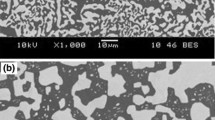
Abstract
This study examines the changes in strain rate dependence and the deformation behavior of near-eutectic Sn-Bi alloys as a function of Sb concentration using nanoindentation. Alloying near-eutectic Sn-Bi solder with Sb has been shown to increase the strain to failure under tensile and shear conditions in solder ball geometries, with Sb additions remaining in solid solution up to 0.5 wt.% Sb. In this study, the resulting hardness of the three Sb-containing Sn-Bi alloys (Bi-42Sn eutectic, Bi-42Sn-0.5Sb, Bi-42Sn-1.0Sb) exhibits little solid solution hardening at room temperature, and the alloys all exhibited similar strain rate sensitivity behavior, independent of composition for this microstructure. Using nanoindentation and post-indentation microscopy to analyze the deformation behavior of these alloys, the out-of-plane deformation and slip behavior does change with composition. Solute Sb increases the strain hardening behavior at low strains while decreasing planar slip and out-of-plane deformation. The observed changes in deformation modes in this nanoindentation study with the addition of Sb as a solid solution alloy (less slip planarity, more uniform deformation, and more strain hardening) could play a role in previously observed changes in tensile failure modes without the formation of SbSn intermetallic compounds.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Mccormack, H.S. Chen, G.W. Kammlott, and S. Jin, Significantly Improved Mechanical Properties of Bi-Sn Solder Alloys by Ag-Doping. J. Electron. Mater. 26, 954–958 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11664-997-0281-7.
X. Hu, X. Yu, Y. Li, Q. Huang, Y. Liu, and Z. Min, Effect of strain rate on interfacial fracture behaviors of Sn-58Bi/Cu solder joints. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25, 57–64 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-013-1548-9.
S. Liu, S. Mcdonald, K. Sweatman, and K. Nogita, The Effects of Precipitation Strengthening and Solid Solution Strengthening on Strain Rate Sensitivity of Lead-Free Solders: Review. Microelectron. Reliabil. 84, 170–180 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2018.03.038.
Z. Zhou, X. Ma, M.B. Zhou, C. Yin, X.P. Zhang, Effect of isothermal aging on mechanical properties and strain rate sensitivity of the eutectic Sn-58Bi solder alloy, in 18th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology, ICEPT 2017, pp 1586–1591. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc. (2017)
S. Sakuyama, T. Akamatsu, K. Uenishi, and T. Sato, Effects of a Third Element on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Eutectic Sn-Bi Solder. Trans. Jpn. Inst. Electron. Packag. 2, 98–103 (2009). https://doi.org/10.5104/jiepeng.2.98.
Z. Wang, Q.K. Zhang, Y.X. Chen, and Z.L. Song, Influences of Ag and In Alloying on Sn-Bi Eutectic Solder and SnBi/Cu Solder Joints. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 30, 18524–18538 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02206-y.
F. Yang, L. Zhang, Z.-Q. Liu, S.-J. Zhong, J. Ma, and L. Bao, Properties and Microstructures of Sn-Bi-X Lead-Free Solders. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9265195.
J.G. Li, X. Ma, M.B. Zhou, X. Ning, X.P. Zhang, Effects of Sb addition on the microstructure and mechanical performance of Sn58Bi based alloys and the solder joints, in Proceedings - 2018 19th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology, ICEPT 2018. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., pp. 457–461 (2018)
C. Zhang, S.D. Liu, G.T. Qian, J. Zhou, and F. Xue, Effect of Sb Content on Properties of Sn-Bi Solders. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China (Eng. Ed.) 24, 184–191 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63046-6.
K.A. Nibur, and D.F. Bahr, Identifying Slip Systems Around Indentations in FCC Metals. Scr. Mater. 49, 1055–1060 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCRIPTAMAT.2003.08.021.
Y. Gaillard, C. Tromas, and J. Woirgard, Study of the Dislocation Structure Involved in a Nanoindentation Test by Atomic Force Microscopy and Controlled Chemical Etching. Acta Mater. 51, 1059–1065 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(02)00509-8.
Z. Li, J. Zhang, Y. Zhai, J. Zhang, X. Wang, Z. Zhang, S. Mao, and X. Han, Dynamic Mechanisms of Strengthening and Softening of Coherent twin Boundary via Dislocation Pile-up and Cross-Slip. Mater. Res. Lett. 10, 539–546 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2022.2065892.
J. Varillas, J. Očenášek, J. Torner, and J. Alcalá, Unraveling Deformation Mechanisms Around FCC and BCC Nanocontacts Through Slip Trace and Pileup Topography Analyses. Acta Mater. 125, 431–441 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACTAMAT.2016.11.067.
J.L. Bucaille, S. Stauss, E. Felder, and J. Michler, Determination of Plastic Properties of Metals by Instrumented Indentation Using Different Sharp Indenters. Acta Mater. 51, 1663–1678 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(02)00568-2.
H.N. Fowler, S.X. Tay, J. Blendell, and C.A. Handwerker, Microalloying Effects of Sb and Ag on the Microstructural Evolution of Eutectic Sn–Bi Alloys. MRS Adv. 2023, 1–5 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/S43580-022-00472-3.
Y. Fan, Y. Wu, T.F. Dale, S.A.P. Lakshminarayana, C.V. Greene, N.U. Badwe, R.F. Aspandiar, J.E. Blendell, G. Subbarayan, and C.A. Handwerker, Influence of Pad Surface Finish on the Microstructure Evolution and Intermetallic Compound Growth in Homogeneous Sn-Bi and Sn-Bi-Ag Solder Interconnects. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 6615–6628 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11664-021-09256-1.
B.N. Lucas, and W.C. Oliver, Indentation Power-Law Creep of High-Purity Indium. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 30, 601–610 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11661-999-0051-7.
L. Shen, P. Septiwerdani, and Z. Chen, Elastic Modulus, Hardness and Creep Performance of SnBi Alloys Using Nanoindentation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 558, 253–258 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.07.120.
L. Shen, P. Lu, S. Wang, and Z. Chen, Creep Behaviour of Eutectic SnBi Alloy and Its Constituent Phases Using Nanoindentation Technique. J. Alloys Compd. 574, 98–103 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.04.057.
F. Wang, A. Luktuke, and N. Chawla, Microstructural Coarsening and Mechanical Properties of Eutectic Sn-58Bi Solder Joint During Aging. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 6607–6614 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11664-021-09255-2.
W.C. Oliver, and G.M. Pharr, An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus Using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation Experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564–1583 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.1992.1564.
M.J. Esfandyarpour, and R. Mahmudi, Microstructure and Tensile Behavior of Sn-5Sb Lead-Free Solder Alloy Containing Bi and Cu. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 530, 402–410 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEA.2011.09.103.
R. Mahmudi, and S. Mahin-Shirazi, Effect of Sb Addition on the Tensile Deformation Behavior of Lead-Free Sn-3.5Ag Solder Alloy. Mater. Des. 32, 5027–5032 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATDES.2011.05.052.
W.D. Nix, and H. Gao, Indentation Size Effects in Crystalline Materials: A Law for Strain Gradient Plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 46, 411–425 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5096(97)00086-0.
A.A. Elmustafa, and D.S. Stone, Nanoindentation and the Indentation Size Effect: Kinetics of Deformation and Strain Gradient Plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 51, 357–381 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5096(02)00033-9.
D.F. Bahr, and W.W. Gerberich, Plastic Zone and Pileup Around Large Indentations. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 27, 3793–3800 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02595628.
R.M. Rahimi, and D.F. Bahr, Individual Phase Deformation and Flow Correlation to Macroscopic Constitutive Properties of DP1180 Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 756, 328–335 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEA.2019.04.063.
C. Tromas, J.C. Girard, and J. Woirgard, Study by Atomic Force Microscopy of Elementary Deformation Mechanisms Involved in Low Load Indentations in MgO Crystals. Philos. Mag. A 80, 2325–2335 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/01418610008216475.
A. Zamiri, T.R. Bieler, and F. Pourboghrat, Anisotropic Crystal Plasticity Finite Element Modeling of the Effect of Crystal Orientation and Solder Joint Geometry on Deformation After Temperature Change. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 231–240 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11664-008-0595-0.
P. Darbandi, T.R. Bieler, F. Pourboghrat, and T.K. Lee, Crystal Plasticity Finite-Element Analysis of Deformation Behavior in Multiple-Grained Lead-Free Solder Joints. J. Electron. Mater. 42, 201–214 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11664-012-2339-4.
P. Darbandi, T.K. Lee, T.R. Bieler, and F. Pourboghrat, Crystal Plasticity Finite Element Study of Deformation Behavior in Commonly Observed Microstructures in Lead Free Solder Joints. Comput Mater Sci 85, 236–243 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COMMATSCI.2014.01.002.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Semiconductor Research Corporation (SRC). We acknowledge additional support from the US Department of Defense [Contract No. W52P1J-22-9-3009]. The views and conclusions contained in this document are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing the official policies, either expressed or implied, of the US Department of Defense or the US Government. The US Government is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for Government purposes, notwithstanding any copyright notation herein.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fowler, H.N., Loaiza, A., Bahr, D.F. et al. Sb Additions in Near-Eutectic Sn-Bi Solder Decrease Planar Slip. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 7365–7370 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10666-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-023-10666-6