Abstract
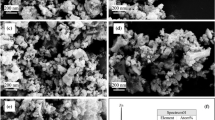
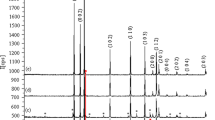
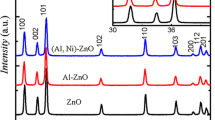
Synthesis of three different ratios of Alx=0.05, 0.10, 0.15 Cox=0.05, 0.10, 0.15ZnOx=0.95, 0.90, 0.85 powders were prepared using sol gel route. Structural and electronic properties of the synthesized material were investigated using X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope, vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), ultraviolet (UV) spectroscopy and dielectric studies. Characterization results reveal that the particle size is of the range 4.84 nm to the maximum size of 19.86 nm with a morphological structures representing rounded and honeycomb shapes at different doping ratios. VSM results of the prepared samples reveal the ferromagnetic nature with the hysteresis curve representation. The optical band gap has been calculated as 3.1–3.8 nm from the UV spectroscopy results. Conductivity of the samples was calculated from dielectric constant and conductivity increases with increasing doping ratios.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Yousefi, Effects of Sn atoms on formation of ZnO nanorings. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 17, 2698 (2015)
S. Dusari, J. Barzola-Qaiquia, P. Esquinazi, Changes in the electrical transport of ZnO under visible light. Solid State Commun. 150, 22–26 (2010)
O.D. Jayakumar, I.K. Gopalakrishnan, S.K. Kulshreshtha, Magnetization study of Fe doped ZnO co-doped with Cu: synthesised by wet chemical method. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 4706–4712 (2006)
T. Zhang, L.X. Song, H.W. Zhang, Origin of ferromagnetism of (Co, Al) codopedZnO from first principle calculations. App. Phys. Lett. 89, 172502 (2006)
D. Iusan, R. Knit, B. Sanyal, O. Eriksson, Electronic structure and chemical and magnetic interactions in ZnO doped with Co and Al: experiments and ab initio density-functional calculations. Phys. Rev. B 78, 085319 (2008)
O.D. Jayakumar, S.N. Achary, C. Sudakar, A.K. Tyagi, Experimental and Theoritical investigation on magnetic behaviour of (Al, Co) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2, 1505–1511 (2010)
C.S. Chang, E.Z. Kurmaev, A. Dinia, Co and Al co-doping for ferromagnetism in ZnO: co diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Phys. Cond. Matter 21, 056002 (2009)
M. Sharma, R.M. Mehra, Effect of thickness on structural, electrical, optical and magnetic properties of Co and Al doped ZnO films deposited by sol–gel route, App. Surf. Sci. 255, 2527–2532 (2008)
X.C. Liu, E.W. Shi, L.X. Song, High temperature ferromagnetism in (Co, Al) codoped ZnO powders. App. Phys. Lett. 88, 252503 (2006)
H.E. Unalan, Y. Zhang, P. Hiralal, G.A.J. Amaratunga, Zinc oxide nanowire networks for macroelectronic devices. App. Phys. Lett. 94, 163501 (2009)
H.E. Unalan, Y. Yang, Y. Zhang, P. Hiralal, G. Amaratunga, ZnO nanowire and WS2 nanotube electronics. IEEE Trans. Electron. Device 55, 2988–3000 (2008)
Flora M. Li, Gen-Wen Hsieh, William I. Milne, Zinc oxide nanostructires and high electron mobility nanocomposite thin film transistors. IEEE Trans Electron. Device 55, 3001–3011 (2008)
E. Lee, D.I. Moon, Y.K. Choi, Transparent zinc oxide gate metal oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor for high responsivity photodetector. IEEE Electron. Device Lett. 30, 493–495 (2009)
J.L. Wang, P.Y. Yang, M.H. Juang, pH sensing characteristics of Hydrothermal Al–doped ZnO nanostructures, J. Nano. Mat. 2013, 1–7 (2013)
Jiang T., Zhou X. and Luo T., A zinc oxide modified porous silicon humidity sensor, Proceeding of the IEEE International Conference on Information Acquisition, (2006)
C.S. Prajapati, P.P. Sahay, Influence in doping on the structural, optical and acetone sensing properties of ZnO nanoparticulate thin films. Mat. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 200–210 (2012)
E.S.P. Leong, M.K. Ching, S.F. Yu, Sol–Gel ZnO–SiO2 composite waveguide Ultravoilet Lasers. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 16, 2418–2420 (2004)
S. Kim, H. Moon, D. Gupta, Y.K. Choi, Resistive switching characteristics of Sol–Gel zinc oxide films for flexible memory applications. IEEE Trans. Elect. Device 56, 696–699 (2009)
C.L. Liao, Y.F. Chang, M.C. Wu, High speed GaN based blue light emitting diodes with gallium DOPED ZnO current spreading layer. IEEE Elect. Dev. Lett. 34, 611–613 (2013)
B. Ling, J.L. Zhao, Z.L. Dong, Electroluminance from ferromagnetic Fe doped ZnONnorod arrays on P- Si. IEEE Trans. Electron. Device 57, 1948–1951 (2010)
Y. Nam, I. Hwang, B.H. Park, Switchable schotty diode characteristics induced by electroforming process in Mn doped ZnO thin films. App. Phys. Lett. 102, 162105 (2013)
H. Emrah Unalan, P.H. Hiralal, M. Chhowalla, Flexible organic photovoltaics from Zinc oxide nanowires grown on transparent and conducting single walled carbon nanotube thin films. J. Mater. Chem. 18, 5909–5912 (2008)
L. Zhifang, C. Guangyu, L. Liwei, Development of aluminiumdoped ZnO films for a Si:h/µc-Si: H solar cell applications. J. Semicond. 34, 063004 (2013)
X. Zhang, X. Huang, H. Jiang, Dye-Sensitized solar cell with energy strorage function through PVDF-ZnO nanocomposite counter electrode. Adv. Mater. 25, 4093–4096 (2013)
A. Kharatzadeh, F. Jamali-Sheini, R. Yousefi, Excellent photocatalytic performance of Zn(1−x)MgxO/rGO nanocomposites under natural sunlight irradiation and their photovoltaic and UV detector applications. Mater. Design 107, 47–55 (2016)
R.F. Dezfulya, R. Yousefib, F. Jamali-Sheini, Photocurrent applications of Zn(1_x)CdxO/rGO nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 42, 7455–7461 (2016)
A. Sa´aedi, R. Yousefi, F. Jamali-Sheini, A.K. Zak, M. Cheraghizade, M.R. Mahmoudian, M.A. Baghchesara, A.S. Dezaki, XPS studies and photocurrent applications of alkali-metals-doped ZnO nanoparticles under visible illumination conditions. Physica E 79, 113–118 (2016)
D. Sridevi, K.V. Rajendran, Synthesis and optical characteristics of ZnO nanocrystals. Bull. Mater. Sci. 32, 165–168 (2002)
Dharma J, Pisal A., Simple method of measuring the band gap energy value TiO2 in powder form using a UV/Vis/NIR spectrometer, Application Note, PerkinElmer Inc
M. Elahi, D. Souri, Study of optical absorption and optical band gap determination of thin amorphous TeO2–V2O5–MoO3 blown films. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 44, 468–472 (2006)
K. Omar, M.D.J. Ooi, M.M. Hassin, Investigation on dielectric constant of Zinc oxide. Mod. Appl. Sci. 3, 110 (2009)
S. Shah, D. Singh, V. Shrinet, Dielectric properties and surface morphology of proton irritated ferric oxalate dispersed PVC films. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 46, 439–442 (2008)
A. Roy, A. Parveen, A. Koppalkar, Microscopic and dielectric studies of ZnO nanoparticles loaded in ortho-chloropolyanilinenanocomposites. J. Nanopart. Res. 15, 3–11 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Management of Saveetha University for the continuous motivation to carry out the research work and for extending all necessary support. We would also like to extend our regards to Sophisticated Analytical Instruments Facility (SAIF), IIT Madras and Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research (IGCAR) for carrying out the material characterizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravindiran, M., Shankar, P. Synthesis and characterization of (Al, Co) co-doped ZnO for electronic applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 4229–4238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6045-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6045-5