Abstract
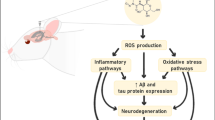
Alzheimer disease represents a major public health issue with limited therapeutic interventions. We explored the possibility of therapeutic approach by repurposing of tramadol in a sporadic animal model of Alzheimer’s type. Streptozocin (STZ 3 mg/kg; bilaterally) was injected to male SD rats through intracerebroventricular (ICV) route. Drug treatment was started just after streptozocin administration and continued for 3 weeks. The rats were killed on the 21st day following the last behavioral test, and cytoplasmic fractions of the hippocampus and pre-frontal cortex were prepared for the quantification of acetylcholinesterase, oxidative stress parameter, mitochondrial enzymes activity and histological examination. Tramadol (5, 10 and 20 mg/kg, i.p.) was used as a treatment drug, and memantine (10 mg/kg, i.p.) was used as a standard. Tramadol significantly attenuated behavioral, biochemical, mitochondrial and histological alterations at low (5 mg/kg) and intermediate (10 mg/kg) dose, suggesting its neuroprotective potential in ICV-STZ-treated rats. Further, the neuroprotective effect of tramadol (10 mg/kg) was comparable to memantine (10 mg/kg). In conclusion, our results indicate the effectiveness of tramadol in preventing ICV-STZ-induced cognitive impairment as well as mito-oxidative stress. Further, these findings reveal the possibility of MOR agonist as a therapeutic approach for sporadic Alzheimer disease.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AChE:
-
Acetylcholinesterase
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- BBB:
-
Blood brain barrier
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- CA-1:
-
Cornus Ammonis-1
- DTNB:
-
5,5′-Dithio-bis-[2-nitrobenzoic acid
- EGTA:
-
Ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid
- GABA-A:
-
Gamma-aminobutyric acid-A
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- HEPES:
-
4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid
- i.p.:
-
Intraperitoneal
- ICV-STZ:
-
Intracerebroventricular-streptozocin
- MORs:
-
Mu-opioid receptors
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- NAD+:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- NMDA:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- sAD:
-
Sporadic Alzheimer disease
- SDH:
-
Succinate dehydrogenase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substance
- TSTQ:
-
Time spent in target quadrant
References
Ansari MA, Scheff SW (2010) Oxidative stress in the progression of Alzheimer disease in the frontal cortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69:155–167
Balaban RS, Nemoto S, Finkel T (2005) Mitochondria, oxidants, and aging. Cell 120:483–495
Ballinger SW (2005) Mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiovascular disease. Free Radic Biol Med 38:1278–1295
Bradford HF, Crowder JM, White EJ (1986) Inhibitory actions of opioid compounds on calcium fluxes and neurotransmitter release from mammalian cerebral cortical slices. Br J Pharmacol 88(1):87–93
Brown MR, Sullivan PG, Dorenbos KA, Modafferi EA, Geddes JW, Steward O (2004) Nitrogen disruption of synaptoneurosomes: an alternative method to isolate brain mitochondria. J Neurosci Methods 137:299–303
Butterfield DA et al (1999) Elevated oxidative stress in models of normal brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci 65:1883–1892
Chartoff EH, Connery HS (2014) It's MORe exciting than mu: crosstalk between mu opioid receptors and glutamatergic transmission in the mesolimbic dopamine system. Front Pharmacol 5:116
Correia SC et al (2012) Insulin signaling, glucose metabolism and mitochondria: major players in Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes interrelation. Brain Res 2:64–78
Dhull DK, Bhateja D, Dhull RK, Padi SS (2012) Differential role of cyclooxygenase isozymes on neuronal density in hippocampus CA1 region of intracerebroventricular streptozotocin treated rat brain. J Chem Neuroanat 43:48–51
Ding YQ, Kaneko T, Nomura S, Mizuno N (1996) Immunohistochemical localization of mu-opioid receptors in the central nervous system of the rat. J Comp Neurol 367(3):375–402
Eckert A, Schmitt K, Götz J (2011) Mitochondrial dysfunction—the beginning of the end in Alzheimer’s disease? Separate and synergistic modes of tau and amyloid-β toxicity. Alzheimers Res Ther 3:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/alzrt74
El-Hamid Mohamed Elwy A, Tabl G (2017) Impact of tramadol and morphine abuse on the activities of acetylcholine esterase, Na +/K + —ATPase and related parameters in cerebral cortices of male adult rats. Electron Phys 9:4027–4034
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Feather-Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Faria J, Barbosa J, Queiros O, Moreira R, Carvalho F, Dinis-Oliveira RJ (2016) Comparative study of the neurotoxicological effects of tramadol and tapentadol in SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicology 360:1–10
Frossi B, Tell G, Spessotto P, Colombatti A, Vitale G, Pucillo C (2002) H(2)O(2) induces translocation of APE/Ref-1 to mitochondria in the Raji B-cell line. J Cell Physiol 193:180–186
Garzón J, Rodríguez-Muñoz M, Sánchez-Blázquez P (2012) Direct association of Mu-opioid and NMDA glutamate receptors supports their cross-regulation: molecular implications for opioid tolerance. Curr Drug Abuse Rev 5(3):199–226
Gibson GE, Shi Q (2010) A mitocentric view of Alzheimer’s disease suggests multi-faceted treatments. J Alzheimer’s Dis JAD 20:2010–100336
Gornall AG, Bardawill CJ, David MM (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem 177:751–766
Grammas P (2011) Neurovascular dysfunction, inflammation and endothelial activation: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 8:1742–2094
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15 N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138
Grond S, Sablotzki A (2004) Clinical pharmacology of tramadol. Clin Pharmacokinet 43:879–923
Grunblatt E, Salkovic-Petrisic M, Osmanovic J, Riederer P, Hoyer S (2007) Brain insulin system dysfunction in streptozotocin intracerebroventricularly treated rats generates hyperphosphorylated tau protein. J Neurochem 101:757–770
Hara K, Minami K, Sata T (2005) The effects of tramadol and its metabolite on glycine, gamma-aminobutyric acidA, and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Anesth Analg 100:1400–1405
Hartrick CT, Rozek RJ (2011) Tapentadol in pain management: a mu-opioid receptor agonist and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor. CNS Drugs 25:359–370
Hosseini-Sharifabad A, Rabbani M, Sharifzadeh M, Bagheri N (2016) Acute and chronic tramadol administration impair spatial memory in rat. Res Pharm Sci 11(1):49–57
Hoyer S (1995) Age-related changes in cerebral oxidative metabolism. Implications for drug therapy. Drugs Aging 6:210–218
Javed H et al (2012) Rutin prevents cognitive impairments by ameliorating oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in rat model of sporadic dementia of Alzheimer type. Neuroscience 210:340–352
Kahn LH, Alderfer RJ, Graham DJ (1997) Seizures reported with tramadol. JAMA 278(20):1661
King TE (1967) Preparation of succinate dehydrogenase and reconstitution of succinate oxidase. In: Estabrook R, Pullman M (eds) Methods in enzymology. Academic, New York, pp 322–331
King TE, Howard RL (1967) Preparations and properties of soluble NADH dehydrogenases from cardiac muscle. In: Estabrook R, Pullman M (eds) Methods in enzymology. Academic, New York, pp 275–294
King’s College London (2015) WAR. The global impact of dementia
Kitamura A, Higuchi K, Okura T, Deguchi Y (2014) Transport characteristics of tramadol in the blood-brain barrier. J Pharm Sci 103:3335–3341
Kono Y (1978) Generation of superoxide radical during autoxidation of hydroxylamine and an assay for superoxide dismutase. Arch Biochem Biophys 186:189–195
Kumar A, Ekavali, Mishra J, Chopra K, Dhull DK (2016) Possible role of P-glycoprotein in the neuroprotective mechanism of berberine in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced cognitive dysfunction. Psychopharmacology 233:137–152
Lazarov O, Marr RA (2010) Neurogenesis and Alzheimer’s disease: at the crossroads. Exp Neurol 223:267–281
Lehmann KA (1997) Tramadol in acute pain. Drugs 2:25–33
Liao D, Lin H, Law PY, Loh HH (2005) Mu-opioid receptors modulate the stability of dendritic spines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(5):1725–1730
Liao D, Grigoriants OO, Loh HH, Law PY (2007) Agonist-dependent postsynaptic effects of opioids on miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents in cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 97(2):1485–1494
Liu Y, Peterson DA, Kimura H, Schubert D (1997) Mechanism of cellular 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction. J Neurochem 69:581–593
Mansour A, Fox CA, Burke S, Meng F, Thompson RC, Akil H, Watson SJ (1994) Mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptor mRNA expression in the rat CNS: an in situ hybridization study. J Comp Neurol 350(3):412–438
Martin G, Nie Z, Siggins GR (1997) mu-Opioid receptors modulate NMDA receptor-mediated responses in nucleus accumbens neurons. J Neurosci 17(1):11–22
Mehla J, Pahuja M, Gupta YK (2013) Streptozotocin-induced sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: selection of appropriate dose. J Alzheimer’s Dis JAD 33:17–21
Mintzer MZ, Lanier RK, Lofwall MR, Bigelow GE, Strain EC (2010) Effects of repeated tramadol and morphine administration on psychomotor and cognitive performance in opioid-dependent volunteers. Drug Alcohol Depend 111:265–268
Morales I, Guzman-Martinez L, Cerda-Troncoso C, Farias GA, Maccioni RB (2014) Neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. A rational framework for the search of novel therapeutic approaches. Front Cell Neurosci 8:112
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
Ostermeier AM, Schlösser B, Schwender D, Sutor B (2000) Activation of mu- and delta-opioid receptors causes presynaptic inhibition of glutamatergic excitation in neocortical neurons. Anesthesiology 93(4):1053–1063
Pagani L, Eckert A (2011) Amyloid-Beta interaction with mitochondria. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:925050. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/925050
Pandanaboina SC, Rajbanshi SL, Kunala PN, Pandanaboina S, Pandanaboina MM, Gopalreddy V, Wudayagiri R (2012) Tramadol safety—cholinergic system of rat brain without nociception. Acta Pol Pharm 69:833–841
Paxinos GWC (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Prince M (2015) World Alzheimer's Report-2015. The Global Impact of Dementia. https://www.alz.co.uk/research/world-report-2015. Accessed 12 July 2017
Raffa RB, Stone DJ Jr (2008) Unexceptional seizure potential of tramadol or its enantiomers or metabolites in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 325:500–506
Sbrenna S, Marti M, Morari M, Calo G, Guerrini R, Beani L, Bianchi C (1999) L-glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid efflux from rat cerebrocortical synaptosomes: modulation by kappa- and mu- but not delta- and opioid receptor like-1 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 291(3):1365–1371
Salkovic-Petrisic M, Hoyer S (2007) Central insulin resistance as a trigger for sporadic Alzheimer-like pathology: an experimental approach. J Neural Transm Suppl 72:217–233
Salkovic-Petrisic M, Tribl F, Schmidt M, Hoyer S, Riederer P (2006) Alzheimer-like changes in protein kinase B and glycogen synthase kinase-3 in rat frontal cortex and hippocampus after damage to the insulin signalling pathway. J Neurochem 96:1005–1015
Scott LJ, Perry CM (2000) Tramadol: a review of its use in perioperative pain. Drugs 60:139–176
Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Masliah E, Hyman BT (2011) Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 1(1):a006189
Shoham S, Bejar C, Kovalev E, Weinstock M (2003) Intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin causes neurotoxicity to myelin that contributes to spatial memory deficits in rats. Exp Neurol 184:1043–1052
Shoham S, Bejar C, Kovalev E, Schorer-Apelbaum D, Weinstock M (2007) Ladostigil prevents gliosis, oxidative-nitrative stress and memory deficits induced by intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin in rats. Neuropharmacology 52:836–843
Smith-Swintosky VL, Mattson MP (1994) Glutamate, beta-amyloid precursor proteins, and calcium mediated neurofibrillary degeneration. J Neural Transm Suppl 44:29–45
Sofic E, Salkovic-Petrisic M, Tahirovic I, Sapcanin A, Mandel S, Youdim M, Riederer P (2015) Brain catalase in the streptozotocin-rat model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease treated with the iron chelator-monoamine oxidase inhibitor, M30. J Neural Transm 122:559–564
Sottocasa GL, Kuylenstierna B, Ernster L, Bergstrand A (1967) An electron-transport system associated with the outer membrane of liver mitochondria. A biochemical and morphological study. J Cell Biol 32:415–438
Swerdlow RH (2011) Brain aging, Alzheimer’s disease, and mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta 12:2
Tahirovic I et al (2007) Reduced brain antioxidant capacity in rat models of betacytotoxic-induced experimental sporadic Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes mellitus. Neurochem Res 32:1709–1717
Wang X, Su B, Zheng L, Perry G, Smith MA, Zhu X (2009) The role of abnormal mitochondrial dynamics in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 1:153–159
Wang X, Wang W, Li L, Perry G, Lee HG, Zhu X (2014) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 8:1
Wills ED (1966) Mechanisms of lipid peroxide formation in animal tissues. Biochem J 99:667–676
Yang TT, Hung CF, Lee YJ, Su MJ, Wang SJ (2004) Morphine inhibits glutamate exocytosis from rat cerebral cortex nerve terminals (synaptosomes) by reducing Ca2+ influx. Synapse 51(2):83–90
Zhu W, Pan ZZ (2004) Synaptic properties and postsynaptic opioid effects in rat central amygdala neurons. Neuroscience 127(4):871–879
Zhu W, Pan ZZ (2005) Mu-opioid-mediated inhibition of glutamate synaptic transmission in rat central amygdala neurons. Neuroscience 133(1):97–103
Zhu X, Raina AK, Lee HG, Casadesus G, Smith MA, Perry G (2004) Oxidative stress signalling in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 12:1–2
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank the financial support of Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (09/135/705/2014- EMR-I), New Delhi, India, for carrying out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhull, D.K., Kumar, A. Tramadol ameliorates behavioural, biochemical, mitochondrial and histological alterations in ICV-STZ-induced sporadic dementia of Alzheimer’s type in rats. Inflammopharmacol 26, 925–938 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0431-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-017-0431-3