Abstract
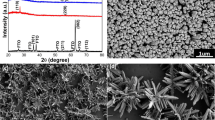
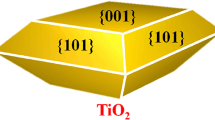
Single-crystalline TiO2 nanosheet array films with tunable percentage of exposed {001} facets were synthesized on FTO by a simple hydrothermal method. The effects of the hydrochloric acid concentration on morphology, crystal structure, and optical property have been investigated by scanning electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, micro-Raman spectroscope system, and UV–Vis spectrophotometer. When the hydrochloric acid concentration increases from 4.8 to 5.2 mol/L, dense regular nanosheets tend to grow perpendicular to the substrate surface, and the percentage of exposed {001} facets is increasing from 76 to 84 %. Evolution of these nanosheet array films has accompanied by significant variations of photoelectronic and photocatalytic properties. The intensity of Raman peak E g at 144 cm−1 decreases, and the photocurrent increases when more proportion areas of {001} facets are exposed. The sample prepared at hydrochloric acid concentration of 4.8 mol/L shows the highest photocatalytic activity. This can be explained by the preferential carrier transport to different facets of the TiO2 crystal with tradeoff relation between the {101} and {001} facets, and a increasing of total catalytic sites.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kruth A, Peglow S, Quade A, Pohl M-M, Foest R, Brüser V, Weltmann KD (2014) Structural and photoelectrochemical properties of DC magnetron-sputtered TiO2 Layers on FTO. J Phys Chem C 118:25234–25244
Lee S, Lee K, Kim WD, Lee S, Shin DJ, Lee DC (2014) Thin amorphous TiO2 shell on CdSe nanocrystal quantum dots enhances photocatalysis of hydrogen evolution from water. J Phys Chem C 118:23627–23634
Qian W, Greaney PA, Fowler S, Chiu SK, Goforth AM, Jiao J (2014) Low-temperature nitrogen doping in ammonia solution for production of N-doped TiO2-hybridized graphene as a highly efficient photocatalyst for water treatment. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:1802–1810
Yan J, Wu G, Dai W, Guan N, Li L (2014) Synthetic design of gold nanoparticles on anatase TiO2 001 for enhanced visible light harvesting. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:1940–1946
Hou Z, Zhang Y, Deng K, Chen Y, Li X, Deng X, Cheng Z, Lian H, Li C, Lin J (2015) UV-emitting upconversion-based TiO2 photosensitizing nanoplatform: near-infrared light mediated in vivo photodynamic therapy via mitochondria-involved apoptosis pathway. ACS Nano 9:2584–2599
Sudhagar P, Devadoss A, Nakata K, Terashima C, Fujishima A (2015) Enhanced photoelectrocatalytic water splitting at hierarchical Gd3+: TiO2 nanostructures through amplifying light reception and surface states passivation. J Electrochem Soc 162:H108–H114
Yang HG, Liu G, Qiao SZ, Sun CH, Jin YG, Smith SC, Zou J, Cheng HM, Lu GQ (2009) Solvothermal synthesis and photoreactivity of anatase TiO2 nanosheets with dominant 001 facets. J Am Chem Soc 131:4078–4083
Zheng Z, Huang B, Qin X, Zhang X, Dai Y, Jiang M, Wang P, Whangbo MH (2009) Highly efficient photocatalyst: TiO2 microspheres produced from TiO2 nanosheets with a high percentage of reactive {001} facets. Chem Eur J 15:12576–12579
Lazzeri M, Vittadini A, Selloni A (2001) Structure and energetics of stoichiometric TiO2 anatase surfaces. Phys Rev B 63:155409
Sugimoto T, Zhou X, Muramatsu A (2003) Synthesis of uniform anatase TiO2 nanoparticles by gel-sol method 4. Shape control. J Colloid Interface Sci 259:53–61
Sugimoto T, Zhou X, Muramatsu A (2002) Synthesis of uniform anatase TiO2 nanoparticles by gel-sol method. 1. Solution chemistry of Ti(OH)(4-n) + (n) complexes. J Colloid Interface Sci 252:339–346
Sugimoto T, Zhou X (2002) Synthesis of uniform anatase TiO2 nanoparticles by the gel-sol method 2. Adsorption of OH- ions to Ti(OH)4 gel and TiO2 particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 252:347–353
Yang HG, Sun CH, Qiao SZ, Zou J, Liu G, Smith SC, Cheng HM, Lu GQ (2008) Anatase TiO2 single crystals with a large percentage of reactive facets. Nature 453:638–641
Sun T, Wang Y, Al-Mamun M, Zhang H, Liu P, Zhao H (2015) Photoelectrochemical determination of intrinsic kinetics of photoelectrocatalysis processes at 001 faceted anatase TiO2 photoanode. RSC Adv 5:12860–12865
Zhang J, Qian L, Fu W, Xi J, Ji Z (2014) Alkaline-earth metal Ca and N codoped TiO2 with exposed 001 facets for enhancing visible light photocatalytic activity. J Am Ceram Soc 97:2615–2622
Van TK, Nguyen CK, Kang YS (2013) Axis-oriented, continuous anatase titania films with exposed reactive 100 facets. Chem Eur J 19:9376–9380
Laskova B, Zukalova M, Kavan L et al (2012) Voltage enhancement in dye-sensitized solar cell using (001)-oriented anatase TiO2 nanosheets. J Solid State Electrochem 16:2993–3001
Tan W, Yin X, Zhou X, Zhang J, Xiao X, Lin Y (2009) Electrophoretic deposition of nanocrystalline TiO2 films on Ti substrates for use in flexible dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim Acta 54:4467–4472
Yu J, Fan J, Lv K (2010) Anatase TiO2 nanosheets with exposed (001) facets: improved photoelectric conversion efficiency in dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale 2:2144–2149
Wang X, Liu G, Wang L, Pan J, Lu GQ, Cheng HM (2011) TiO2 films with oriented anatase 001 facets and their photoelectrochemical behavior as CdS nanoparticle sensitized photoanodes. J Mater Chem 21:869–873
Liu B, Aydil ES (2011) Anatase TiO2 films with reactive 001 facets on transparent conductive substrate. Chem Commun 47:9507–9509
Wang B, Leung MKH, Lu XY, Chen SY (2013) Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of boron and fluorine codoped TiO2 nanosheets with reactive facets. Appl Energy 112:1190–1197
Wang B, Lu XY, Lawrence KY, Xuan J, Leung MK, Guo H (2014) Facile synthesis of TiO2 hollow spheres composed of high percentage of reactive facets for enhanced photocatalytic activity. CrystEngComm 16:10046–10055
Devi LG, Kottam N, Kumar SG (2009) Preparation and characterization of Mn-doped titanates with a bicrystalline framework: correlation of the crystallite size with the synergistic effect on the photocatalytic activity. J Phys Chem C 113:15593–15601
Kwon SJ, Im HB, Nam JE, Kang JK, Hwang TS, Yi KB (2014) Hydrothermal synthesis of rutile–anatase TiO2 nanobranched arrays for efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Appl Surf Sci 320:487–493
Antony RP, Mathews T, Dash S, Tyagi AK (2013) Kinetics and physicochemical process of photoinduced hydrophobic <-> superhydrophilic switching of pristine and N-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays. J Phys Chem C 117:6851–6860
Xu Y, Zhang M, Zhang M, Lv J, Jiang X, He G, Song X, Sun Z (2014) Controllable hydrothermal synthesis, optical and photocatalytic properties of TiO2 nanostructures. Appl Surf Sci 315:299–306
Zheng Z, Xie W, Lim ZS, You L, Wang J (2014) CdS sensitized 3D hierarchical TiO2/ZnO heterostructure for efficient solar energy conversion. Sci Rep 4:5721
Tian F, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Pan C (2012) Raman spectroscopy: a new approach to measure the percentage of anatase TiO2 exposed (001) facets. J Phys Chem C 116:7515–7519
Roy N, Sohn Y, Pradhan D (2013) Synergy of low-energy 101 and high-energy 001 TiO2 crystal facets for enhanced photocatalysis. ACS Nano 7:2532–2540
Diebold U (2003) The surface science of titanium dioxide. Surf Sci Rep 48:53–229
Xu F, Dai M, Lu Y, Sun L (2010) Hierarchical ZnO nanowire–nanosheet architectures for high power conversion efficiency in dye-sensitized solar cells. J Phys Chem C 114:2776–2782
Riegel G, Bolton JR (1995) Photocatalytic efficiency variability in TiO2 particles. J Phys Chem 99:4215–4224
Liu G, Sun C, Yang HG, Smith SC, Wang L, Lu GQM, Cheng HM (2010) Nanosized anatase TiO2 single crystals for enhanced photocatalytic activity. Chem Commun 46:755–757
Pan J, Liu G, Lu GQ, Cheng HM (2011) On the true photoreactivity order of {001}, {010}, and {101} facets of anatase TiO2 crystals. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:2133–2137
Fang X, Bando Y, Liao M, Gautam UK, Zhi C, Dierre B, Liu B, Zhai T, Sekiguchi T, Koide Y, Golberg D (2009) Single-crystalline ZnS nanobelts as ultraviolet-light sensors. Adv Mater 21:2034–2039
Liu G, Hoivik N, Wang X, Lu S, Wang K, Jakobsen H (2013) Photoconductive, free-standing crystallized TiO2 nanotube membranes. Electrochim Acta 93:80–86
Zou J, Zhang Q, Huang K, Marzari N (2010) Ultraviolet photodetectors based on anodic TiO2 nanotube arrays. J Phys Chem C 114:10725–10729
Meng F, Song X, Sun Z (2009) Photocatalytic activity of TiO2 thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 83:1147–1151
Krýsa J, Waldner G, Měšt’ánková H, Jirkovský J, Grabner G (2006) Photocatalytic degradation of model organic pollutants on an immobilized particulate TiO2 layer: roles of adsorption processes and mechanistic complexity. Appl Catal B 64:290–301
Xie Y (2006) Photoelectrochemical application of nanotubular titania photoanode. Electrochim Acta 51:3399–3406
Liu S, Yu J, Jaroniec M (2010) Tunable photocatalytic selectivity of hollow TiO2 microspheres composed of anatase polyhedra with exposed 001 facets. J Am Chem Soc 132:11914–11916
Gordon TR, Cargnello M, Paik T, Mangolini F, Weber RT, Fornasiero P, Murray CB (2012) Nonaqueous synthesis of TiO2 nanocrystals using TiF4 to engineer morphology, oxygen vacancy concentration, and photocatalytic activity. J Am Chem Soc 134:6751–6761
Zhao X, Jin W, Cai J, Ye J, Li Z, Ma Y, Xie J, Qi L (2011) Shape-and size-controlled synthesis of uniform anatase TiO2 nanocuboids enclosed by active {100} and {001} facets. Adv Funct Mater 21:3554–3563
áToby Kelsey E (1997) Atomistic simulation of the surface structure of the TiO2 polymorphs rutileand anatase. J Mater Chem 7:563–568
Murakami N, Kurihara Y, Tsubota T, Ohno T (2009) Shape-controlled anatase titanium (IV) oxide particles prepared by hydrothermal treatment of peroxo titanic acid in the presence of polyvinyl alcohol. J Phys Chem C 113:3062–3069
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51472003 and 51272001) and the National Key Basic Research Program (2013CB632705), The authors would like to thank Yonglong Zhuang and Zhongqing Lin of the Experimental Technology Center of Anhui University, for the electron microscope test and discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Zhang, Q., Wang, W. et al. Tuning the photoelectronic and photocatalytic properties of single-crystalline TiO2 nanosheet array films with dominant {001} facets by controlling the hydrochloric acid concentration. J Mater Sci 51, 950–957 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9424-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9424-z