Abstract
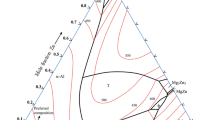
Zn–1.26 wt% Al alloy was directionally solidified upward with a constant growth rate (V = 16.6 μm/s) in a wide range of temperature gradients (1.94–5.15 K/mm) and with a constant temperature gradient (G = 5.15 K/mm) in a wide range of growth rates (8.3–500 μm/s) with a Bridgman-type directional solidification furnace. The microhardness (HV) and tensile strength (σ) of alloy were measured from directionally solidified samples. The dependency of the microhardness, tensile strength for directionally solidified Zn–1.26 wt% Al alloy on the solidification parameters (G, V) and microstructure parameters (λ1, λ2) were investigated and the relationships between them were experimentally obtained using regression analysis. According to present results, the microhardness and tensile strength of directionally solidified Zn–1.26 wt% Al alloy increase with increasing solidification processing parameters and decrease with the microstructure parameters. Variations of electrical resistivity (ρ) with the temperature in the range of 300–650 K were also measured using a standard dc four-point probe technique for cast samples. The enthalpy of fusion and specific heat for same alloy was also determined by means of differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) from heating trace during the transformation from solid to liquid.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yılmaz F, Elliott R (1989) J Mater Sci 24:2065. doi:10.1007/BF02385422
Grugel RN (1995) Metall Mater Trans A 26:496
Çadırlı E, Gündüz M (2000) J Mater Sci 35:3837. doi:10.1023/A:1004829413966
Mullis AM (2003) J Mater Sci 38:2517. doi:10.1023/A:1023977723475
Li L, Zhang Y, Esling C, Zhao Z, Zuo Y, Zhang H, Cui J (2009) J Mater Sci 44:1063. doi:10.1007/s10853-008-3158-0
Kumar A, Dutta P (2009) J Mater Sci 44:3952. doi:10.1007/s10853-009-3539-z
Pandey JP, Prasad BK (1998) Metall Mater Trans A 29:1245
Calayag TS (1986) Zinc–aluminium (ZA) cast alloys. Proc Int Symp CIM, Toronto
Zhu YH, Man HC, Dorantes-Rosales HJ, Lee WB (2003) J Mater Sci 38:2925. doi:10.1023/A:1024457109307
Abou El-khair MT, Daoud A, Ismail A (2004) Mater Lett 58:1754
Ravindranathan P, Patil KC (1987) J Mater Sci 22:3261. doi:10.1007/BF01161190
Zhu Y, Yan B, Huang W (1995) J Mater Sci Tech 11:109
Hung FY, Lui TS, Chen LH, You JG (2007) J Mater Sci 42:3865. doi:10.1007/s10853-006-0463-3
Krupinska B, Dobrzanski LA, Rdzawski ZM, Labisz K (2010) Arch Mater Sci Eng 43:13
Morgan SWK (1985) Zinc and its alloys and compounds. Wiley, New York
Flores OV, Kennedy C, Murr LE, Brown D, Pappu S, Nowak BM, McClure JC (1998) Scr Mater 38:703
Park HS, Kimura T, Murakami T, Nagano Y, Nakata K, Ushio M (2004) Mater Sci Eng A 371:160
Pürcek G (2005) J Mater Process Technol 169:242
Osorio WR, Freire CM, Garcia A (2005) J Mater Sci 40:4493. doi:10.1007/s10853-005-0852-z
Osorio WR, Freire CM, Garcia A (2005) J Alloys Compd 397:179
Santos GA, Neto CM, Osorio WR, Garcia A (2007) Mater Des 28:2425
Ding GL, Tewari SN (2002) J Cryst Growth 236:42
Hui J, Tiwari R, Wu X, Tewari SN, Trivedi R (2002) Metall Mater Trans A 33:3499
Feng J, Huang WD, Lin X, Pan QY, Li T, Zhou YH (1999) J Cryst Growth 197:393
Ganesan S, Chan CL, Poirier DR (1992) Mater Sci Eng A 151:97
Bhat MS, Poirier DR, Heinrich JC (1995) Metall Mater Trans B 26:1049
Smiths FM (1958) Bell Syst Tech J 37:711
Valdes LB (1954) Proc IRE 42:420
Arı M, Saatçi B, Gündüz M, Meydaneri F, Bozoklu M (2008) Mater Charact 59:624
Robinson P (2003) Practical specific heat determination by power compensation DSC. Perkin Elmer, Seer Gren
Massalski TB (ed) (1990) Binary alloy phase diagrams, vol 3. ASM International, Materials Park
Böyük U, Kaya H, Çadırlı E, Maraşlı N, Ülgen A (2010) J Alloys Compd 491:143
Kaya H, Çadırlı E, Böyük U, Maraşlı N (2008) App Surf Sci 255:307
Kaya H, Böyük U, Çadırlı E, Ocak Y, Akbulut S, Keşlioğlu K, Maraşlı N (2008) Met Mater Int 14:575
Vnuk F, Sahoo M, Van De Merwe R, Smith RW (1979) J Mater Sci 14:975. doi:10.1007/BF00550730
Vnuk F, Sahoo M, Baragor D, Smith RW (1980) J Mater Sci 15:2573. doi:10.1007/BF00550762
Telli AI, Kısakürek SE (1988) Mater Sci Technol 4:153
Rosenberger MR, Ares AE, Gatti IP, Schvezov CE (2010) Wear 268:1533
Kaya H, Gündüz M, Çadırlı E, Uzun O (2004) J Mater Sci 39:6571. doi:10.1023/B:JMSC.0000044897.98694.be
Kaya H, Çadırlı E, Gündüz M, Ülgen A (2003) J Mater Eng Perform 12:544
Khan S, Ourdjini A, Hamed QS, Najafabadi MAA, Elliott R (1993) J Mater Sci 28:5957. doi:10.1007/BF00365208
Osorio WR, Garcia A (2002) Mater Sci Eng A 325:103
Ares AE, Schvezov CE (2007) Metall Mater Trans A 38:1485
Feng J, Huang WD, Lin X, Pan QY, Li T, Zhou YH (1999) J Mater Sci Lett 18:29
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the Niğde University Scientific Research Project Unit under Contract No: FEB 2009/02. Authors would like to thank to the Niğde University Scientific Research Project Unit for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Çadırlı, E., Şahin, M. Investigation of mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties of a Zn–1.26 wt% Al alloy. J Mater Sci 46, 1414–1423 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4936-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4936-z