Abstract
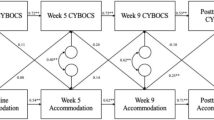
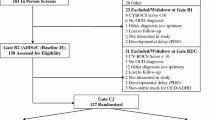
Pediatric obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a chronic condition affecting millions of children. Though well intentioned, accommodation (i.e., a parent’s attempt to assuage their child’s distress and anxiety) is thought to increase OCD symptom severity and may cause greater OCD-related impairment. The present study sought to examine the relative contribution of parental accommodation in predicting OCD symptom severity. Children between the ages of 6 and 18 (and their parents) participated in a prospective, longitudinal study investigating the course of pediatric OCD utilizing a longitudinal design. Data was collected at intake (n = 30) and two-years (n = 22) post-intake controlling for age, anxiety and depression. Parental accommodation (measured at intake) significantly predicted OCD symptom severity and was the strongest predictor at both intake and two-year follow-up. These preliminary findings highlight the importance of further research seeking to delineate factors relevant to the development and maintenance of accommodation as well as parent-level variables that might mediate the relationship between accommodation and OCD symptom severity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert, U., Bogetto, F., Maina, G., Saracco, P., Brunatto, C., & Mataix-Cols, D. (2010). Family accommodation in obsessive-compulsive disorder: Relation to symptom dimensions, clinical and family characteristics. Psychiatry Research, 179(2), 204–211.
American Psychological Association. (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th edn., text rev.) (Vol. 4). Washington, DC: Author.
Barrett, P. M., Farrell, L., Pina, A. A., Peris, T. S., & Piacentini, J. (2008). Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for child and adolescent obsessive-compulsive disorder. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 37(1), 131–155.
Birmaher, B., Khetarpal, S., Brent, D., Cully, M., Balach, L., Kaufman, J., & Neer, S. M. (1997). The screen for child anxiety related emotional disorders (SCARED): Scale construction and psychometric characteristics. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36(4), 545–553.
Calvocoressi, L., Lewis, B., Harris, M., Trufan, S. J., Goodman, W. K., McDougle, C. J., & Price, L. H. (1995). Family accommodation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry, 152(3), 441–443.
Calvocoressi, L., Mazure, C. M., Kasl, S. V., Skolnick, J., Fisk, D., Vegso, S. J., et al. (1999). Family accommodation of obsessive-compulsive symptoms: Instrument development and assessment of family behavior. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases, 187(10), 636–642.
First, M., Spitzer, R., Gibbon, M., & et al. (1996). Structured clinical interview for DSM_IV Axis I disorder, Patient Edition (SCID-P).
Flessner, C. A., Freeman, J. B., Sapyta, J., Garcia, A., Franklin, M. E., March, J. S., & Foa, E. (2011). Predictors of parental accommodation in pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder: Findings from the pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder treatment study (POTS) trial. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 50(7), 716–725.
Flessner, C. A., Sapyta, J., Garcia, A., Freeman, J. B., Franklin, M. E., Foa, E., & March, J. (2009). Examining the psychometric properties of the family accommodation scale-parent-report (FAS-PR). Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 31(1), 38–46.
Freeman, J. B., Garcia, A. M., Coyne, L., Ale, C., Przeworski, A., Himle, M., et al. (2008). Early childhood OCD: Preliminary findings from a family-based cognitive-behavioral approach. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 47(5), 593–602.
Geller, D. A. (2006). Obsessive-compulsive and spectrum disorders in children and adolescents. Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 29(2), 353–370.
Geller, D. A., Biederman, J., Griffin, S., Jones, J., & Lefkowitz, T. R. (1996). Comorbidity of juvenile obsessive-compulsive disorder with disruptive behavior disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 35(12), 1637–1646.
Goodman, W. K., Price, L. H., Rasmussen, S. A., Mazure, C., Delgado, P., Heninger, G. R., & Charney, D. S. (1989a). The Yale-Brown obsessive compulsive scale. II. Validity. Archives of General Psychiatry, 46(11), 1012–1016.
Goodman, W. K., Price, L. H., Rasmussen, S. A., Mazure, C., Fleischmann, R. L., Hill, C. L., et al. (1989b). The Yale-Brown obsessive compulsive scale. I. Development, use, and reliability. Archives of General Psychiatry, 46(11), 1006–1011.
Hanna, G. L. (1995). Demographic and clinical-features of obsessive-compulsive disorder in children and adolescents. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 34(1), 19–27.
Kaufman, J., Birmaher, B., Brent, D., Rao, U., Flynn, C., Moreci, P., et al. (1997). Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children-present and lifetime version (K-SADS-PL): Initial reliability and validity data. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36(7), 980–988.
Kovacs, M. (1992). Children’s depression inventory. New York: Multi-Health Systems.
Langley, A. K., Lewin, A. B., Bergman, R. L., Lee, J. C., & Piacentini, J. (2010). Correlates of comorbid anxiety and externalizing disorders in childhood obsessive compulsive disorder. European Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 19(8), 637–645.
Leon, A. C. (2011). Evaluation of psychiatric interventions in an observational study: Issues in design and analysis. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 13(2), 191–198.
Lewin, A. B., Storch, E. A., Geffken, G. R., Goodman, W. K., & Murphy, T. K. (2006). A neuropsychiatric review of pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder: Etiology and efficacious treatments. Neuropsychiatric Disorders and Treatment, 2(1), 21–31.
Lin, H. Q., Katsovich, L., Ghebremichael, M., Findley, D. B., Grantz, H., Lombroso, P. J., et al. (2007). Psychosocial stress predicts future symptom severities in children and adolescents with Tourette syndrome and/or obsessive-compulsive disorder. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48(2), 157–166.
Maina, G., Saracco, P., Albert, U., & Bogetto, F. (2006). Family-focused treatments for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Clinical Neuropsychiatry, 3(6), 382–390.
Mancebo, M. C., Garcia, A. M., Pinto, A., Freeman, J. B., Przeworski, A., Stout, R., et al. (2008). Juvenile-onset OCD: Clinical features in children, adolescents and adults. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 118(2), 149–159.
March, J. S., Parker, J. D., Sullivan, K., Stallings, P., & Conners, C. K. (1997). The Multidimensional Anxiety Scale for Children (MASC): Factor structure, reliability, and validity. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36(4), 554–565.
Merlo, L. J., Lehmkuhl, H. D., Geffken, G. R., & Storch, E. A. (2009). Decreased family accommodation associated with improved therapy outcome in pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 77(2), 355–360.
Miller, I. W., Bishop, S., Norman, W. H., & Maddever, H. (1985). The modified Hamilton rating scale for depression: Reliability and validity. Psychiatry Research, 14(2), 131–142.
Peris, T. S., Bergman, R. L., Asarnow, J. R., Langley, A., McCracken, J. T., & Piacentini, J. (2010). Clinical and cognitive correlates of depressive symptoms among youth with obsessive compulsive disorder. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 39(5), 616–626.
Peris, T. S., Bergman, R. L., Langley, A., Chang, S., McCracken, J. T., & Piacentini, J. (2008). Correlates of accommodation of pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder: Parent, child, and family characteristics. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 47(10), 1173–1181.
Piacentini, J., Bergman, R. L., Chang, S., Langley, A., Peris, T., Wood, J. J., & McCracken, J. (2011). Controlled comparison of family cognitive behavioral therapy and psychoeducation/relaxation training for child obsessive-compulsive disorder. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 50(11), 1149–1161.
Piacentini, J., Peris, T. S., Bergman, R. L., Chang, S., & Jaffer, M. (2007). Functional impairment in childhood OCD: Development and psychometrics properties of the child obsessive-compulsive impact scale-revised (COIS-R). Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 36(4), 645–653.
Pinto, A., Mancebo, M. C., Eisen, J. L., Pagano, M. E., & Rasmussen, S. A. (2006). The Brown Longitudinal Obsessive Compulsive Study: Clinical features and symptoms of the sample at intake. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 67(5), 703–711.
Rasmussen, S. A., & Eisen, J. L. (1992). The epidemiology and clinical features of obsessive compulsive disorder. Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 15(4), 743–758.
Saylor, C. F., Finch, A. J, Jr, Spirito, A., & Bennett, B. (1984). The children’s depression inventory: A systematic evaluation of psychometric properties. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 52(6), 955–967.
Scahill, L., Riddle, M. A., McSwiggin-Hardin, M., Ort, S. I., King, R. A., Goodman, W. K., et al. (1997). Children’s Yale-Brown obsessive compulsive scale: Reliability and validity. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36(6), 844–852.
Steketee, G., & Van Noppen, B. (2003). Family approaches to treatment for obsessive compulsive disorder. Revista Brasileira Psiquiatria, 25(1), 43–50.
Stengler-Wenzke, K., Kroll, M., Matschinger, H., & Angermeyer, M. C. (2006). Quality of life of relatives of patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 47(6), 523–527.
Storch, E. A., Geffken, G. R., Merlo, L. J., Jacob, M. L., Murphy, T. K., Goodman, W. K., et al. (2007). Family accommodation in pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 36(2), 207–216.
Valleni-Basile, L. A., Garrison, C. Z., Jackson, K. L., Waller, J. L., McKeown, R. E., Addy, C. L., & Cuffe, S. P. (1994). Frequency of obsessive-compulsive disorder in a community sample of young adolescents. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 33(6), 782–791.
Wood, J. J., Piacentini, J. C., Bergman, R. L., McCracken, J., & Barrios, V. (2002). Concurrent validity of the anxiety disorders section of the Anxiety Disorders Interview Schedule for DSM-IV: Child and parent versions. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolecsent Psychology, 31(3), 335–342.
Zohar, A. H. (1999). The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in children and adolescents. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, 8(3), 445–460.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by a Grant awarded to Dr. Rasmussen from the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD (Grant Number: R01-MH-060218).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Francazio, S.K., Flessner, C.A., Boisseau, C.L. et al. Parental Accommodation Predicts Symptom Severity at Long-Term Follow-Up in Children with Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder: A Preliminary Investigation. J Child Fam Stud 25, 2562–2570 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-016-0408-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-016-0408-7