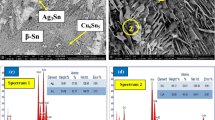
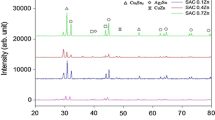
Abstract
As a result of extensive studies, nearternary-eutectic Sn-Ag-Cu (SAC) alloys have been identified as the leading lead-free solder candidates to replace lead-bearing solders for ball-grid array module assembly. However, recent studies revealed several potential reliability risk factors associated with the alloy system. The formation of large Ag3Sn plates in solder joints, especially when solidified at a relatively slow cooling rate, poses a reliability concern. In this study, the effect of adding a minor amount of zinc in SAC alloy was investigated. The minor zinc addition was shown to reduce the amount of undercooling during solidification and thereby suppress the formation of large Ag3Sn plates. In addition, the zinc was found to cause changes in both the microstructure and interfacial reaction of the solder joint. The interaction of zinc with other alloying elements in the solder was also investigated for a better understanding of the role of zinc during solidification of the nearternary-eutectic alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
2002 Lead-Free Roadmap (Tokyo, Japan: Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association, 2002).
J. Bath, C. Handwerker, and E. Bradley: “Research Update: Lead Free Solder Alternatives,” Circuits Assembly, 11, (2000), pp. 45–52.
I.E. Anderson et al., J. Electronic Materials, 30 (2001), pp. 1050–1059.
K.W. Moon et al., J. of Electronic Materials, 29 (2000), pp. 1122–1136.
I. Ohnuma et al., J. of Electronic Materials, 29 (2000), pp. 1137–1144.
D.R. Frear et al., JOM, 53 (6) (2001), pp. 28–32.
K.S. Kim, S.H. Huh, and K. Suganuma, Materials Science and Engineering, A333 (2002), pp. 106–114.
D.W. Henderson et al., J. of Materials Research, 17 (11) (2002), pp. 2775–2778.
S.K. Kang et al., Proc. 53rd ECTC (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2003), pp. 64–70.
S.K. Kang et al., JOM, 55 (6) (2003), pp. 61–65.
K.L. Buckmaster et al. (Paper presented at the 2003 TMS Fall Meeting, Chicago, November 2003).
S.K. Kang et al. (Paper presented at 2004 TMS Annual Meeting, Charlotte, NC, March 2004).
A. Ohno and T. Motegi, J. of Japan Inst Metals, 37 (1973), pp. 777–780.
P. Lauro et al., J. Electronic Materials, 32 (12) (2003), pp. 1432–1440.
S.K. Kang et al., Proc. 52nd ECTC (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2002), pp. 147–153.
P. Harris, Surface Mount Tech. (U.K.) 11 (3) (1999), pp. 46–52.
S.K. Kang et al., to be published in Materials Transactions (The Japan Inst. Metals in 2004).
S.K. Kang et al., to be published in Proc. Electronic Comp. Tech. Conf. (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, June 2004).
K. Zeng and K.N. Tu, Materials Sci. & Eng., R 38 (2002), pp. 55–105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
For more information, contact Sung K. Kang, IBM T.J. Watson Research Center, 1101 Kitchawan Road, Route 134, P.O. Box 218, Yorktown Heights, NY 10598; (914) 945-3932; fax (914) 945-2141; e-mail kang@us.ibm.com.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, S.K., Shih, DY., Leonard, D. et al. Controlling Ag3Sn plate formation in near-ternary-eutectic Sn-Ag-Cu solder by minor Zn alloying. JOM 56, 34–38 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-004-0108-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-004-0108-4