Abstract
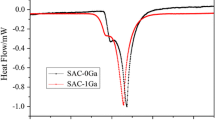
The effects of minor additives, that is, Co and Ni, on the microstructural and mechanical properties of Sn–3.0 mass%Ag–0.5 mass%Cu (SAC305) bulk solder were investigated. The addition of Co and/or Ni resulted in microstructural changes of the SAC305 solder, such as the formation of new intermetallic compounds (IMCs) and the refinement of grain size, as well as the suppression of undercooling. The single addition of Co in SAC305 solder resulted in the formation of CoSn2 IMCs and undercooling suppression, whereas the single addition of Ni accelerated the appearance of rod-shaped (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 IMCs inside the β-Sn dendrites during the solidification process. The dual addition of Co–Ni resulted in refined β-Sn grains and suppression of undercooling, as well as the formation of CoSn2 IMCs. In tensile tests, Co and/or Ni additives had little effect on the tensile strength of SAC305 solder, but obviously suppressed the elongation ratio and reduction of area. During tensile deformation in samples with existing thin plate-like CoSn2 IMCs, micro-cracks or cavities were easily initiated through the interface between CoSn2 and the solder matrix, which was responsible for the decrease of ductility.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson IE, Foley JC, Cook BA, Harringa JL, Terpstra RL, Unal O (2001) J Electron Mater 30:1050
Zeng K, Tu KN (2002) Mat Sci Eng R38:55
Takemoto T, Takemoto M (2006) Solder Surf Mount Technol 18:20
Nishikawa H, Komatsu A, Takemoto T (2005) Mater Trans 46(11):2394
Kang SK, Shih DY, Leonard D, Henderson DW (2004) JOM 56:34
Kitajima M, Shono T (2005) Microelectron Reliab 45:1208
Gourly CM, Nogita K, Mcdonald SD, Nishimora T (2006) Scripta Mater 54:1557
Zhao J, Qi L, Wang XM, Wang L (2004) J Alloy Compd 375:196
Sharif A, Chan YC (2005) J Alloy Compd 390:67
Liu LB, Andersson C, Liu J (2004) J Electron Mater 33:935
Kim KS, Huh SH, Suganuma K (2003) Microelectron Reliab 43:259
Dudek MA, Sidhu RS, Chawla N (2006) JOM 58:57
Wu CML, Yu DQ, Law CMT, Wang L (2004) Mater Sci Eng R44:1
Anderson IE, Cook BA, Harringa J, Terpstra RL (2002) J Electron Mater 31:1166
Nishikawa H, Komatsu A, Takemoto T (2005) Mater Trans 46:2394
Gao F, Takemoto T, Nishikawa H (2006) Mat Sci Eng A420:39
Gao F, Takemoto T, Nishikawa H, Komatsu A (2006) J Electron Mater 35:905
Laurila T, Vuorinen V, Kivilahti JK (2005) Mat Sci Eng R49:1
Lin CH, Chen SW, Wang C-H (2002) J Electron Mater 31:907
Anderson IE, Cook BA, Harringa JL, Terpstra RL (2002) JOM 54:26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, F., Nishikawa, H. & Takemoto, T. Microstructural and mechanical properties of Sn–Ag–Cu lead-free solders with minor addition of Ni and/or Co. J Mater Sci 43, 3643–3648 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2580-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2580-7