Abstract
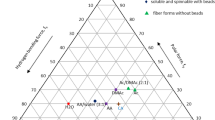
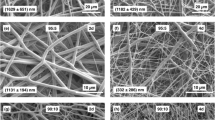
Non-woven structures of cellulose acetate (CA) fibres of 90 nm–5 μm in diameter (spinning parameters 90 nm beaded fibres: 12% CA in EtOH-DMSO 1/1, 22 kV, 30 cm, 0.5 mL/h; maximum 5 μm diameter fused fibres spun with 14% CA in Ac-BenzOH 2/1, 22 kV, 24 cm, 13 mL/h) were produced by electrospinning. On the basis of Hansen solubility theory, composition of binary solvent mixtures (ketones—acetone, methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), and alcohols—benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol and dimethylsulphoxide) was optimized with respect to control of fibre felt morphology. Fibre networks of high packing density were obtained with binary low-volatile alcohols/MEK solvent mixtures, a decreased spinning distance and an increased feed rate. Substituting MEK by acetone in the solvent mixture resulted in the formation of nanofibre felt with a low degree of fibre cross-links. Thus, solvent control is a key aspect for control of electrospun fibre felt structures, which may serve as scaffolds for tissue engineering.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Subbiah T, Bhat GS, Tock RW, Pararneswaran S, Ramkumar SS (2005) J Appl Polym Sci 96:557
Li D, Xia YN (2004) Adv Mater 16:1151
Huang Z-M, Zhang Y-Z, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2003) Compos Sci Technol 63:2223
Reneker DH, Yarin AL, Fong H, Koombhongse S (2000) J Appl Phys 87:4531
Shin YM, Hohman MM, Brenner MP, Rutledge GC (2001) Appl Phys Lett 78:1149
Yoshimoto H, Shin YM, Terai H, Vacanti JP (2003) Biomaterials 24:2077
Laurencin CT, Ambrosio AMA, Borden MD, Cooper JA (1999) Ann Rev Biomed Eng 1:19
Kumbar SG, Nukavarapu SP, James R, Nair LS, Laurencin CT (2008) Biomaterials 29:4100
Schiffman JD, Schauer CL (2008) Polym Rev 48:317
Liu HQ, Tang CY (2007) Polym J 39:65
Carrizales C, Pelfrey S, Rincon R, Eubanks TM, Kuang A, McClure MJ, Bowlin GL, Macossay J (2008) Polym Adv Technol 19:124
Inai R, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2005) Nanotechnology 16:208
Courtney T, Sacks MS, Stankus J, Guan J, Wagner WR (2006) Biomaterials 27:3631
Teo WE, Ramakrishna S (2006) Nanotechnology 17:R89
Greiner A, Wendorff JH (2007) Angew Chem Int Ed 46:5670
Ma ML, Hill RM, Lowery JL, Fridrikh SV, Rutledge GC (2005) Langmuir 21:5549
Liu H, Hsieh Y-L (2002) J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys 40:2119
Son WK, Youk JH, Lee TS, Park WH (2004) J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys 42:5
Tungprapa S, Puangparn T, Weerasombut M, Jangchud I, Fakum P, Semongkhol S, Meechaisue C, Supaphol P (2007) Cellulose 14:563
Jarusuwannapoom T, Hongrojjanawiwat W, Jitjaicham S, Wannatong L, Nithitanakul M, Pattamaprom C, Koombhongse P, Rangkupan R, Supaphol P (2005) Eur Pol J 41:409
Barton AFM (1985) Handbook of solubility parameters and other cohesion parameters. CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton, FL
Hoernschemeyer D (1974) J Appl Polym Sci 18:61
Shenoy SL, Bates WD, Frisch HL, Wnek GE (2005) Polymer 46:3372
Gupta P, Elkins C, Long TE, Wilkes GL (2005) Polymer 46:4799
Colby RH, Rubinstein M, Daoud M (1994) J Phys II 4:1299
Fong H, Chun I, Reneker DH (1999) Polymer 40:4585
McKee MG, Wilkes GL, Colby RH, Long TE (2004) Macromolecules 37:1760
McKee MG, Elkins CL, Long TE (2004) Polymer 45:8705
He JH, Wan YQ, Yu MY (2004) Int J Nonlin Sci Num 5:243
Baumgarten PK (1971) J Colloid Interf Sci 36:71
Yarin AL, Koombhongse S, Reneker DH (2001) J Appl Phys 89:3018
Reneker DH, Fong H (2005) Polymeric nanofibers. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC
Eda E, Shivkumar S (2007) J Appl Polym Sci 106:475
Choktaweesap N, Arayanarakul K, Aht-ong D, Meechaisue C, Supaphol P (2007) Polym J 39:622
Tan SH, Inai R, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2005) Polymer 46:6128
Lee SJ, Oh SH, Liu J, Soker S, Atala A, Yoo JJ (2008) Biomaterials 29:1422
Acknowledgements
Special thanks go to Dr. Jochen Kaschta from the chair of polymer materials for helpful discussions. Financial support from German Science Foundation (DFG) under contract number GR 961/26-1 is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haas, D., Heinrich, S. & Greil, P. Solvent control of cellulose acetate nanofibre felt structure produced by electrospinning. J Mater Sci 45, 1299–1306 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-4082-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-4082-7