Investigation on spinel MnCo2O4 electrode material prepared via controlled and uncontrolled synthesis route for supercapacitor application. J. Mater. Sci. 50, 5833–5843 (2015)
C. Binet, A. Badri, J.C. Lavalley, A spectroscopic characterization of the reduction of ceria from electronic transitions of intrinsic point defects. J. Phys. Chem. 98, 6392–6398 (1994)
C. Ho, J.C. Yu, T. Kwong, A.C. Mak, S. Lai, Morphology-controllable synthesis of mesoporous CeO2 nano- and microstructures. Chem. Mater. 17, 4514–4522 (2005)
R. Tholkappiyan, K. Vishista, Synthesis and characterization of barium zinc ferrite nanoparticles: working electrode for dye sensitized solar cell applications. Sol. Energy 106, 118–128 (2014)
B. Choudhury, A. Choudhurya, Room temperature ferromagnetism in defective TiO2 nanoparticles: role of surface and grain boundary oxygen vacancies. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 203906 (2013)
B. Choudhury, P. Chetri, A. Choudhury, Oxygen defects and formation of Ce3+ affecting the photocatalytic performance of CeO2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 4, 4663–4671 (2014)
Y. Lei, L.D. Zhang, G.W. Meng, G.H. Li, X.Y. Zhang, C.H. Liang, W. Chen, S.X. Wang, Preparation and photoluminescence of highly ordered TiO2 nanowire arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 1125 (2001)
S. Gnanam, V. Rajendran, Synthesis of CeO2 or a-Mn2O3 nanoparticles via sol–gel process and their optical properties. J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol. 58, 62–69 (2011)
Y.F. Huang, Y.B. Cai, D.K. Qiao, H. Liu, Morphology-controllable synthesis and characterization of CeO2 nanocrystals. Particuology 9, 170–173 (2011)
A.H. Morshed, M.E. Moussa, S.M. Bedair, R. Leonard, S.X. Liu, N. El-Masry, Violet/blue emission from epitaxial cerium oxide films on silicon substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 1647 (1997)
F.M. Meng, L.N. Wang, J.B. Cui, Controllable synthesis and optical properties of nano-CeO2via a facile hydrothermal route. J. Alloy. Compd. 556, 102–108 (2013)
W.M. Kwok, A.B. Djurisic, Y.H. Leung, W.K. Chan, D.L. Phillips, Time-resolved photoluminescence from ZnO nanostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 223111 (2005)
J.X. Duan, X.T. Huang, H. Wang, Q. Zhong, F.L. Sunand, X. He, Synthesis of porous ZnO micro-flakes via an integrated autoclave and pyrolysis process. Mater. Chem. Phys. 106, 181–186 (2007)
F. Abbas, J. Iqbal, T. Jan, M. Sajjad, H. Naqvi, A. Gul, R. Abbasi, A. Mahmood, I. Ahmad, M. Ismail, Differential cytotoxicity of ferromagnetic Co doped CeO2 nanoparticles against neuroblastoma cancer cells. J. Alloy. Compd. 648, 1060–1066 (2015)
V. Ferrari, A.M. Llois, V. Vildosola, Co-doped ceria: tendency towards ferromagnetism driven by oxygen vacancies. J. Phys. 22, 276002 (2010)
S.D. Yoon, Y. Chen, A. Yang, T.L. Goodrich, X. Zuo, D.A. Arena, K. Ziemer, C. Vittoria, V.G. Harris, Oxygen-defect-induced magnetism to 880 K in semi-conducting anatase TiO2−δ films. J. Phys. 18, L355-L361 (2006)
S. Phokha, J. Klinkaewnarong, S. Hunpratub, K. Boonserm, E. Swatsitang, S. Maensiri, Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped MgO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 27, 33–39 (2016)
X. Bie, C. Wang, H. Ehrenberg, Y. Wei, G. Chen, X. Meng, G. Zou, F. Du, Room-temperature ferromagnetism in pure ZnO nanoflowers. Solid State Sci. 12, 1364–1367 (2010)
R.K. Singhal, P. Kumari, A. Samariya, S. Kumar, S.C. Sharma, Y.T. Xing, E.B. Saitovitch, Role of electronic structure and oxygen defects in driving ferromagnetism in nondoped bulk CeO2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 172503 (2010)
S. Phokha, S. Pinitsoontorn, P. Chirawatkul, Y. Poo-Arporn, S. Maensiri, Synthesis, characterization, and magnetic properties of monodisperse CeO2nanospheres prepared by PVP-assisted hydrothermal method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 425–438 (2012)
J.M.D. Coey, M. Venkatesan, C.B. Fitzgerald, Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides. Nat. Mater. 4, 173–179 (2005)
J.M.D. Coey, A.P. Douvalis, C.B. Fitzgerald, M. Venkatesan, Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped SnO2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1332–1334 (2004)
Z.V. Popovic, Z.D. Dohcevic-Mitrovic, N. Paunovic, M. Radovic, Evidence of charge delocalization in Ce1−xFex 2+(3+)O2−y nanocrystals (x = 0, 0.06, 0. Phys. Rev. B 85(12), 014302 (2012)
S. Aškrabić, Z.D. Dohčević-Mitrović, V.D. Araújo, G. Ionita, M.M. de Lima Jr, F-centre luminescence in nanocrystalline CeO2. J. Phys. D 46, 495306–495315 (2013)
C. Juna, L. Lin, T. Lu, L. Yong, Electronic structure of F, F+-center in MgO. Eur. Phys. J. B 9, 593–598 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bharathi, R.N., Sankar, S. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Pr doped CeO2 nanoparticles synthesized by citrate–nitrate auto combustion method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 6679–6691 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8654-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8654-7