Abstract
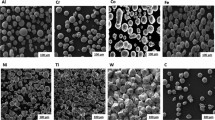
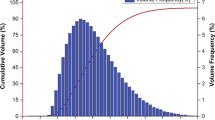
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are a new class of advanced metallic alloys that have received significant attention in recent years due to their stable microstructures and promising properties. However, exploration of the functional properties of these alloys as thermal-sprayed coatings has not been undertaken so far. In the present study, novel equiatomic AlCoCrFeMo, AlCoCrFeMoW, and AlCoCrFeMoV HEA coatings were fabricated using flame spraying to understand the impact of tungsten (W) and vanadium (V) additions in AlCoCrFeMo HEA coatings on microstructure evolutions, phase formations, microhardness, and electrical resistivity. The microstructure revealed the occurrence of mixed oxides and BCC phases, with an apparent porosity range between 2 and 4%. Despite the lower fraction of oxide phases, higher hardness was achieved for AlCoCrFeMoV HEA coatings (714 ± 64 HV), followed by AlCoCrFeMoW (609 ± 61 HV) and AlCoCrFeMo (592 ± 58 HV) HEA coatings. The higher hardness might be attributed to combined interactions of hard oxide phases, solid solution strengthening, and BCC phases. The electrical resistivity values showed a noticeable difference between HEA coatings and control Ni–20Cr coatings, whereby higher electrical resistivity values were achieved for AlCoCrFeMo HEA coatings due to topological lattice distortion and higher oxide fractions. Joule heating testing showed a higher rate of increase in surface temperature for all the HEA coatings than that of Ni–20Cr flame-sprayed coatings for a given electrical power input. The results suggest that the improved electrical properties and heating performance capabilities of flame-sprayed HEA coatings make them an excellent choice for use in high load resistive heating applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeh JW, Chen SK, Lin SJ et al (2004) Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv Eng Mater 6:299–303. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200300567
Cantor B, Chang ITH, Knight P, Vincent AJB (2004) Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 375–377:213–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2003.10.257
Murty BS, Yeh JW, Ranganathan S, Bhattacharjee PP (2019) High-entropy alloys. Elsevier
Chou TH, Huang JC, Yang CH et al (2020) Consideration of kinetics on intermetallics formation in solid-solution high entropy alloys. Acta Mater 195:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.015
Senkov ON, Miracle DB (2016) A new thermodynamic parameter to predict formation of solid solution or intermetallic phases in high entropy alloys. J Alloys Compd 658:603–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.10.279
Gludovatz B, Hohenwarter A, Catoor D et al (2014) A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 345:1153–1158. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254581
Chuang MH, Tsai MH, Wang WR et al (2011) Microstructure and wear behavior of AlxCo 1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater 59:6308–6317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2011.06.041
Cheng KH, Lai CH, Lin SJ, Yeh JW (2011) Structural and mechanical properties of multi-element (AlCrMoTaTiZr)N x coatings by reactive magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 519:3185–3190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2010.11.034
Fu Z, Yang B, Gan K et al (2021) Improving the hydrogen embrittlement resistance of a selective laser melted high-entropy alloy via modifying the cellular structures. Corros Sci 190:109695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2021.109695
Chen YY, Duval T, Hung UD et al (2005) Microstructure and electrochemical properties of high entropy alloys-a comparison with type-304 stainless steel. Corros Sci 47:2257–2279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2004.11.008
Chen YY, Hong UT, Shih HC et al (2005) Electrochemical kinetics of the high entropy alloys in aqueous environments—A comparison with type 304 stainless steel. Corros Sci 47:2679–2699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2004.09.026
Quiambao KF, McDonnell SJ, Schreiber DK et al (2019) Passivation of a corrosion resistant high entropy alloy in non-oxidizing sulfate solutions. Acta Mater 164:362–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2018.10.026
Jeng YR, Tsai PC, Chiang SH (2013) Effects of grain size and orientation on mechanical and tribological characterizations of nanocrystalline nickel films. Wear 303:262–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2013.02.019
Anupam A, Kottada RS, Kashyap S et al (2020) Understanding the microstructural evolution of high entropy alloy coatings manufactured by atmospheric plasma spray processing. Appl Surf Sci 505:144117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144117
Patel P, Alidokht SA, Sharifi N et al (2022) Microstructural and tribological behavior of thermal spray CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy coatings. J Therm Spray Technol 31:1285–1301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-022-01350-y
Nair RB, Perumal G, McDonald A (2022) Effect of microstructure on wear and corrosion performance of thermally-sprayed AlCoCrFeMo high entropy alloy coatings. Adv Eng Mater 2101713:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.202101713
Li W, Liu P, Liaw PK (2018) Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloy films and coatings: a review. Mater Res Lett 6:199–229. https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2018.1434248
Wang C, Li X, Li Z et al (2020) The resistivity–temperature behavior of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy films. Thin Solid Films. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2020.137895
Shafeie S, Guo S, Erhart P et al (2019) Balancing scattering channels: a panoscopic approach toward zero temperature coefficient of resistance using high-entropy alloys. Adv Mater 31:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201805392
Huang M, Jiang J, Wang Y et al (2022) Effects of milling process parameters and PCAs on the synthesis of Al0.8Co0.5Cr1.5CuFeNi high entropy alloy powder by mechanical alloying. Mater Des 217:110637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2022.110637
ASTM E1920–03, 2014. Standard guide for metallographic preparation of thermal sprayed coatings.
ASTM E384–17, Standard test method for microindentation hardness of materials, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA 2017.
Rezvani Rad M, Mohammadian Bajgiran M, Moreau C, McDonald A (2020) Fabrication of thermally sprayed coating systems for mitigation of ice accumulation in carbon steel pipes and prevention of pipe bursting. Surf Coatings Technol 397:126013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126013
Meghwal A, Anupam A, Luzin V et al (2021) Multiscale mechanical performance and corrosion behaviour of plasma sprayed AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings. J Alloys Compd 854:157140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157140
Meghwal A, Anupam A, Murty BS et al (2020) Thermal Spray High-Entropy Alloy Coatings: A Review. Springer, US
Bergant Z, Grum J (2011) Porosity evaluation of flame-sprayed and heat treated nickel-based coatings using image analysis. Image Anal Stereol 30:53–62. https://doi.org/10.5566/ias.v30.p53-62
Coatings AA, Tillmann W, Khalil O, Abdulgader M (2019) Porosity characterization and its effect on thermal properties of APS-sprayed alumina coatings. Coatings 9(10):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9100601
Liu WH, Lu ZP, He JY et al (2016) Ductile CoCrFeNiMox high entropy alloys strengthened by hard intermetallic phases. Acta Mater 116:332–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.06.063
Dong Y, Zhou K, Lu Y et al (2014) Effect of vanadium addition on the microstructure and properties of AlCoCrFeNi high entropy alloy. Mater Des 57:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.12.048
Yin B, Maresca F, Curtin WA (2020) Vanadium is an optimal element for strengthening in both fcc and bcc high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater 188:486–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.01.062
Prudenziati M, Gualtieri ML (2008) Electrical properties of thermally sprayed Ni- and Ni20Cr-based resistors. J Therm Spray Technol 17:385–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-008-9187-z
Dehaghani ST, McDonald A, Dolatabadi A (2019) An experimental study of the performance of flame-sprayed Ni-based metal matrix composite coatings as resistive heating elements. Proc Int Therm Spray Conf 527–534
Kim H, Nam S, Roh A et al (2019) Mechanical and electrical properties of NbMoTaW refractory high-entropy alloy thin films. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 80:286–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2019.02.005
Zhang Y, Zuo T, Cheng Y, Liaw PK (2013) High-entropy alloys with high saturation magnetization, electrical resistivity, and malleability. Sci Rep 3:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01455
Kretova MA, Konchakov RA, Kobelev NP, Khonik VA (2020) Point defects and their properties in the Fe20Ni20Cr20Co20Cu20 high-entropy alloy. JETP Lett 111:679–684. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364020120097
Yeh JW (2015) Physical metallurgy of high-entropy alloys. Jom 67:2254–2261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1583-5
Niu G, Saint-Girons G, Vilquin B (2013) Epitaxial systems combining oxides and semiconductors. Elsevier
Mooij JH (1973) Electrical conduction in concentrated disordered transition metal alloys. Phys Status Solidi 17:521–530. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.2210170217
Ciuchi S, Di Sante D, Dobrosavljević V, Fratini S (2018) The origin of Mooij correlations in disordered metals. Npj Quantum Mater. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41535-018-0119-y
Mueller R, Agyeman K, Tsuei CC (1980) Negative-temperature coefficients of electrical resistivity in amorphous La-based alloys. Phys Rev B 22:2665–2669. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.22.2665
Aug N (2016) The resistance and thermoelectric properties of the transition metals Author (s): N. F. Mott Source: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Published by: Royal Society Stable URL: http://www.jstor.org/stab. 156:368–382
Lopera-Valle A, McDonald A (2015) Application of flame-sprayed coatings as heating elements for polymer-based composite structures. J Therm Spray Technol 24:1289–1301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-015-0302-7
Tanimoto H, Hozumi R, Kawamura M (2022) Electrical resistivity and short-range order in rapid-quenched CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. J Alloys Compd 896:163059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.163059
Lopera-Valle A, McDonald A (2016) Flame-sprayed coatings as de-icing elements for fiber-reinforced polymer composite structures: modeling and experimentation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 97:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.01.079
Evans, M.J. and Rosenthal, J.S., (2004). Probability and statistics: The science of uncertainty. Macmillan.
Dehaghani ST, Dolatabadi A, McDonald A (2021) Thermally sprayed metal matrix composite coatings as heating systems. Appl Therm Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2021.117321
Bobzin K, Wietheger W, Knoch MA, Schacht A (2020) Heating behaviour of plasma sprayed TiOx/Cr2O3 coatings for injection moulding. Surf Coatings Technol 399:126199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126199
Prudenziati M (2008) Development and the implementation of high-temperature reliable heaters in plasma spray technology. J Therm Spray Technol 17:234–243
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada Discovery Grant Program (Award Number: RGPIN-2018-04298) and the Department of National Defence Innovation for Defence Excellence and Security program (W7714-228267). The authors are also thankful to Nathan Gerein, Guibin Ma, and Rebecca Feng of the Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences for their help with SEM and XRD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Megumi Kawasaki.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pal, S., Nair, R.B. & McDonald, A. Toward understanding the microstructure and electrical resistivity of thermal-sprayed high-entropy alloy coatings. J Mater Sci 57, 20928–20944 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07921-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07921-2