Abstract
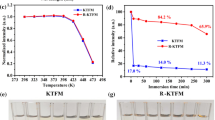
The red fluoride phosphor K2XF6:Mn4+ was prepared by co-precipitation with partial HF in placed with glacial acetic acid. The phase structures and photoluminescence (PL) properties of the red fluoride phosphor K2XF6:Mn4+ phosphor have been investigated in detail. Reliability test show that the relative PL intensity of KSFM, K(S,G)FM and KTFM decreased by 14.95%, 18.22% and 67.21% after the ambient condition of high temperature and high humidity (85 °C/RH 85%) for the exposure time of 168 h. The thermal cycling testing results show that the relative PL intensity of KSFM, K(S,G)FM and KTFM decreased by 0.41%, 5.55% and 1.14% after storing the phosphors into an ambient condition of 120 °C for 1 h and − 40 °C for 1 h by turns for five times. The relative PL intensity of KSFM, K(S,G)FM and KTFM decreased by 89.09%, 91.93% and 99.94% after soaking into boiled water for 3 h. It can be summarized that KSFM has the best reliability and KTFM has the worst reliability. Then by mixing the YAG:Ce3+ and KXFM phosphor and commercial green phosphor with appropriate proportion of the components, it can be found that the luminous efficacy of K2XF6:Mn4+ (KSFM, K(S,G)FM, KTFM) after 85°C/RH 85% decreased by 0.14%, 0.54% and 1.06%, after thermal cycling decreased by 2.60%, 1.53% and 3.17% and after hydrolysis decreased by 14.49%, 9.65% and 47.66%. The KTFM after hydrolysis and YAG:Ce3+ encapsulated WLEDs have the most reduced luminous efficacy. Moreover, the luminous efficacy of K(S,G)FM after hydrolysis and YAG:Ce3+ encapsulated WLEDs is better than KSFM after hydrolysis and YAG:Ce3+ encapsulated WLEDs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Nizamoglu, T. Erdem, H.V. Demir, High scotopic/photopic ratio white-light-emitting diodes integrated with semiconductor nanophosphors of colloidal quantum dots. Opt. Lett. 36, 1893–1895 (2011)
J. Lim, S. Jun, E. Jang, H. Baik, H. Kim, J. Cho, Preparation of highly luminescent nanocrystals and their application to light-emitting diodes. Adv. Mater. 19, 1927–1932 (2007)
M.H. Chang, D. Das, P.V. Varde, M. Pecht, Light emitting diodes reliability review. Microlelctron. Relieab. 52, 762–782 (2012)
H. Daicho, T. Iwasaki, K. Enomoto, Y. Sasaki, Y. Maeno et al., A novel phosphor for glareless white light-emitting diodes. Nat. Commun. 3, 1132–1139 (2012)
I. Ahemen, D.K. De, A.N. Amah, A review of solid state white light emitting diode and its potentials for replacing conventional lighting technologies in developing countries. Appl. Phys. Res. 6, 1188–1194 (2014)
T.Y. Seong, J. Han, H. Amano, H. Morkoc, III-Nitride based light emitting diodes and applications. Top. Appl. Phys. 126, V-VI (2014)
C. J. Humphreys, Solid-state lighting. Mrs. Bull. 33 (2008) 459–470
S. Neeraj, N. Kijima, A.K. Cheetham, Novel red phosphors for solid-state lighting: the system NaM(WO4)2–x (MoO4)x:Eu3+ (M = Gd, Y, Bi). Chem. Phys. Lett. 387, 2–6 (2004)
H. Zhan, Z. Xu, C. Tian, Y. Wang, M. Chen et al., Achieving standard wide color gamut by tuning LED backlight and color filter spectrum in LCD. J. Soc. Inf. Display. 22, 545–551 (2015)
S. Lee, M.G. Kim, J.B. Song, S.Y. Kim, S. Tamura et al., Highly efficient and wide color gamut white OLED architecture for display application. Sid Sym. Digest. Tech. 39, 826–829 (2008)
G. Blasse, B.C. Grabmaier, Luminescent Materials (Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 1994)
M.H. Du, Chemical trends of Mn4+ emission in solids. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2, 2475–2481 (2014)
H.F. Sijbom, J.J. Joos, L.I.D.J. Martin et al., Luminescent behavior of the K2SiF6:Mn4+ red phosphor at high fluxes and at the microscopic level. ECS J. Solid State. Sci. Technol. 5, 3040–3048 (2016)
C. Liao, R. Cao, Z. Ma, Y. Li et al., Synthesis of K2SiF6:Mn4+, phosphor from SiO2, powders via redox reaction in HF/ KMnO4, solution and their application in warm-white LED. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 3552–3556 (2013)
S. Adachi, T. Takahashi, Direct synthesis and properties of K2SiF6:Mn4+ phosphor by wet chemical etching of Si wafer. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 317 (2008)
Z.L. Wang, Y.Y. Zhou, Z.Y. Yang, Y. Liu et al., Synthesis of K2XF6:Mn4+, (X = Ti, Si and Ge) red phosphors for white LED applications with low-concentration of HF. Opt. Mater. 49, 235–240 (2015)
H. Zhu, C.C. Lin, W. Luo, S. Shu et al., Highly efficient non-rare-earth red emitting phosphor for warm white light-emitting diodes. Nat. Commun. 5, 4312 (2014)
T.M. Wang, Y. Gao, Z.P. Chen, Q.Y. Huang, B.L. Song, Y.H. Huang, S. Liao, H.X. Zhang, Cation exchange synthesis and cations doped effects of red emitting phosphors K2TiF6:Mn4+, M+(M = Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, and Zn). J. Mater Sci. 28, 1878–11885 (2017)
T.M. Wang, Y. Gao, Z.P. Chen, Q.Y. Huang, L.N. Wu, Y.H. Huang, S. Liao, H.X. Zhang, The formation of KF induced red-emitting phosphors K2TiF6*BaF(HF2):Mn4+ by cation exchange. J. Lumin. 188, 307–312 (2017)
L. Huang, Y. Zhu, X. Zhang, R. Zou et al., HF-free hydrothermal route for synthesis of highly efficient narrow-band red emitting phosphor K2Si1−xF6: xMn4+ for warm white light-emitting diodes. Chem. Mater. 28, 1495–1502 (2016)
Y.K. Xu, S. Adachi, Properties of Na2SiF6:Mn4+ and Na2GeF6:Mn4+ red phosphors synthesized by wet chemical etching. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 339 (2009)
Y.W. Zhu, L. Huang, R. Zou, J.H. Zhang et al., Hydrothermal synthesis, morphology and photoluminescent properties of an Mn4+-doped novel red fluoride phosphor elpasolite K2LiAlF6. J. Mater. Chem. C. 4, 5690–5695 (2016)
L.L. Wei, C. Lin, M.H. Fang, M. Brik et al., A low-temperature co-precipitation approach to synthesize fluoride phosphors K2MF6:Mn4+ (M = Ge, Si) for white LED applications. J. Mater. Chem. C. 3, 1655–1660 (2015)
L. Lv, Z. Chen, G. Liu, S. Huang, Y. Pan, Optimized photoluminescence of red phosphor K2TiF6:Mn4+ synthesized at room temperature and its formation mechanism. J. Mater. Chem. C. 3, 1935–1941 (2015)
A.A. Setlur, R.J. Lyons, J.E. Murphy, N.P. Kumar et al., Blue Light-emitting diode phosphors based upon oxide, oxyhalide, and halide hosts. ECS J. Solid State. Sci. Technol. 2, 3059–3070 (2012)
R. Kasa, Y. Arai, T. Takahashi, S. Adachi, Photoluminescent properties of cubic K2MnF6 particles synthesized in metal immersed HF/KMnO4 solutions. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 339 (2015)
M.G. Brik, A.M. Srivastava, On the optical properties of the Mn4+ ion in solids. J. Lumin. 133, 69–72 (2013)
T. Takahashi, S. Adachi, Mn4+-activated red photoluminescence in K2SiF6 phosphor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 155, 183–188 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Science and Technology Planning Project of Zhejiang Province, China (2018C01046), Enterprise-funded Latitudinal Research Projects (J2016-141; J2017-171; J2017-293 and J2017-243), Sponsored by Shanghai Sailing Program (18YF1422500) and Research start-up project of Shanghai Institute of Technology (YJ2018-9).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, F., Zou, J., Yang, B. et al. Reliability of fluoride phosphor K2XF6:Mn4+ (K2SiF6:Mn4+, K2(Si,Ge)F6:Mn4+, K2TiF6:Mn4+) for LED application. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 21061–21071 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0253-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0253-0