Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to peruse anatomic features of the cranial aperture of the optic canal (CAOC) for obtaining an extended morphometric dataset in children.
Methods
Computed tomography images of 200 children were included in this retrospective work to analyze the shape, location and diameters of the CAOC.
Results
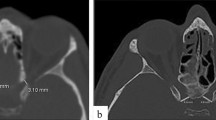
The CAOC area, width and height were observed as 17.53 ± 2.80 mm2, 6.12 ± 0.84 mm, and 4.35 ± 0.64 mm, respectively. The angle of the optic canal in axial plane was found as 39.28 ± 5.13°, while in sagittal plane as 16.01 ± 6.76°. The distance between the CAOC and the midsagittal line was 7.17 ± 1.48 mm. The CAOC was measured as 54.04 ± 5.23 mm and 42.55 ± 3.28 mm away from the anterior and lateral boundary of the anterior skull base, respectively. The CAOC shape was described as the tear-drop (186 foramina, 46.5%), triangular (156 foramina, 39%), oval (47 foramina, 11.8%), and round (11 foramina, 2.8%).
Conclusion
The depth, angle and diameter measurements belonging to the CAOC were changing according to its shape or demographic data (e.g., sex and age). Therefore, preoperative radiologic evaluation containing the shape, location and size of the CAOC should be considered by multidisciplinary operating teams in terms of surgical interventions such as implant positioning.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akdemir G, Tekdemir I, Altın L (2004) Transethmoidal approach to the optic canal: surgical and radiological microanatomy. Surg Neurol 62:268–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2004.01.022
Beer-Furlan A, Evins AI, Rigante L, Burrell JC, Anichini G, Stieg PE, Bernardo A (2014) Endoscopic extradural anterior clinoidectomy and optic nerve decompression through a pterional port. J Clin Neurosci 21:836–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2013.10.006
Beger O (2020) Assessment of the optic foramen shape and size in human fetuses. J Craniofac Surg 31:2021–2024. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000006610
Beger O, Taghipour P, Çakır S, Hamzaoğlu V, Özalp H, Kara E, Vayisoğlu Y, Dağtekin O, Dağtekin A, Bağdatoğlu C, Öztürk AH, Talas DÜ (2020) Fetal anatomy of the optic strut and prechiasmatic sulcus with a clinical perspective. World Neurosurg 136:e625–e634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2020.01.125
Beger O, Ten B, Balcı Y, Çakır S, Özalp H, Hamzaoğlu V, Vayisoğlu Y, Dağtekin A, Bağdatoğlu C, Talas DÜ (2020) A computed tomography study of the prechiasmatic sulcus anatomy in children. World Neurosurg 141:e118–e132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2020.05.023
Berlis A, Putz R, Schumacher M (1992) Direct and CT measurements of canals and foramina of the skull base. Brit J Radiol 65:653–661. https://doi.org/10.1259/0007-1285-65-776-653
Caporlingua A, Prior A, Cavagnaro MJ, Winston G, Oliveira DL, Sadwhani SD, Arias GA, Schwalb JN, Akhbari M, Evins AI (2019) The intracranial and intracanalicular optic nerve as seen through different surgical windows: endoscopic versus transcranial. World Neurosurg 124:522–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.122
Cares H, Bakay L (1971) The clinical significance of the optic strut. J Neurosurg 34:355–364. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1971.34.3.0355
Chang JT, Morrison CS, Styczynski JR, Mehan W, Sullivan SR, Taylor HO (2015) Pediatric orbital depth and growth: a radiographic analysis. J Craniofac Surg 26:1988–1991. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000001974
Cheng A, Lucas P, Yuen H, Lam D, So K (2008) Surgical anatomy of the Chinese orbit. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 24:136–141. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0b013e31816704f5
Cheng Y, Liu M, Zhang S, Tian Y, Song D, Li Y, Luo Q (2013) Optic canal (OC) and internal carotid artery (ICA) in sellar region. Surg Radiol Anat 35:797–801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-013-1193-2
Gagliardi F, Donofrio CA, Spina A, Bailo M, Gragnaniello C, Gallotti AL, Elbabaa SK, Caputy AJ, Mortini P (2016) Endoscope-assisted transmaxillosphenoidal approach to the sellar and parasellar regions: an anatomic study. World Neurosurg 95:246–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.08.034
Gil Z, Constantini S, Spektor S, Abergel A, Khafif A, Beni-Adani L, Leonor T, DeRowe A, Fliss D (2005) Skull base approaches in the pediatric population. Head Neck 27:682–689. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.20226
Giovannetti F, Mussa F, Priore P, Scagnet M, Arcovio E, Valentini V, Genitori L (2018) Endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery in pediatric patients. A single center experience. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 46:2017–2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2018.09.013
Goldberg RA, Hannani K, Toga AW (1992) Microanatomy of the orbital apex: computed tomography and microcryoplaning of soft and hard tissue. Ophthalmology 99:1447–1452. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0161-6420(92)31785-3
Govsa F, Erturk M, Kayalioglu G, Pinar Y, Ozer M, Ozgur T (1999) Neuro-arterial relations in the region of the optic canal. Surg Radiol Anat 21:329–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01631334
Guseva Y, Denisov S (2006) Structure of the optic canal in human ontogenesis. Ann Anat 188:103–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2005.05.007
Guthikonda B, Tobler WD Jr, Froelich SC, Leach JL, Zimmer LA, Theodosopoulos PV, Tew JM Jr, Keller JT (2010) Anatomic study of the prechiasmatic sulcus and its surgical implications. Clin Anat 23:622–628. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.21002
Güler TM, Yılmazlar S, Özgün G (2019) Anatomical aspects of optic nerve decompression in transcranial and transsphenoidal approach. J Craniomaxillofac 47:561–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2019.01.027
Hart CK, Theodosopoulos PV, Zimmer LA (2009) Anatomy of the optic canal: a computed tomography study of endoscopic nerve decompression. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 118:839–844. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348940911801203
Harwood-Nash D (1970) Axial tomography of the optic canals in children. Radiology 96:367–374. https://doi.org/10.1148/96.2.367
Hayashi N, Masuoka T, Tomita T, Sato H, Ohtani O, Endo S (2004) Surgical anatomy and efficient modification of procedures for selective extradural anterior clinoidectomy. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 47:355–358. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-830121
Kalthur S, Periyasamy R, Kumar S, Gupta C, D’souza AS, (2015) A morphometric evaluation of the optic canal: Comparative study between computerized tomographic study and direct anatomic study. Saudi J Med Med Sci 3:204. https://doi.org/10.4103/1658-631X.161997
Karampatakis V, Natsis K, Gigis P, Stangos N (1998) Orbital depth measurements of human skulls in relation to retrobulbar anesthesia. Eur J Ophthalmol 8:118–120. https://doi.org/10.1177/112067219800800212
Katsev DA, Drews RC, Rose BT (1989) An anatomic study of retrobulbar needle path length. Ophthalmology 96:1221–1224. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0161-6420(89)32748-5
Kumar A, Tripathi A, Jain S, Khare S, Kaushik RK, Kausar H, Arora S (2019) Anatomical and morphometric study of optic foramen in north indian population. Natl J Clin Anat 8:053–056. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1689079
Locatelli M, Di Cristofori A, Draghi R, Bertani G, Guastella C, Pignataro L, Mantovani G, Rampini P, Carrabba G (2017) Is complex sphenoidal sinus anatomy a contraindication to a transsphenoidal approach for resection of sellar lesions? Case series and review of the literature. World Neurosurg 100:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.12.123
Maniscalco JE, Habal MB (1978) Microanatomy of the optic canal. J Neurosurg 48:402–406. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1978.48.3.0402
Mazzatenta D, Zoli M, Guaraldi F, Ambrosi F, Fustini MF, Pasquini E, Asioli S, Zucchelli M (2020) Outcome of endoscopic endonasal surgery in pediatric craniopharyngiomas. World Neurosurg 134:e277–e288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.10.039
Mcqueen CT, Diruggiero DC, Campbell JP, Shockley WW (1995) Orbital osteology: a study of the surgical landmarks. Laryngoscope 105:783–788. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-199508000-00003
Öztürk A, Bozbuga M, Bayraktar B, Arı Z, Sahinoglu K, Polat G, Gürel I (1999) Surgical anatomy and morphometric analysis of the optico-chiasmatic apparatus, optic canal and sphenoid ridge. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 75:319–322. https://doi.org/10.2535/ofaj1936.75.6_319
Park S-J, Yoo J-N, Yoo M-S, Heo Y-C (2017) A study on double angle of optic foramen in the rhese method. J Korean Soc Radiol 11:313–319. https://doi.org/10.7742/jksr.2017.11.5.313
Prado PA, Ribeiro EC, De Angelis MA, Smith RL (2007) Biometric study of the optic canal during cranial development. Orbit 26:107–111. https://doi.org/10.1080/01676830600987540
Purohit BJ, Singh PR (2016) An osteologic study of cranial opening of optic canal in Gujarat region. J Clin Diagn Res 10:AC08-AC11. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2016/22110.8929
Puzzilli F, Ruggeri A, Mastronardi L, Agrillo A, Ferrante L (1999) Anterior clinoidal meningiomas: report of a series of 33 patients operated on through the pterional approach. Neuro Oncol 1:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/1.3.188
Radunovic M, Vukcevic B, Radojevic N, Vukcevic N, Popovic N, Vuksanovic-Bozaric A (2019) Morphometric characteristics of the optic canal and the optic nerve. Folia Morphol 78:39–46. https://doi.org/10.5603/FM.a2018.0065
Rajeswaran SA, Mohanraj KG, Babu KY (2019) An osteologic study of the cranial opening of optic canal in dry human skulls. Drug Invent Today 12:2051–2053. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2016/22110.8929
Shibata T, Tanikawa M, Sakata T, Mase M (2018) Urgent optic nerve decompression via an endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach for craniopharyngioma in a 12-month-old infant: a case report. Pediatr Neurosurg 53:182–187. https://doi.org/10.1159/000487086
Shlomi B, Chaushu S, Gil Z, Chaushu G, Fliss DM (2007) Effects of the subcranial approach on facial growth and development. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otohns.2006.07.019
Slavin KV, Dujovny M, Soeira G, Ausman JI (1994) Optic canal: microanatomic study. Skull Base Surg 4:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1058965
Standring S, Borley N, Collins P, Crossman A, Gatzoulis M, Healy J (2008) Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Elsevier, London
Tao H, Ma Z, Dai P, Jiang L (1999) Computer-aided three-dimensional reconstruction and measurement of the optic canal and intracanalicular structures. Laryngoscope 109:1499–1502. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-199909000-00026
Ten B, Beger O, Direk MÇ, Balcı Y, Çiçek F, Özalp H, Hamzaoğlu V, Temel G, Vayisoğlu Y, Bağdatoğlu C, Talas DÜ (2020) Radiologic analysis of the location, shape and size of the external aperture of the carotid canal in children. Surg Radiol Anat 42:749–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-020-02448-0
Vohra ST, Escott EJ, Stevens D, Branstetter BF (2011) Categorization and characterization of lesions of the orbital apex. Neuroradiology 53:89–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0712-7
Wasserzug O, DeRowe A, Ringel B, Fishman G, Fliss DM (2018) Open approaches to the anterior skull base in children: review of the literature. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base 79:42–46. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1621739
Weninger WJ, Müller GB (1999) The parasellar region of human infants: cavernous sinus topography and surgical approaches. J Neurosurg 90:484–490. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1999.90.3.0484
Yilmazlar S, Saraydaroglu O, Korfali E (2012) Anatomical aspects in the transsphenoidal–transethmoidal approach to the optic canal: an anatomic–cadaveric study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 40:e198–e205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2011.10.008
Zhang H, Liu X, Cheng Y, Zhang S, Wang C, Cui D, Li Y, Fu Y, Wang Y (2013) A new method of locating the optic canal based on structures in sella region: computed tomography study. J Craniofac Surg 24:1011–1015. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e318287d228
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BT, OB, KE, EK, DÜT: Project development, Data collection, Data analysis, Manuscript writing, Manuscript editing. SSA, ECH, FÇ, PT, YV: Data analysis, Manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ten, B., Beger, O., Esen, K. et al. Anatomic features of the cranial aperture of the optic canal in children: a radiologic study. Surg Radiol Anat 43, 187–199 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-020-02604-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-020-02604-6