Abstract
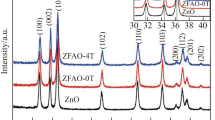
A highly valuable co-precipitation technique was used for the preparation of ZnO, Zn0.98Al0.02O and Zn0.96Al0.02Ni0.02O semiconductor nanoparticles. X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy measurements reveal that the samples are nano-columns with a hexagonal wurtzite crystal structure. A significant enhancement in dielectric constant resulted from the substitution of (Al, Ni) co-doped ZnO lattice while an opposite trend was observed for dielectric loss. With the substitution of both Al and Ni, the electrical conductivity was found to be increased in comparison with that of ZnO nanoparticles due to the increase of available charge carriers after replacement of Zn ions by Ni ions. The magnetic property measurements revealed well room-temperature ferromagnetism, RTFM (Diluted magnetic semiconductor behavior) for the Ni co-doped samples in comparison with that of single Al–ZnO. The origin of high ferromagnetic may arise from the metallic Ni and intrinsic property of the doped ZnO.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.A. Wolf, D.D. Awschalom, R.A. Buhrman, J.M. Daughton, S. von Molnar, M.L. Roukes, A.Y. Chtchelkanova, D.M. Treger, Spintronics: a spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science 294, 1488–1495 (2001)
Y.Q. Chang, D.B. Wang, X.H. Luo, X.Y. Xu, X.H. Chen, L. Li, C.P. Chen, R.M. Wang, J. Xu, D.P. Yu, Synthesis, optical, and magnetic properties of diluted magnetic semiconductor Zn1−xMnxO nanowires via vapor phase growth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 4020–4022 (2003)
Y. Ohno, D.K. Young, B. Beshoten, F. Matsukura, H. Ohno, D.I. Awschalom, Electrical spin injection in a ferromagnetic semiconductor heterostructure. Nature 402, 790–792 (1999)
Q. Wang, Q. Sun, P. Jena, Ab initio study of electronic and magnetic properties of the C-codoped Ga1−xMnxN (10ī0) surface. Phys. Rev. B. 75, 035322 (2007)
C. Klingshirn, Optical properties of bound and localized excitons and of defect states. Phys. Status Solidi B 71, 547–556 (1975)
A.F. Fert, Origin, development, and future of spintronics (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. 47, 5956–5967 (2008)
T. Dietl, H. Ohno, F. Matsukura, J. Cibert, D. Ferrand, Zener model description of ferromagnetism in Zinc-Blend magnetic semiconductors. Science 287, 10191022 (2000)
X.Y. Xu, C.B. Cao, Structure and ferromagnetic properties of co-doped ZnO powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2216–2219 (2009)
T. Dietl, A ten-year perspective on dilute magnetic semiconductors and oxides. Nat. Mater. 9, 965974 (2010)
K. Sato, H.K. Yoshida, Material design for transparent ferromagnets with ZnO-based magnetic semiconductors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 39, L555 (2000)
G. Li, L. Qiang, Z. Qing-Xun, G.J. Xin, Z. Yang, J.L. Tao, G. Bo, L.B. Ting, First principles study of the optical properties of ZnO doped with Al, N. Acta Phys. Sin. 58, 5624–5631 (2009)
Z. Jin, L. Qiao, C. Guo, Z. He, L. Liu, M. Rong, First-priniciple study of electrical and optical properties of (Al, Sn) co-doped ZnO. Optik—Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 127, 1988–1992 (2016)
Y. Lin, D. Jiang, L. Fan, W. Shi, X. Ma, Fe-doped ZnO magnetic semiconductor by mechanical alloying. J. Alloy. Compd. 436, 30–33 (2007)
C.J. Cong, J.H. Hong, Q.Y. Liu, L. Liao, K.L. Zhang, Synthesis, structure and ferromagnetic properties of Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. 138, 511–515 (2006)
Yu. Mingpeng, H. Qiu, X. Chen, H. Liu, M. Wang, Structural and physical properties of Ni and Al co-doped ZnO films grown on glass by direct current magnetron co-sputtering. Phys. B 404, 1829–1834 (2009)
G. Goncalves, A. Pimentel, E. Fortunato, R. Martins, E.L. Queiroz, R.F. Bianchi, R.M. Faria, UV and ozone influence on the conductivity of ZnO thin films. J. Non Cryst. Solids 352, 1444–1447 (2006)
A.S. Fawzi, A.D. Sheikh, V.L. Mathe, Structural, dielectric properties and ac conductivity of Ni(1−x)ZnxFe2O4 spinel ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 502, 231–237 (2010)
C.A. Barbosa, J.M. Henriques, E.L. Albuquerque, V.N. Freire, Thermal effect on the dielectric function and small polaron hopping conduction in inorganic molecular crystals. Phys. Lett. A 372, 3725–3728 (2008)
N. Chandel, N. Mehta, A. Kumar, Investigation of ac conductivity measurements in a-Se80Te20 and a-Se80Te10M10 (M = Cd, In, Sb) alloys using correlated barrier hopping model. Curr. Appl. Phys. 12, 405–412 (2012)
D.A. Molodov, P.J. Konijnenberg, Grain boundary and grain structure control through application of a high magnetic field. Scr. Mater. 54, 977–981 (2006)
R. Zamiri, B. Singh, M.S. Belsleyc, J.M.F. Ferreiraa, Structural and dielectric properties of Al-doped ZnO nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 40, 6031–6036 (2014)
A. Verma, F. Khan, D. Kumar, M. Kar, B. Chakravarty, S. Singh, M. Husain, Sol–gel derived aluminum doped zinc oxide for application as anti-reflection coating interrestrial silicon solar cells. Thin Solid Films 518, 2649–2653 (2010)
R. Khan, S. Zulfiqar, M.U.Rahman Fashu, Effects of Ni codoping concentrations on dielectric and magnetic properties of (Co, Ni) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2016). doi:10.1007/s10854-016-4759-z
R. Khan, S. Zulfiqar, Y.Zaman Fashu, Magnetic and dielectric properties of (Co, Zn) co-doped SnO2 diluted magnetic semiconducting nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2016). doi:10.1007/s10854-016-4517-2
R. Khan, M.U. Zulfiqar, S.Fashu Rahman, Effect of annealing temperature on the dielectric and magnetic response of (Co, Zn) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. (2016). doi:10.1007/s10854-016-5844-z
R. Khan, Y. Zulfiqar, Zaman, Effect of annealing on structural, dielectric, transport and magnetic properties of (Zn, Co) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 27, 4003–4010 (2016). doi:10.1007/s10854-015-4254-y
R. Khan, F.M. Hu, Dielectric and magnetic properties of (Zn, Co) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Chin. Phys. B 24(12), 127803 (2015)
X.S. Fang, C.H. Ye, L.D. Zhang, T. Xie, Twinning mediated growth of Al2O3 nanobelts and their enhanced dielectric responses. Adv. Mater. 17, 1661–1665 (2005)
J.G. Han, Z.Y. Zhu, S. Ray, A.K. Azad, W.L. Zhang, M.X. He, S.H. Li, Y.P. Zhao, Optical and dielectric properties of ZnO tetrapod structures at terahertz frequencies. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 031107 (2006)
F. Gu, S.F. Wang, M.K. Lu, G.J. Zhou, D. Xu, D.R. Yuan, Photoluminescence properties of SnO2 nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel method. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 8119–8123 (2004)
J.C. Maxwell, Electric and Magnetism (Oxford University Press, NewYork, 1973), p. 828
I.H. Gul, A.Z. Abbasi, F. Amin, M.A. Rehman, A. Maqsood, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 311, 494 (2007)
C. León, A. Rivera, A. Várez, J. Sanz, J. Santamaria, K.L. Ngai, Origin of constant loss in ionic conductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 1279–1282 (2001)
P.S. Sz, Y.C. Lin, AC impedance studies of copper doped silica glass. Phys. Chem. Mater. 82, 295–300 (2003)
O. Pakma, N. Serin, T. Serin, S. Altindal, Influence of frequency and bias voltage on dielectric properties and electrical conductivity of Al/TiO2/p-Si/p + (MOS) structures. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 4, 215103 (2008)
C.H. Ho, C.D. Liu, C.H. Hsieh, K.H. Hsieh, S.N. Lee, High dielectric constant polyaniline/poly(acrylic acid) composites prepared by in situ polymerization. Synth. Met. 158, 630–637 (2008)
R. Cusc, E. Alarcn-Llad, J. Ibez, L. Arts, J. Jimnez, B. Wang, M.J. Callahan, Native point defects in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B. 75, 165202 (2009)
C.J. Cong, L. Liao, Q.Y. Liu, J.C. Li, K.L. Zhang, Effects of temperature on the ferromagnetism of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles and Mn-related Raman vibration. Nanotechnology 17, 1520–1526 (2006)
L.W. Yang, X.L. Wu, G.S. Huang, T. Qiu, Y.M. Yang, In situ synthesis of Mn-doped ZnO multi leg nanostructures and Mn-related Raman vibration. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 014308 (2005)
R.B.H. Tahar, N.B.H. Tahar, Mechanism of carrier transport in aluminum-doped zinc oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 4498–4501 (2002)
R. Elilarassi, G. Chandrasekaran, Synthesis and characterization of ball milled Fe-doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductor. Optoelectron. Lett. 8, 109–112 (2012)
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the Departments of Physics and Material Science Zhejiang University for materials provision and characterization of samples. Finally, special thanks to the Chinese Government Scholarship for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, R., Fashu, S. & Zia-Ur-Rehman Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of (Al, Ni) co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 4333–4339 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6058-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6058-0