Abstract
Purpose
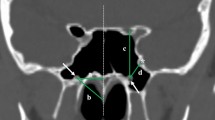
This study aimed to classify the morphometry and variations of optic canal by examining its changes according to gender and body side, and developments according to age.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated the orbit and paranasal sinus computerized tomography images of 200 individuals (age range 3 months-90 years;106 female, 94 male). In this study, three different parts of optic canal in evaluated morphometric and morphological.
Results
The intracranial aperture was found to be statistically significantly wide in males than females on both sides (p ˂ 0.05). When optic canal types were evaluated, the most common type among healthy individuals was conical type (right: 68%, left:67.5%), and the least common type was irregular type (right and left:1.5%). According to the type of optic waist, the most common was triangle type.
Conclusion
Considering the possible effect of optic canal size on pathologies, it is important to establish a basis for the parameters of this structure in healthy individuals. In this study, both the morphology and morphometry of the canal as well as variations were examined and it was determined that the structure was affected by gender, body side and age group. Knowledge of anatomic morphometry, variations and complexities arising from these are important for clinical diagnosis and management.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are available upon request.
References
Akdemir G, Tekdemir I, Altın L (2004) Transethmoidal approach to the optic canal: surgical and radiological microanatomy. Surg Neurol 62:268–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2004.01.022
Alkofide EA (2007) The shape and size of the sella turcica in skeletal Class I, Class II, and Class III Saudi subjects. Eur J Orthod 29:457–463. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejo/cjm049
Berlis A, Putz R, Schumacher M (1992) Direct and CT measurements of canals and foramina of the skull base. Br J Radiol 65:653–661. https://doi.org/10.1259/0007-1285-65-776-653
Bertelli E (2014) Metoptic canal, duplication of the optic canal and Warwick’s foramen in human orbits. Anat Sci Int 89:34–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-013-0197-7
Caporlingua A, Prior A, Cavagnaro MJ, Winston G, Oliveira DL, Sadwhani SD, Arias GA, Schwalb JN, Akhbari M, Evins AI (2019) The intracranial and intracanalicular optic nerve as seen through different surgical windows: endoscopic versus transcranial. World Neurosurg 124:522–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.122
Chauhan P, Kalra S, Mongia SM, Ali S, Anurag A (2014) Morphometric analysis of sella turcica in North Indian population: a radiological study. Int J Res Med Sci 2:521–526. https://doi.org/10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20140529
Goldberg RA, Hannani K, Toga AW (1992) Microanatomy of the orbital apex: computed tomography and microcryoplaning of soft and hard tissue. Ophthalmology 99:1447–1452. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0161-6420(92)31785-3
Govsa F, Erturk M, Kayalioglu G, Pinar Y, Ozer M, Ozgur T (1999) Neuro-arterial relations in the region of the optic canal. Surg Radiol Anat 21:329–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01631334
Guseva Y, Denisov S (2006) Structure of the optic canal in human ontogenesis. Ann Anat 188:103–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2005.05.007
Hariri F, Farhana NA, Abdullah NA, Ibrahim N, Ramli NM, Abdullah AAM, May CM, Khaliddin N (2021) Optic canal characteristics in pediatric syndromic craniosynostosis. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 49:1175–1181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2021.06.017
Hart CK, Theodosopoulos PV, Zimmer LA (2009) Anatomy of the optic canal: a computed tomography study of endoscopic nerve decompression. Ann Otol Rhino Laryngol 118:839–844. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348940911801203
Hayreh SS (1964) Pathogenesis of oedema of the optic disc (papilloedema): a preliminary report. Br J Ophthalmol 48:522. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.48.10.522
Jiang P-F, Dai X-Y, Lv Y, Liu S, Mu X-Y (2015) Imaging study on the optic canal using sixty four-slice spiral computed tomography. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:21247–21251
Kalthur S, Periyasamy R, Kumar S, Gupta C, D’souza AS (2015) A morphometric evaluation of the optic canal: Comparative study between computerized tomographic study and direct anatomic study. Saudi J Med Med Sci 3:204–208
Kline LB, Morawetz RB, Swaid SN (1984) Indirect injury of the optic nerve. Neurosurgery 14(6):756–764
Killer H, Laeng H, Flammer J, Groscurth P (2003) Architecture of arachnoid trabeculae, pillars, and septa in the subarachnoid space of the human optic nerve: anatomy and clinical considerations. Br J Ophthalmol 87:777–781. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.87.6.777
Kumar A, Tripathi A, Jain S, Khare S, Kaushik RK, Kausar H, Arora S (2019) Anatomical and morphometric study of optic foramen in North Indian population. Natl J Clin Anat 8:53–56. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1689079
Lang J (1977) Structure and postnatal organization of heretofore uninvestigated and infrequent ossifications of the sella turcica region. Acta Anat (Basel) 99:121–139. https://doi.org/10.1159/000144840
Lang J (1981) Neuroanatomie der Nn. opticus, trigeminus, facialis, glossopharyngeus, vagus, accessorius und hypoglossus. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 231:1–69
Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR (2010) Clinically Oriented Anatomy, Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, p. 889-
Prado PA, Ribeiro EC, De Angelis MA, Smith RL (2007) Biometric study of the optic canal during cranial development. Orbit 26:107–111. https://doi.org/10.1080/01676830600987540
Radunovic M, Vukcevic B, Radojevic N, Vukcevic N, Popovic N, Vuksanovic-Bozaric A (2019) Morphometric characteristics of the optic canal and the optic nerve. Folia Morphol 78:39–46. https://doi.org/10.5603/FM.a2018.0065
Sinanoglu A, Orhan K, Kursun S, Inceoglu B, Oztas B (2016) Evaluation of optic canal and surrounding structures using cone beam computed tomography: considerations for maxillofacial surgery. J Craniofac Surg 27(5):1327–1330. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000002726
Suprasanna K, Ravikiran S, Kumar A, Chavadi C, Pulastya S (2015) Optic strut and para-clinoid region–assessment by multi-detector computed tomography with multiplanar and 3 dimensional reconstructions. J Clin Diagn Res 9:6–9. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2015/15698.6615
Ten B, Esen K, Adanır SS, Hamzaoglu EC, CiCek F, Taghipour P, Kara E, Vayisoglu Y, Talas DU (2021) Anatomic features of the cranial aperture of the optic canal in children: a radiologic study. Surg Radiol Anat 43:187–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-020-02604-6
Zhang H, Liu X, Cheng Y, Zhang S, Wang C, Cui D, Li Y, Fu Y, Wang Y (2013) A new method of locating the optic canal based on structures in sella region: computed tomography study. J Craniofac Surg 24:1011–1015. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e318287d228
Zhang X, Lee Y, Olson D, Fleischman D (2019) Evaluation of optic canal anatomy and symmetry using CT. BMJ Open Ophth 4:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjophth-2019-000302
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BP contributed to project development, data collection, data management, data analysis and manuscript writing. Project development, data management, data analysis, manuscript editing, study supervision were by ZF. MK performed the data collection. NUD and AKK contributed to data management and manuscript editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Ethical approval (approval number 2020/01) was given by the Local Ethics Committee of the Medical Faculty. This single-center retrospective study was approved by the local institutional review board with a waiver of the requirement for written, informed consent. This study was conducted at Selcuk University Faculty of Medicine.
Informed consent
An informed consent procedure was waived due to the retrospective nature of this study by the local institutional review board.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pirinc, B., Fazliogullari, Z., Koplay, M. et al. Morphometric and morphological evaluation of the optic canal in three different parts in MDCT images. Int Ophthalmol 43, 2703–2720 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-023-02670-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-023-02670-w