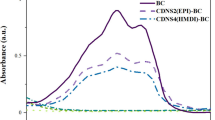
Abstract
Reactive oxygen species triggered oxidative stress contributes to the pathogenesis of numerous ailments such as myocardial infraction, inflammation, atherosclerosis, and pigmentation disorders. ROS scavengers, particularly natural bioactives are one of the possible options to reduce this stress. However, these bioactives possess certain formulation challenges owing to their poor solubility, stability, and bioavailability. Therefore, the design of a stable formulation that can deal these challenges, while preserving the antioxidant efficacy is of great significance. In this view, the current study was aimed at fabrication of p-Coumaric acid loaded nanosponges employing melt method. The spectroscopy resulting nanosponges were appropriately characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction, differential scanning calorimetry, thermogravimetric analysis, nuclear magnetic resonance, FE-SEM (field emission scanning electron microscopy) and TEM (transmission electron microscopy). The particle size of PCA-CDNS (p-Coumaric acid nanosponges) was in nano range, with low PDI (polydispersity index), acceptable zeta potential and delayed release. Molecular docking studies for PCA using mushroom tyrosinase (TYR) were also carried out. Further, the antioxidant and antityrosinase studies were also performed. In nutshell, the findings herein revealed that encasement of PCA in NS led to an enhancement in efficacy of this bioactive in terms of safety, solubility, and release, while preserving its antioxidant and antityrosinase effects. On the basis of the present results, we expect that PCA nanosponges can be seen as promising carriers for addressing depigmention, particularly associated with ROS overexpression.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lima, L.C., Buss, G.D., Ishii-Iwamoto, E.L., Salgueiro-Pagadigorria, C., Comar, J.F., Bracht, A., Constantin, J.: Metabolic effects of p-coumaric acid in the perfused rat liver. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 20, 18–26 (2006)
An, S.M., Koh, J.-S., Boo, Y.C.: p-coumaric acid not only inhibits human tyrosinase activity in vitro but also melanogenesis in cells exposed to UVB. Phytother Res. 24, 1175–1180 (2010)
PubChem: PubChem, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
Taofiq, O., González-Paramás, A.M., Barreiro, M.F., Ferreira, I.C.: Hydroxycinnamic acids and their derivatives: cosmeceutical significance, challenges and future perspectives, a review. Molecules 22, 281 (2017)
Neog, M.K., Rasool, M.: Targeted delivery of p-coumaric acid encapsulated mannosylated liposomes to the synovial macrophages inhibits osteoclast formation and bone resorption in the rheumatoid arthritis animal model. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 133, 162–175 (2018)
Huang, H., Belwal, T., Liu, S., Duan, Z., Luo, Z.: Novel multi-phase nano-emulsion preparation for co-loading hydrophilic arbutin and hydrophobic coumaric acid using hydrocolloids. Food Hydrocoll. 93, 92–101 (2019)
Tzankova, V., Aluani, D., Yordanov, Y., Kondeva-Burdina, M., Petrov, P., Bankova, V., Simeonova, R., Vitcheva, V., Odjakov, F., Apostolov, A.: Micellar propolis nanoformulation of high antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity. Rev. bras. farmacogn. 29, 364–372 (2019)
Corciova, A., Burlec, A.F., Gheldiu, A.M., Fifere, A., Lungoci, A.L., Marangoci, N., Mircea, C.: Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using licorice extract and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Rev. Chim. 70 (2019)
Pinheiro Machado, G.T., Veleirinho, M.B., Mazzarino, L., Machado Filho, L.C.P., Maraschin, M., Cerri, R.L.A., Kuhnen, S.: Development of propolis nanoparticles for the treatment of bovine mastitis: in vitro studies on antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 99, 713–723 (2019)
Muhammad, D.R.A., Doost, A.S., Gupta, V., bin Sintang, M.D., Van de Walle, D., Van der Meeren, P., Dewettinck, K.: Stability and functionality of xanthan gum–shellac nanoparticles for the encapsulation of cinnamon bark extract. Food Hydrocoll. 100, 105377 (2020)
Kumar, S., Rao, R.: Analytical tools for cyclodextrin nanosponges in pharmaceutical field: a review. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 1–20 (2019)
Rezaei, A., Varshosaz, J., Fesharaki, M., Farhang, A., Jafari, S.M.: Improving the solubility and in vitro cytotoxicity (anticancer activity) of ferulic acid by loading it into cyclodextrin nanosponges. Int J Nanomedicine. 14, 4589 (2019)
Dhakar, N.K., Caldera, F., Bessone, F., Cecone, C., Pedrazzo, A.R., Cavalli, R., Dianzani, C., Trotta, F.: Evaluation of solubility enhancement, antioxidant activity, and cytotoxicity studies of kynurenic acid loaded cyclodextrin nanosponge. Carbohydr. Polym. 224, 115168 (2019)
Pawar, S., Shende, P., Trotta, F.: Diversity of β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges for transformation of actives. Int. J. Pharm. 565, 333–350 (2019)
Kumar, S., Trotta, F., Rao, R.: Encapsulation of babchi oil in cyclodextrin-based nanosponges: physicochemical characterization, photodegradation, and in vitro cytotoxicity studies. Pharmaceutics. 10, 169 (2018)
Anandam, S., Selvamuthukumar, S.: Fabrication of cyclodextrin nanosponges for quercetin delivery: physicochemical characterization, photostability, and antioxidant effects. J. Mater. Sci. 49, 8140–8153 (2014)
Ramírez-Ambrosi, M., Caldera, F., Trotta, F., Berrueta, L.Á., Gallo, B.: Encapsulation of apple polyphenols in β-CD nanosponges. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 80, 85–92 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-014-0393-7
Swaminathan, S., Vavia, P.R., Trotta, F., Cavalli, R., Tumbiolo, S., Bertinetti, L., Coluccia, S.: Structural evidence of differential forms of nanosponges of beta-cyclodextrin and its effect on solubilization of a model drug. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 76, 201–211 (2013)
Rao, M., Bajaj, A., Khole, I., Munjapara, G., Trotta, F.: In vitro and in vivo evaluation of β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges of telmisartan. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 77, 135–145 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-012-0224-7
Hua, S.: Comparison of in vitro dialysis release methods of loperamide-encapsulated liposomal gel for topical drug delivery. Int J Nanomedicine. 9, 735 (2014)
ElMeshad, A.N., Mortazavi, S.M., Mozafari, M.R.: Formulation and characterization of nanoliposomal 5-fluorouracil for cancer nanotherapy. J. Liposome Res. 24, 1–9 (2014)
RCSB PDB - Search Results, http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/results/results.do?tabtoshow=Current&qrid=31D5FFB5
Huey, R., Morris, G.M., Olson, A.J., Goodsell, D.S.: A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J. Comput. Chem. 28, 1145–1152 (2007)
Pushpalatha, R., Selvamuthukumar, S., Kilimozhi, D.: Cross-linked, cyclodextrin-based nanosponges for curcumin delivery - Physicochemical characterization, drug release, stability and cytotoxicity. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 45, 45–53 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2018.03.004
Padamwar, M.N., Pokharkar, V.B.: Development of vitamin loaded topical liposomal formulation using factorial design approach: drug deposition and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 320, 37–44 (2006)
Müller, R.H., MaÈder, K., Gohla, S.: Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery–a review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 50, 161–177 (2000)
Garrido, B., González, S., Hermosilla, J., Millao, S., Quilaqueo, M., Guineo, J., Acevedo, F., Pesenti, H., Rolleri, A., Shene, C., Rubilar, M.: Carbonate-β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponge as a nanoencapsulation system for piperine: physicochemical characterization. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 19, 620–630 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00062-7
Fachriyah, E., Ayu, T., Kusrini, D.: Identification of Phenolic acid from ethanol extract leaves binahong (Anredera cordifolia (ten) stennis) and antioxidant activity test. In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series. p. 012051. IOP Publishing (2019)
Świs\locka, R., Kowczyk-Sadowy, M., Kalinowska, M., Lewandowski, W.: Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman, 1H and 13C NMR) and theoretical studies of p-coumaric acid and alkali metal p-coumarates. Spectroscopy. 27, 35–48 (2012)
Karthikeyan, R., Devadasu, C., Srinivasa Babu, P.: Isolation, characterization, and RP-HPLC estimation of P-coumaric acid from methanolic extract of durva grass (Cynodon dactylon Linn.)(Pers.). Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, (2015)
Zainuddin, R., Zaheer, Z., Sangshetti, J.N., Momin, M.: Enhancement of oral bioavailability of anti-HIV drug rilpivirine HCl through nanosponge formulation. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 43, 2076–2084 (2017)
Dora, C.P., Trotta, F., Kushwah, V., Devasari, N., Singh, C., Suresh, S., Jain, S.: Potential of erlotinib cyclodextrin nanosponge complex to enhance solubility, dissolution rate, in vitro cytotoxicity and oral bioavailability. Carbohydr. Polym. 137, 339–349 (2016)
Kumar, S., Prasad, M., Rao, R.: Topical delivery of clobetasol propionate loaded nanosponge hydrogel for effective treatment of psoriasis: Formulation, physicochemical characterization, antipsoriatic potential and biochemical estimation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 119, 111605 (2021)
Sapino, S., Carlotti, M.E., Cavalli, R., Ugazio, E., Berlier, G., Gastaldi, L., Morel, S.: Photochemical and antioxidant properties of gamma-oryzanol in beta-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 75, 69–76 (2013)
Kiliç, I., Yeşiloğlu, Y.: Spectroscopic studies on the antioxidant activity of p-coumaric acid. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 115, 719–724 (2013)
Benbettaieb, N., Nyagaya, J., Seuvre, A.-M., Debeaufort, F.: Antioxidant activity and release kinetics of caffeic and p-Coumaric acids from hydrocolloid-based active films for healthy packaged food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66, 6906–6916 (2018)
Acknowledgements
The researchers would like to acknowledge Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam Central Instrument Laboratory, Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Guru Jambheshwar, University of Science and Technology, Hisar for providing necessary facilities for present investigation. Jay Chem Marketing, Mumbai is also acknowledged for providing a gift sample of β-cyclodextrin. The authors also wish to thank Dr. Ajmer Singh, Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Chitkara University, Rajpura (India) for molecular docking studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Rao, R. Formulation and modification of physicochemical parameters of p-Coumaric acid by cyclodextrin nanosponges. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 102, 313–326 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-021-01121-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-021-01121-2