Abstract
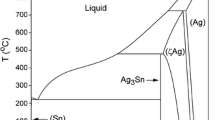
The creep mechanisms of eutectic Sn–Bi alloy were evaluated with indentation constant strain rate (CSR) method at elevated temperatures. The activation energy (Q) and creep stress exponent (n) of eutectic Sn–Bi alloy and other alloy compositions were measured in the temperature range from 25 to 100 °C. Prior to this, the indentation CSR testing protocol for evaluation of Q and n was validated through evaluating the pure Sn (grain size >100 µm) at various temperatures. The creep mechanism of large grain-sized Sn was found to be dislocation climb controlled by core diffusion in bulk. Dislocation climb though core diffusion and power-law breakdown were suggested to be the deformation mechanism for pure Bi and Sn–3%Bi alloy, respectively. For the two-phased eutectic Sn–Bi alloy, the creep mechanism was found to be strain rate and temperature dependent. Individual constituent phases were found to take turns to dominate the creep rate at different strain rates.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.H. Raeder, D. Mitlin, R.W. Messler Jr., Modelling the creep rates of eutectic Bi–Sn solder using the data from its constitutive phases. J. Mater. Sci. 33, 4503–4508 (1998)
C.H. Raeder, G.D. Schmeelk, D. Mitlin, T. Barbieri, W. Yang, L.F. Felton, R.W. Messler, D.B. Knorr, D. Lee, Isothermal Creep of Eutectic SnBi and SnAg Solder and Solder Joints, in Sixteenth IEEE/CPMT International Electronics Manufacturing Technology Symposium (1994), pp. 1–6
M.D. Mathew, H. Yang, S. Movva, K.L. Murty, Creep deformation characteristics of tin and tin-based electronic solder alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36A, 99–105 (2005)
J.L.F. Goldstein, J.W. Morris, Microstructural development of eutectic Bi–Sn and eutectic In–Sn during high-temperature deformation. J. Electron. Mater. 23, 477–486 (1994)
Z. Mei, J.W. Morris Jr., Characterization of eutectic Sn–Bi solder joints. J. Electron. Mater. 21, 599–607 (1992)
D. Mitlin, C.H. Raeder, R.W. Messler Jr., Solid solution creep behavior of Sn–xBi alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30A, 115–122 (1999)
X.Q. Shi, Z.P. Wang, Q.J. Yang, H.L.J. Pang, Creep behavior and deformation mechanism map of Sn–Pb eutectic solder alloy. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME 125, 81–88 (2003)
M.M. El-Bahay, M.E. El Mossalamy, M. Mahdy, A.A. Bahgat, Some mechanical properties of Sn–3.5 Ag eutectic alloy at different temperatures. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 15, 519–526 (2004)
V.M.F. Marques, B. Wunderle, C. Johnston, P.S. Grant, Nanomechanical characterization of Sn–Ag–Cu/Cu joints—part 2: nanoindentation creep and its relationship with uniaxial creep as a function of temperature. Acta Mater. 61, 2471–2480 (2013)
H.L. Reynolds, Creep of two-phase microstructure for microelectronic applications (Department of Materials Science and Mineral Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, 1998), p. 98
J.W. Morris Jr., J.L.F. Goldstein, Z. Mei, Microstructure and mechanical-properties of Sn–In and Sn–Bi solders. JOM 45, 25–27 (1993)
T. Reinikainen, J. Kivilahti, Deformation behavior of dilute SnBi(O.5 to 6 At. Pct) solid solutions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30, 123–132 (1999)
L. Shen, W.C.D. Cheong, Y.L. Foo, Z. Cheng, Nanoindentation creep of tin and aluminium: a comparative study between constant load and constant strain rate methods. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 532, 505–510 (2012)
L. Shen, P. Lu, S. Wang, Z. Chen, Creep behaviour of eutectic SnBi alloy and its constituent phases using nanoindentation technique. J. Alloys Compd. 574, 98–103 (2013)
L. Shen, P. Septiwerdani, Z. Chen, Elastic modulus, hardness and creep performance of SnBi alloys using nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 558, 253–258 (2012)
L. Shen, Z.Y. Tan, Z. Chen, Nanoindentation study on the creep resistance of SnBi solder alloy with reactive nano-metallic fillers. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 561, 232–238 (2013)
J. Dean, A. Bradbury, G. Aldrich-Smith, T.W. Clyne, A procedure for extracting primary and secondary creep parameters from nanoindentation data. Mech. Mater. 65, 124–134 (2013)
B.N. Lucas, W.C. Oliver, Indentation power-law creep of high-purity indium. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30, 601–610 (1999)
M.J. Mayo, R.W. Siegel, A. Narayanasamy, W.D. Nix, Mechanical-properties of nanophase TiO2 as determined by nanoindentation. J. Mater. Res. 5, 1073–1082 (1990)
S.N.G. Chu, J.C.M. Li, Impression creep of beta-tin single-crystals. Mater. Sci. Eng. 39, 1–10 (1979)
R.E. Frenkel, O.D. Sherby, J.E. Dorn, Activation energies for creep of cadmium, indium, and tin. Acta Metall. 3, 470–472 (1955)
S. Otake, Y. Ishii, N. Matsuno, Migration energy of vacancies in bismuth. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 20, 1037–1040 (1981)
H.J. Frost, M.F. Ashby, Deformation-mechanism maps: the plasticity and creep of metals and ceramics (Pergamon Press, New York, 1982)
H.J. Frost, M.F. Ashby, Web source from Thayer School of Engineering at Dartmouth. Deformation-mechanism maps: the plasticity and creep of metals and ceramics. http://engineering.dartmouth.edu/defmech/
J.M. Wheeler, D.E.J. Armstrong, W. Heinz, R. Schwaiger, High temperature nanoindentation: the state of the art and future challenges. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 19, 354–366 (2015)
V. Raman, R. Berriche, An investigation of the creep processes in tin and aluminum using a depth-sensing indentation technique. J. Mater. Res. 7, 627–638 (1992)
M.J. Mayo, W.D. Nix, A micro-indentation study of superplasticity in Pb, Sn, and Sn–38 wt%-Pb. Acta Metall. 36, 2183–2192 (1988)
E.A. Brandes, G.B. Brook, Smithells Metals Reference Book (Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, London, 1988)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, L., Wu, Y., Wang, S. et al. Creep behavior of Sn–Bi solder alloys at elevated temperatures studied by nanoindentation. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 4114–4124 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6031-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6031-y