Abstract
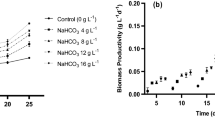
Cyanobacterium aponinum is a thermotolerant cyanobacterium species isolated from different thermal springs and showing potential therapeutic application thanks to the synthesis and release of exopolysaccharides with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating properties. This work investigates the effects of temperature and light on growth rate, biomass yield, and released polysaccharides (RPS) synthesis in C. aponinum cultures. The highest biomass productivity was obtained at 40 °C (about 92 mg L−1 d−1), while the highest RPS synthesis rate (about 10 mg L−1 d−1) was detected at 35 °C. At this temperature, the influence of light intensities, between 15 and 650 μmol photons m−2 s−1, was also evaluated. C. aponinum showed the highest productivity in biomass (about 280 mg L−1 d−1) and RPS (about 20 mg L−1 d−1) at 500 μmol photons m−2 s−1. Interestingly, this strain also had the ability to accumulate other high-value compounds such as phycocyanin, zeaxanthin, and β-carotene suggesting that C. aponinum can be used for the industrial production of multiple molecules of biotechnological interest.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed RMM, Dobretsov S, Sudesh K (2009) Applications of cyanobacteria in biotechnology. J Appl Microbiol 106:1–12
Alcantara S, Sanchez S (1999) Influence of carbon and nitrogen sources on Flavobacterium growth and zeaxanthin biosynthesis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 23:697–700
Bennett A, Bogorad L (1973) Complementary chromatic adaption in a filamentous blue-green alga. J Cell Biol 58:419–435
Bonnefond H, Moelants N, Talec A, Mayzaud P, Bernard O, Sciandra A (2017) Coupling and uncoupling of triglyceride and beta-carotene production by Dunaliella salina under nitrogen limitation and starvation. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:1–10
Chi Z, Elloy F, Xie Y, Hu Y, Chen S (2014) Selection of microalgae and cyanobacteria strains for bicarbonate-based integrated carbon capture and algae production system. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:447–457
De Philippis R, Vincenzini M (1998) Exocellular polysccharides from cyanobacteria and their possible applications. FEMS Microbiol Rev 22:151–175
De Philippis R, Vincenzini M (2003) Outermost polysaccharidic investments of cyanobacteria: nature, significance and possible applications. Recent Res Dev Microbiol 7:13–22
DuBois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Ducat DC, Way JC, Silver PA (2011) Engineering cyanobacteria to generate high-value products. Trends Biotechnol 29:95–103
Ehling-Schulz M, Bilger W, Scherer S (1997) UV-B-induced synthesis of photoprotective pigments and extracellular polysaccharides in the terrestrial cyanobacterium Nostoc commune. J Bacteriol 179:1940–1945
Eriksen NT (2008) Production of phycocyanin - a pigment with applications in biology, biotechnology, foods and medicine. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:1–14
Färber A, Jahns P (1998) The xanthophyll cycle of higher plants: influence of antenna size and membrane organization. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg 1363:47–58
Fiali Mouhim R, Cornet J-F, Fontane T, Fournet B, Dubertret G (1993) Production, isolation and preliminary characterization of the exopolysaccharide of the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. Biotechnol Lett 15:567–572
Fiedor J, Burda K (2014) Potential role of carotenoids as antioxidants in human health and disease. Nutrients 6:466–488
Fu FX, Warner ME, Zhang Y, Feng Y, Hutchins DA (2007) Effects of increased temperature and CO2 on photosynthesis, growth, and elemental ratios in marine Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus (cyanobacteria). J Phycol 43:485–496
Gris B, Morosinotto T, Giacometti GM, Bertucco A, Sforza E (2014) Cultivation of Scenedesmus obliquus in photobioreactors: effects of light intensities and light-dark cycles on growth, productivity, and biochemical composition. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:2377–2389
Gudmundsdottir AB, Omarsdottir S, Brynjolfsdottir A, Paulsen BS, Olafsdottir ES, Freysdottir J (2015) Exopolysaccharides from Cyanobacterium aponinum from the blue Lagoon in Iceland increase IL-10 secretion by human dendritic cells and their ability to reduce the IL-17+RORγt+/IL-10+FoxP3+ ratio in CD4+ T cells. Immunol Lett 163:157–162
Han PP, Sun Y, Jia SR, Zhong C, Tan ZL (2014) Effects of light wavelengths on extracellular and capsular polysaccharide production by Nostoc flagelliforme. Carbohydr Polym 105:145–151
Karatay SE, Donnmez G (2011) Microbial oil production from thermophile cyanobacteria for biodiesel production. Appl Energy 88:3632–3635
Kumar M, Kulshreshtha J, Pal Singh G (2011) Growth and biopigment accumulation of cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis at different light intensities and temperature. Brazilian J Microbiol 42:1128–1135
La Rocca N, Moro I, Rascio N (2016) Excess light and limited carbon two problems that cyanobacteria and microalgae have to cope with. In: Pessarakli M (ed) Handbook of photosynthesis. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 349–368
Lau NS, Matsui M, Abdullah AAA (2015) Cyanobacteria: photoautotrophic microbial factories for the sustainable synthesis of industrial products. Biomed Res Int 2015:1–9
Markou G, Chatzipavlidis I, Georgakakis D (2012) Effects of phosphorus concentration and light intensity on the biomass composition of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:2661–2670
Markou G, Vandamme D, Muylaert K (2014) Microalgal and cyanobacterial cultivation: the supply of nutrients. Water Res 65:186–202
Moro I, Rascio N, Di Bella M, Andreoli C, La Rocca N (2007) Cyanobacterium aponinum, a new Cyanoprokaryote from the microbial mat of Euganean thermal springs (Padua, Italy). Arch Hydrobiol Suppl Algol Stud 123:1–15
Mota R, Guimarães R, Büttel Z, Rossi F, Colica G, Silva CJ, Santos C, Gales L, Zille A, De Philippis R, Pereira SB, Tamagnini P (2013) Production and characterization of extracellular carbohydrate polymer from Cyanothece sp. CCY 0110. Carbohydr Polym 92:1408–1415
Nicolaus B, Panico A, Lama L, Romano I, Manca MC, De Giulio A, Gambacorta A (1999) Chemical composition and production of exopolysaccharides from representative members of heterocystous and non-heterocystous cyanobacteria. Phytochemistry 52:639–647
Nikulin SM (2011) Student test. Encyclopedia of Mathematics. URL: http://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php?title=Student_test&oldid=17068. Accessed 24 February 2017.
Paliwal C, Pancha I, Ghosh T, Maurya R, Chokshi K, Bharadwaj VSV, Ram S, Mishra S (2015) Selective carotenoid accumulation by varying nutrient media and salinity in Synechocystis sp. CCNM 2501. Bioresour Technol 197:363–368
Pereira S, Zille A, Micheletti E, Moradas-Ferreira P, De Philippis R, Tamagnini P (2009) Complexity of cyanobacterial exopolysaccharides: composition, structures, inducing factors and putative genes involved in their biosynthesis and assembly. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:917–941
Petusdottir SK, Solveig K, Bjornsdottir SH, Hreggvidsson GO, Hjorleifsdottir S, K J (2009) Analysis of the unique geothermal microbial ecosystemof the Blue Lagoon. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:425–432
Piven I, Friedrich A, Duhring U, Baier K, Inaba M, Shi T, Wang K, Enke H, Kramer D (2014) Cyanobacterium sp. host cell and vector for production of chemical compounds in cyanobacterial cultures. US Patent Application 0178973 A1
Prasanna R, Sood a, Jaiswal P, Nayak S, Gupta V, Chaudhary V, Joshi M, Natarajan C (2010) Rediscovering cyanobacteria as valuable sources of bioactive compounds. Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol 46:133–147
Rascio N, La Rocca N (2013) Biological nitrogen fixation. In: Elias SA (ed) Reference module in earth systems and environmental sciences. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp 412–419
Richert L, Golubic S, Le Guédès R, Ratiskol J, Payri C, Guezennec J (2005) Characterization of exopolysaccharides produced by cyanobacteria isolated from Polynesian microbial mats. Curr Microbiol 51:379–384
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61
Sekar S, Chandramohan M (2008) Phycobiliproteins as a commodity: trends in applied research, patents and commercialization. J Appl Phycol 20:113–136
Setyoningrum TM, Nur MMA (2015) Optimization of C-phycocyanin production from S. platensis cultivated on mixotrophic condition by using response surface methodology. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 4:603–607
Singh S, Kate BN, Banerjee UC (2005) Bioactive compounds from cyanobacteria and microalgae: an overview. Crit Rev Biotechnol 25:73–95
Singh JS, Kumar A, Rai AN, Singh DP (2016) Cyanobacteria: a precious bio-resource in agriculture, ecosystems, and environmental sustainability. Front Microbiol 7:1–19
Thajuddin N, Subramanian G (2005) Cyanobacterial biodiversity and potential applications in biotechnology. Curr Sci 89:47–57
Thawornwiriyanum P, Tanasupawat S, Dechsakulwatana C, Techkarnjanaruk S, Suntornsuk W (2012) Identification of newly zeaxanthin-producing bacteria isolated from sponges in the Gulf of Thailand and their zeaxanthin production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 167:2357–2368
Weiss A, Johannisbauer W, Gutsche B, Cordero BF, Martin L, Rodriguez H, Vargas MA, Obraztsova I (2007) Process for obtaining zeaxanthin from algae. US Patent 2007/0190595 A1
Winckelmann D, Bleeke F, Bergmann P, Klöck G (2015) Growth of Cyanobacterium aponinum influenced by increasing salt concentrations and temperature. 3 Biotech 5:253–260
Winckelmann D, Bleeke F, Bergmann P, Elle C, Klöck G (2016) Detection of weed algae in open pond cultures of Cyanobacterium aponinum using PAM. Int Aquat Res 8:81–90
Xie Y, Jin Y, Zeng X, Chen J, Lu Y, Jing K (2015) Fed-batch strategy for enhancing cell growth and C-phycocyanin production of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis under phototrophic cultivation. Bioresour Technol 180:281–287
Yan R, Zhu D, Zhang Z, Zeng Q, Chu J (2012) Carbon metabolism and energy conversion of Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942 under mixotrophic conditions: comparison with photoautotrophic condition. J Appl Phycol 24:657–668
Yu H, Jia S, Dai Y (2009) Growth characteristics of the cyanobacterium Nostoc flagelliforme in photoautotrophic, mixotrophic and heterotrophic cultivation. J Appl Phycol 21:127–133
Yu J, Liberton M, Cliften PF, Head RD, Jacobs JM, Smith RD, Koppenaal DW, Brand JJ, Pakrasi HB (2015) Synechoccus elongatus UTEX 2973, a fast growing cyanobacterial chassis for biosynthesis using light and CO2. Sci Rep 5:1–10
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funds from Progetto di Ateneo (PRAT) 2011, University of Padova “High-value compound production by photo-oxygenic microorganisms under selected growth conditions” (grant no. CPDA113758) and Progetti di Ricerca di Rilevante Interesse Nazionale (PRIN) 2012 “Improving biofuels and high added value molecules production from unicellular algae” (grant no. 2012XSAWYM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gris, B., Sforza, E., Morosinotto, T. et al. Influence of light and temperature on growth and high-value molecules productivity from Cyanobacterium aponinum . J Appl Phycol 29, 1781–1790 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-017-1133-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-017-1133-3