Abstract
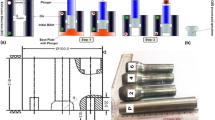
A commercial Al-7075 alloy was processed by the severe plastic deformation (SPD) procedures of equal-channel angular pressing (ECAP) and high-pressure torsion (HPT) and by a combination of these two techniques. The results show samples processed by a combination of ECAP and HPT have smaller grain sizes and higher saturation hardnesses than samples processed separately by ECAP or HPT. Microstructural observations reveal grain refinement after each SPD technique, and the minimum grain size was ~200 nm after processing by a combination of ECAP for eight passes and HPT for 20 turns. It is demonstrated that the saturation hardness is dependent upon the microstructure of the sample introduced in any processing step prior to the HPT processing.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langdon TG (2013) Twenty-five years of ultrafine-grained materials: achieving exceptional properties through grain refinement. Acta Mater 61:7035–7059
Valiev RZ, Estrin Y, Horita Z, Langdon TG, Zehetbauer MJ, Zhu YT (2006) Producing bulk ultrafine-grained materials by severe plastic deformation. JOM 58(4):33–39
Hall EO (1951) The deformation and ageing of mild steel: III discussion of results. Proc Phys Soc B 64:747–753
Petch NJ (1953) Cleavage strength of polycrystals. J Iron Steel Inst 174:25–28
Valiev RZ, Islamgaliev RK, Alexandrov IV (2000) Bulk nanostructured materials from severe plastic deformation. Prog Mater Sci 45:103–189
Valiev RZ, Zhilyaev AP, Langdon TG (2014) Bulk nanostructured materials: fundamentals and applications. Wiley, Hoboken
Valiev RZ, Langdon TG (2006) Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement. Prog Mater Sci 51:881–981
Zhilyaev AP, Langdon TG (2008) Using high-pressure torsion for metal processing: fundamentals and applications. Prog Mater Sci 53:893–979
Iwahashi Y, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (1998) The process of grain refinement in equal-channel angular pressing. Acta Mater 46:3317–3331
Komura S, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (1999) Influence of stacking fault energy on microstructural development in equal-channel angular pressing. J Mater Res 14:4044–4050
Zhao YH, Liao XZ, Jin Z, Valiev RZ, Zhu YT (2004) Microstructures and mechanical properties of ultrafine grained 7075 Al alloy processed by ECAP and their evolutions during annealing. Acta Mater 52:4589–4599
Kawasaki M, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2009) Microstructural evolution in high purity aluminum processed by ECAP. Mater Sci Eng A524:143–150
Xu J, Shirooyeh M, Wongsa-Ngam J, Shan D, Guo B, Langdon TG (2013) Hardness homogeneity and micro-tensile behavior in a magnesium AZ31 alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Mater Sci Eng A586:108–114
Xu C, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2008) The evolution of homogeneity in an aluminum alloy processed using high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater 56:5168–5176
Duan ZC, Liao XZ, Kawasaki M, Figueiredo RB, Langdon TG (2010) Influence of high-pressure torsion on microstructural evolution in an Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloy. J Mater Sci 45:4621–4630. doi:10.1007/s10853-010-4400-0
Wongsa-Ngam J, Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2012) Achieving homogeneity in a Cu-Zr alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J Mater Sci 47:7782–7788. doi:10.1007/s10853-012-6587-8
Torbati-Sarraf SA, Langdon TG (2014) Properties of a ZK60 magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J Alloys Compd 613:357–363
Zhilyaev AP, Kim BK, Nurislamova GV, Baró MD, Szpunar JA, Langdon TG (2002) Orientation imaging microscopy of ultrafine-grained nickel. Scr Mater 46:575–580
Zhilyaev AP, Nurislamova GV, Kim BK, Baró MD, Szpunar JA, Langdon TG (2003) Experimental parameters influencing grain refinement and microstructural evolution during high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater 51:753–765
Wongsa-Ngam J, Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2013) A comparison of microstructures and mechanical properties in a Cu–Zr alloy processed using different SPD techniques. J Mater Sci 48:4653–4660. doi:10.1007/s10853-012-7072-0
Zhilyaev AP, Gubicza J, Nurislamova G, Revesz A, Surinach S, Baro MD, Ungar T (2003) Microstructural characterization of ultrafine-grained nickel. Phys Status Solidi A198:263–271
Sato YS, Kurihara Y, Park SHC, Kokawa H, Tsuji N (2004) Friction stir welding of ultrafine grained Al alloy 1100 produced by accumulative roll-bonding. Scr Mater 50:57–60
Lugo N, Llorca N, Cabrera JM, Horita Z (2008) Microstructures and mechanical properties of pure copper deformed severely by equal-channel angular pressing and high pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A477:366–371
Wongsa-Ngam J, Wen H, Langdon TG (2013) Microstructural evolution in a Cu–Zr alloy processed by a combination of ECAP and HPT. Mater Sci Eng A579:126–135
Zhilyaev AP, Baró MD, Langdon TG, McNelley TR (2004) An examination of microtexture and microstructure in ultrafine-grained nickel. Rev Adv Mater Sci 7:41–49
Stolyarov VV, Zhu YT, Lowe TC, Islamgaliev RK, Valiev RZ (1999) A two step SPD processing of ultrafine-grained titanium. Nanostruct Mater 11:947–954
Xu C, Furukawa M, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2005) The evolution of homogeneity and grain refinement during equal-channel angular pressing: a model for grain refinement in ECAP. Mater Sci Eng A398:66–76
Xu C, Xia K, Langdon TG (2007) The role of back pressure in the processing of pure aluminum by equal-channel angular pressing. Acta Mater 55:2351–2360
Wongsa-Ngam J, Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2012) The development of hardness homogeneity in a Cu–Zr alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing. Mater Sci Eng A556:526–532
Prell M, Xu C, Langdon TG (2008) The evolution of homogeneity on longitudinal sections during processing by ECAP. Mater Sci Eng A480:449–455
Veveçka A, Cabibbo M, Langdon TG (2013) A characterization of microstructure and microhardness on longitudinal planes of an Al-Mg-Si alloy processed by ECAP. Mater Charact 84:126–133
Xu C, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2007) The evolution of homogeneity in processing by high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater 55:203–212
Kawasaki M, Figueiredo RB, Langdon TG (2011) An investigation of hardness homogeneity throughout disks processed by high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater 59:308–316
Kawasaki M, Alhajeri SN, Xu C, Langdon TG (2011) The development of hardness homogeneity in pure aluminum and aluminum alloy disks processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A529:345–351
Valiev RZ, Ivanisenko YuV, Rauch EF, Baudelet B (1996) Structure and deformation behaviour of Armco iron subjected to severe plastic deformation. Acta Mater 44:4705–4712
Wetscher F, Vorhauer A, Stock R, Pippan R (2004) Structural refinement of low alloyed steels during severe plastic deformation. Mater Sci Eng A387–389:809–816
Estrin Y, Molotnikov A, Davies CHJ, Lapovok R (2008) Strain gradient modeling of high-pressure torsion. J Mech Phys Solids 56:1186–1202
Pippan R, Wetscher F, Hafok M, Vorhauer A, Sabirov I (2006) The limits of refinement by severe plastic deformation. Adv Eng Mater 8:1046–1056
Pippan R, Scheriau S, Taylor A, Hafok M, Hohenwarter A, Bachmaier A (2010) Saturation of fragmentation during severe plastic deformation. Ann Rev Mater Res 40:319–343
Horita Z, Fujinami T, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (2000) Equal-channel angular pressing of commercial aluminum alloys: grain refinement, thermal stability and tensile properties. Metall Mater Trans 31A:691–701
Figueiredo RB, Cetlin PR, Langdon TG (2007) The processing of difficult-to-work alloys by ECAP with an emphasis on magnesium alloys. Acta Mater 55:4769–4779
Kim WJ, Kim JK, Kim HK, Park JW, Jeong YH (2008) Effect of post-equal-channel-angular pressing aging on the modified 7075 alloy containing Sc. J Alloys Compd 450:222–228
Turba K, Málek P, Rauch EF, Robaut F, Cieslar M (2009) The optimization of ECAP conditions to achieve high strain-rate superplasticity in a Zr- and Sc-modified AA 7075 aluminum alloy. Int J Mater Res 100:851–857
Iwahashi Y, Wang J, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (1996) Principle of equal-channel angular pressing for the processing of ultrafine-grained materials. Scr Mater 35:143–146
Furukawa M, Iwahashi Y, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (1998) The shearing characteristics associated with equal-channel angular pressing. Mater Sci Eng A257:328–332
Oh-ishi K, Horita Z, Furukawa M, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (1998) Optimizing the rotation conditions for grain refinement in equal-channel angular pressing. Metall Mater Trans 29A:2011–2013
Xu C, Horita Z, Langdon TG (2010) Microstructural evolution in pure aluminum in early stages of processing by high-pressure torsion. Mater Trans 51:2–7
Figueiredo RB, Cetlin PR, Langdon TG (2011) Using finite element modeling to examine the flow processes in quasi-constrained high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A528:8198–8204
Figueiredo RB, Pereira PHR, Aguilar MTP, Cetlin PR, Langdon TG (2012) Using finite element modeling to examine the temperature distribution in quasi-constrained high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater 60:3190–3198
Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2008) The significance of strain reversals during processing by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A498:341–348
Berbon PB, Furukawa M, Horita Z, Nemoto M, Langdon TG (1999) Influence of pressing speed on microstructural development in equal-channel angular pressing. Metall Mater Trans A 30A:1989–1997
Sabbaghianrad S, Kawasaki M, Langdon TG (2012) Microstructural evolution and the mechanical properties of an aluminum alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. J Mater Sci 47:7789–7795. doi:10.1007/s10853-012-6524-x
Sabbaghianrad S, Langdon TG (2014) A critical evaluation of the processing of an aluminum 7075 alloy using a combination of ECAP and HPT. Mater Sci Eng A596:52–58
Sabbaghianrad S, Langdon TG (2014) An investigation of mechanical properties and microstructural evolution in an aluminum alloy processed by severe plastic deformation. Adv Mater Res 922:610–615
Mackenzie JK, Thomson MJ (1957) Some statistics associated with the random disorientation of cubes. Biometrika 44:205–210
Mackenzie JK (1958) Second paper on statistics associated with the random disorientation of cubes. Biometrika 45:229–240
Tóth LS, Beausir B, Gu CF, Estrin Y, Scheerbaum N, Davies CHJ (2010) Effect of grain refinement by severe plastic deformation on the next-neighbor misorientation distribution. Acta Mater 58:6706–6716
Toth LS, Gu C (2014) Ultrafine-grain metals by severe plastic deformation. Mater Charact 92:1–14
Vorhauer A, Pippan R (2004) On the homogeneity of deformation by high pressure torsion. Scr Mater 51:921–925
Edalati K, Fujioka T, Horita Z (2009) Evolution of mechanical properties and microstructures with equivalent strain in pure Fe processed by high pressure torsion. Mater Trans 50:44–50
Loucif A, Figueiredo RB, Baudin T, Brisset F, Langdon TG (2010) Microstructural evolution in an Al-6061 alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A527:4864–4869
Edalati K, Horita Z (2010) Universal plot for hardness variation in pure metals. Mater Trans 51:1051–1054
Kawasaki M (2014) Different models of hardness evolution in ultrafine-grained materials processed by high-pressure torsion. J Mater Sci 49:18–34. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7687-9
Shahmir H, Nili-Ahmadabadi M, Huang Y, Langdon TG (2014) Evolution of microstructure and hardness in NiTi shape memory alloys processed by high-pressure torsion. J Mater Sci 49:2998–3009. doi:10.1007/s10853-013-7985-2
Sharman K, Bazarnik P, Brynk T, Bulutsuz AG, Lewandowska M, Huang Y, Langdon TG (2015) Enhancement in mechanical properties of a β-titanium alloy by high-pressure torsion. J Mater Res Technol 4:79–83
Serre P, Figueiredo RB, Gao N, Langdon TG (2011) Influence of strain rate on the characteristics of a magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A528:3601–3608
Mohamed FA, Dheda SS (2012) On the minimum grain size attainable by high-pressure torsion. Mater Sci Eng A558:59–63
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation of the United States under Grant No. DMR-1160966 and in part by the European Research Council under ERC Grant Agreement No. 267464-SPDMETALS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabbaghianrad, S., Langdon, T.G. An evaluation of the saturation hardness in an ultrafine-grained aluminum 7075 alloy processed using different techniques. J Mater Sci 50, 4357–4365 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-8989-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-8989-x