Abstract
The Regional Coordinating Unit of the Convention for Co-operation in the Protection and Development of the Marine and Coastal Environment for West and Central Africa (the Abidjan Convention) has under its wings several multilateral environmental agreements including those addressing shipping pollution. Shipping, potentially, has negative impacts on marine fauna and flora and air quality, with implications for public health. The Regional Coordinating Unit seeks to strengthen implementation of the Abidjan Convention by party-states through co-operation with state actors using various pathways based on its internal resources and competencies but the Unit is also starting to explore engagement with potential non-state actors. The ability of the Unit to exert influence on implementation is constrained by domestic politico-administrative institutions. This paper seeks to understand the influence of the Regional Coordinating Unit on the implementation of the Abidjan Convention in the field of shipping pollution. It uses three theoretical perspectives for the analysis: the influence of international environmental bureaucracies, domestic regulatory-politics and transnational governance. The paper shows how these theories are complementary because the influence of international bureaucracies such as the Regional Coordinating Unit cannot be adequately understood through factors internal to their organisation alone but needs to be analysed in relation also to external factors, both domestic politico-institutional ones in states that international bureaucracies work with, and the role of relevant non-state actors in the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements. It is concluded that, although influence cannot be measured directly, it is likely that Regional Coordinating Unit’s influence through its autonomy-centred efforts are quiet strong but negatively constrained by the traditional state-centric responsibility for implementation of international legal instruments where domestic regulatory-politics lack sufficient political will and support from and engagement with non-state actors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The Convention for Co-operation in the Protection and Development of the Marine and Coastal Environment for the West and Central Africa (WCA) Region, referred to as the Abidjan Convention, is a treaty adopted in 1981 (UNEP 1981) catalysed by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). The treaty is a comprehensive regional legal framework agreement for preventing marine pollution in WCA region through inter-governmental co-operation and lists shipping pollution as one of its foci. The Abidjan Convention is a regionally specific agreement that takes an integrative approach through putting many other agreements under its wings.
Party-states (from now on Parties) to the Convention designated UNEP as its secretariat and established a small Regional Coordinating Unit (RCU) based in the city of Abidjan to support and strengthen national regulatory measures for its implementation. Within the context of Biermann and Siebenhüner’s (2009) analytical conceptualisation of secretariats for multilateral environmental agreements as international bureaucracies as well as Dessai’s (2010) model of multilateral environmental agreement secretariats, the RCU reflects the characteristics of both a treaty secretariat and an international bureaucracy. This is depicted in Table 1. It was referred to as a ‘one-man show’ by its coordinator during the Ninth Conference of Parties in 2011 in Accra, Ghana, as he was the only staff then. However, it has since been resourced with permanent offices in Abidjan by the government of Ivory Coast (Cote d’Ivoire in French) and complementary staff. The RCU can thus be distinguished as a secretariat within UNEP much in the same way as the smaller secretariats linked to the Montreal Protocol (Bauer 2009a) and the UN Convention on Desertification (Bauer 2009b).
The implementation of Abidjan Convention has been slow and its performance rather staggering (UNEP 2005a). However, the Seventh Conference of Parties took decisions (UNEP 2005a: six; UNEP 2005b:78)Footnote 1 in 2005 to have it revitalised, strengthen its implementation and make the RCU autonomous and effective. This paper seeks to analyse the ability of the RCU as an international bureaucracy to strengthen the implementation of the Abidjan Convention, particularly on preventing pollution from shipping, by exerting influence on the behaviour of Parties. Shipping, potentially, has negative impacts on marine fauna and flora and air quality, with implications for public health. It is associated with ballast water discharge, which is a source for the transfer of marine invasive species; operational and accidental oil spills, which can have detrimental consequences on marine fauna and flora; ship-generated and hazardous wastes, which require adequate collection and treatment facilities in ports, to avert soil, air and water pollution and consequent negative public health effects (see Van Wingerde 2015); and air pollution, that impact air quality. The impacts are prevented and addressed through international marine environment agreements, particularly those of the International Maritime Organisation. However, due to lacks in human, technological, finance and infrastructure capabilities, WCA ports have gaps in complying with the international regulations.
This paper focuses on two of the shipping pollution sources—ballast water and oil spills. These two sources have regional policies and regulations translated from relevant international regulations for implementation under the Abidjan Convention. Two questions are investigated. First, how does the RCU influence the implementation of the Abidjan Convention, with regard to shipping pollution prevention from ballast water and oil spill? Second, what are the constraints to and opportunities for strengthening RCU’s influence on implementation of the Convention?
This paper combines Biermann and Siebenhüner’s (2009) concept of influence of international bureaucracies and Raustiala’s (1997) regulatory-politics framework with the transnational governance perspective as a conceptual framework. The motivation for this is that understanding the influence of international bureaucracies in the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements goes beyond factors internal to the organisation of international bureaucracies alone but needs to be analysed in relation also to external factors: both domestic politico-institutional ones in states that international bureaucracies work with (Raustiala 1997; Bauer et al. 2009), and the role of relevant non-state actors in the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements (Andonova et al. 2009; Okereke et al. 2009; Abbott 2012; Kuyper and Bäckstrand 2016). The concept of non-state actors is used to mean all actors operating at sub-national, national and across borders who are not associated with national government, the state. This includes, for example, port authorities and environmental non-governmental organisations.
The RCU and four Parties to Abidjan Convention—Cameroon, Ghana, Ivory Coast and Nigeria—with their respective port authorities of Douala, Tema, Abidjan and Lagos are used as case studies of RCU influence. These Parties have all served on the bureau of the Convention in various capacities. Additionally, with their dependence on oil import to meet domestic energy needs, their ports face similar shipping pollution risks from ballast water and oil spill. Data collection involved a mix of face-to-face semi-structured interviews and distributed questionnaire. These were conducted and administered during Abidjan Convention’s Ninth and Tenth Conference of Parties meetings in Accra, 2011 and Pointe Noire, 2012, respectively; the First Panel of Experts’ Meeting on Strategic Assessment of Port Environmental Issues, Policies and Programmes (SAPEIPP) in WCA, in Abidjan, 2015; and visits to the selected ports. Key informants included officials of the RCU, UNEP, Interim Guinea Current Commission, Port Management Association of West and Central Africa (PMAWCA), National Focal Points of the Abidjan Convention from case study Parties and the International Maritime Organisation’s Regional Representative in Accra, as well as Environmental Managers of port authorities of case study Parties. All respondents were guaranteed anonymity and therefore their responses are identified by institutional affiliation. We also draw upon our own observations during meetings and field visits. The first author’s role in Ports Environmental Network-Africa (PENAf)Footnote 2 facilitated his participation in Conference of Parties meetings and co-organising SAPEIPP. Finally, the paper relies on review of primary and secondary sources of information, including relevant literature, reports and working documents of the RCU, and governments and port authorities.
The next section introduces the conceptual framework for the study. It is followed by the results of the analysis of RCU’s influence, potential opportunities for how that influence can be strengthened and finally discussing the results and drawing some conclusions.
2 Conceptualising influence: international bureaucracies and MEA implementation
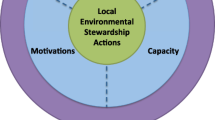
Three different theoretical perspectives: ‘autonomy-centred’, ‘regulatory-politics’ and ‘transnational governance’ are combined in a re-conceptualised framework for analysing the ability of international bureaucracies to exert influence on implementation of multilateral environmental agreements. Biermann and Siebenhüner (2009) characterise three ‘autonomy-centred’ pathways: cognitive, normative and executive in analysing how international bureaucracies exert influence. These pathways relate to factors internal to the organisation of international bureaucracies, specifically, their resources and competencies (Bauer et al. 2009). However, there are external factors that influence the ability of international bureaucracies to exert influence. First, international bureaucracies ‘act within a chain of principal–agent relationship’, with states as principals and international bureaucracies as agents (Bauer et al. 2009: 27). This is associated with ‘regulatory-politics’ (Raustiala 1997) in domestic settings that can constrain the influence of international bureaucracies on implementation. Second, non-state actor constellations operate beyond borders and engage with regional and international environmental governance through ‘transnational governance’ approaches (Pattberg et al. 2011; Biermann and Pattberg 2012; Duffy 2013). Such approaches could be potentially relevant for strengthening efforts of international bureaucracies in implementing multilateral environmental agreements. In summary, domestic factors and non-state actor interactions across borders may influence the ‘uptake’ of efforts by international bureaucracies to strengthen implementation of multilateral environmental agreements. The following subsections describe each of the three theoretical perspectives in turn (Fig. 1).
2.1 Autonomy-centred influence of international bureaucracies
Biermann and Siebenhüner (2009) synthesise three notions to conceptualise the ‘autonomy-centred’ perspective of the influence of international bureaucracies. Cognitive elements of social constructivists (Barnett and Finnemore 1999), normative elements from regime theorists (Young 1982) and capacity-building notions from principal-agent theorists (see Pollack 1997; Hawkins et al. 2006) are used in classifying three analytical pathways of the influence of international bureaucracies in global environmental governance, relating to environmental protection—cognitive, normative and executive. International bureaucracies are in this way conceptualised as ‘analytically apart from the collectivity of member-states of international organisations’ (Bauer et al. 2012). The analytical pathways are specifically applied to the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements in this study.
Cognitive pathway: International bureaucracies as knowledge brokers conduct scientific studies on specific environmental issues to generate information, which are disseminated to all kinds of actors including states and non-state actors. International bureaucracies thereby create convergence around policy-relevant solutions and influence the interest and behaviour of actors towards specific environmental issues in international environmental governance. The taking up and using of such information and knowledge by relevant actors ultimately raises the prospects of the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements (Miles et al. 2001).
Normative pathway International bureaucracies facilitate international discussions and negotiations among actors in international governance arenas on specific environmental issues. In the process, international bureaucracies influence which actors participate in negotiations, define and drive policy agenda, and draft decisions. They in effect shape inter-governmental co-operation and the institutionalisation of specific environmental issues and solutions. Even though international bureaucracies may not be key players during international negotiations, their influence can be substantial (Young 1994).
Executive pathway Through the provisioning of direct assistance in the form of trainings and workshops for national actors, international bureaucracies support capacity building for local and national level implementation of multilateral environmental agreements and decisions at negotiations (Widerberg and van Laerhoven 2014). Stronger administrative and regulatory capacities better position states to implement multilateral environmental agreements (Biermann and Siebenhüner 2009).
2.2 Regulatory-politics and state receptivity to the influence of international bureaucracies
States are assumed to negotiate multilateral environmental agreements in good faith and expected to implement them (Chayes and Chayes 1993), but domestic regulatory processes determine implementation. Using the divergent responses by UK and USA to the United Nations Convention of Biological Diversity regime, Raustiala (1997) theorises the interplay of three domestic variables—domestic institutions, societal actors and political commitment—as ‘regulatory-politics’ that influence state choice towards the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements.
Domestic institutions are structured and supported by varying political systems. The regulatory arrangements that flow from them constrain or enhance measures for the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements by governments.
Societal actors include firms and environmental organisations who lobby governments in line with their interests, but whose expectations are determined by regulatory processes for domestic implementation of multilateral environmental agreements.
Political commitment of governments to the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements can be undermined by economic development. Governments use resources towards what favours their agenda. Those focusing on environmental benefits may comply with obligations to multilateral environmental agreements, while others concerned with immediate economic benefits may deviate in compliance.
The domestic variables point to the centrality of domestic institutions in the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements and could constrain the uptake of measures of international bureaucracies. Although Raustiala (1997) does not consider the role of international bureaucracies, possibly because of a focus on OECD countries where domestic capacity is not a constraint for the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements, in many non-OECD countries, weak implementation mechanisms for multilateral environmental agreements (Gray 2003) means they rely on the support of international bureaucracies for implementation (Biermann and Siebenhüner 2013).
2.3 Transnational governance prospects for the influence of international bureaucracies
A state-centric inter-governmental approach to global environmental governance, where multilateral environmental agreements are developed and implemented primarily by states, is limiting both in theoretical and empirical terms. It can be slow and cumbersome in addressing complex transnational environmental problems (Tatenhove and Leroy 2003; Biermann and Pattberg 2012), particularly where the willing co-operation of societal actors directly engaged in the causation or prevention of environmental degradation is required. As shown in climate discussions, when the implementation ambition for multilateral environmental agreements by governments is too weak due to lack of political will, non-state actors may fill the ‘gap’ in regulatory ambition (Pattberg and Stripple 2008; Bulkeley and Newell 2010; Dellas et al. 2011). The literature on transnational governance re-conceptualises the increasing relevance of border-spanning private and public–private approaches, using two central elements. First, there is agency beyond the state, which emphasises the contribution (positive and negative) of different actors and the source of authority outside the domain of states and inter-governmental arrangements to address environmental problems. Second, there is architecture, which highlights institutional arrangements, inter-linkages, principles and mode of steering among the different actors. These elements add new dimensions to how the influence of international bureaucracies on the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements can be externally influenced.
3 RCU and three autonomy-centred pathways
This section explores the ability of the RCU to influence the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements through the three autonomy-centred parts of the conceptual framework. That is, the cognitive, normative and executive pathways of the RCU in influencing behavioural change among Parties towards ballast water and oil spill in preventing shiping pollution.
3.1 Cognitive pathway: brokering knowledge
The RCU generates and disseminates knowledge, and raises awareness to inform the understanding of Parties on marine environment issues. It has been involved in the preparation of the WCA component of the Marine Biodiversity Assessment Outlook Report,Footnote 3 which provided information on and flagged the rise in invasive species often from ships’ ballast water. Potential dangers associated with ships’ ballast water have been addressed under the Guinea Current Large Marine Ecosystem project initiated under the framework of the Abidjan Convention. The project undertook surveys to identify and evaluate WCA’s shared marine environment concerns and framed policy responses for reversing the degradation of the region’s marine and coastal environment (Ibe and Sherman 2002). Under the project, a regional strategic action plan for ballast water management (regional ballast water action plan) was developed in partnership with GloBallastFootnote 4 (IGCC 2009a). The regional ballast water action plan is a framework for minimising the transfer of invasive aquatic organisms in the Abidjan Convention region in line with International Maritime Organisation’s International Convention on the Management of Ships’ Ballast Water and Sediments (ballast water convention). Additionally, large amounts of data and information on marine pollution from oil spills have been generated in which the RCU under UNEP has been involved. These have included WCA marine pollution studies one (WACAF/1) on the institution and coordination of national contingency plans, and development of a regional oil spill contingency plan (UNEP 2011a), in collaboration with the International Maritime Organisation under the Global Initiative for West, Central and Southern Africa (GI-WACAF).Footnote 5
Information shared by the RCU was mostly circulated among national focal points, who are designated national representatives such as environment ministry or agencies, to Abidjan Convention’s Conference of Parties with responsibility for coordinating national implementation efforts. It seems not to have been much further shared with, e.g. port authorities who are key actors.
Beyond generating information and knowledge, the RCU maintains a webpage. The webpage links that of UNEP and other UN and international organisations from which scientific findings on regional seas including those on shipping pollution can be accessed. The actual use of the RCU webpage and by whom was not possible to ascertain. The RCU acknowledged its low visibility and had engaged a communication specialist to improve the situation. It was also working together with IOC/ODINAFRICAFootnote 6 on a regional data exchange and information management. Nonetheless, the potential for cognitive influence of the RCU is quite strong.
3.2 Normative pathway: facilitating negotiations
The RCU coordinates Abidjan Convention’s action plan through the facilitation of inter-governmental discussions and negotiations on courses of action towards implementation. In doing this, the RCU prepares documents, translates, communicates and operationalises decisions made by national focal points, ministerial committees, extraordinary and Conference of Parties meetings.
Following decision by Parties at the Seventh Conference of Parties meeting in 2005 to revitalise and strengthen the Convention, (UNEP 2005a: 6, b:78)Footnote 7 the RCU facilitated consultations and stakeholder meetings with key actors implementing marine and coastal programmes and projects in the Convention region to gather recommendations on how to proceed. The RCU further organised a review of recommendations by the ministerial committee, which were adopted by Parties at the Eighth Conference of Parties meeting in 2007 (UNEP 2008).Footnote 8 Subsequently, the RCU organised the first extraordinary meeting of Parties in June 2008 to approve recommendations for the revitalisation process (UNEP 2009).Footnote 9 The organisation of these meetings showed the RCU’s ability to bring a variety of actors together. Parties, non-Parties and non-state actors as, the African Union, and the IUCN were present.
The RCU also collaborated with the International Maritime Organisation in 2007 to bring together legal and technical experts on the revision of the Convention’s first Protocol, the Protocol Concerning Co-operation in Combating Marine Pollution in Cases of Emergency. This was to make provision for monitoring mechanisms, reporting and dissemination of pollution information (UNEP 2011b) for enforcing implementation and compliance with International Maritime Organisation’s International Convention on Oil Pollution Preparedness, Response and Co-operation (OPRC). The collaboration culminated in the Protocol’s amendment, adoption of the regional oil spill contingency plan,Footnote 10 and the creation of a regional centre for coordination in cases of emergencyFootnote 11 at the Ninth Conference of Parties meeting (UNEP 2011b).Footnote 12 Parties are required to adopt the regional oil spill contingency plan into national contingency plans and subsequently, sub-national contingency plans by actors having oil-handling facilities, such as ports. Though the ballast water was then yet to come into force, technical experts from Parties—mostly national focal points—and international partners were brought together at several meetings including those in Accra, 2006; Accra, 2009; and Lagos, 2010, to harmonise and synthesise ballast water actions and procedures under the Guinea Current Large Marine Ecosystems project. The meetings adopted the regional ballast water action plan (IGCC 2009a) in Abidjan in 2009 (IGCC 2009b) and revised it in Lomé in 2011 (GCLME 2011). Parties are required to develop monitoring and enforcement programmes in their ports to implement the regional ballast water action plan. The plan is, however, yet to be adopted by Abidjan Convention’s Conference of Parties. Altogether, RCU’s potential for normative influence can be said to be very strong despite its limited size.
3.3 Executive pathway: capacity building
Efforts at training and technical assistance to strengthen skills and competencies of Parties started in earnest at the coming into force of the Convention, but faded earlier than anticipated due to inadequate funding. Parties did not honour their commitment to the trust fund set up to replace UNEP’s catalytic funding for capacity-building efforts (UNEP 2005a). However, through RCU’s collaboration with a number of multilateral partners, some technical assistance and trainings continue to be delivered. Collaboration with International Maritime Organisation’s Technical Co-operation Programme has for instance supported some Parties to consolidate their various marine environment regulations into a comprehensive marine pollution legislation (personal communication, Accra, 2011). Similar collaboration with the OSPAR Commission has delivered workshops and trainings on marine pollution including those from oil spills. The International Maritime Organisation and GloBallast partnership under the Guinea Current Large Marine Ecosystem project has also organised a number of ballast water workshops to strengthen regional and national capacity to ensure protection from marine invasive species.
The trainings and workshops have mostly targeted national focal points and other state bureaucrats. However, officials from Douala and Tema ports participated in the 2009 ballast water workshops in Accra and Abidjan (personal communication, Tema, 2014). The potential for RCU’s executive influence has been generally weak.
In sum, the RCU is making efforts to influence shipping pollution prevention with measures for ballast water and oil spill. However, while the potential for RCU’s cognitive effort is quite considerable, its normative effort is very strong. Nonetheless, its executive effort is generally weak. Put together, RCU’s autonomy-centred efforts can be said to be inadequate.
4 National regulatory-politics
We now turn to the regulatory-politics part of our analytical framework to analyse the receptivity and uptake of measures from RCU’s efforts by parties through the interplay of their domestic institutions, interests of societal actors and political commitment.
4.1 Domestic institutions
The domestic politico-administrative institutions of Parties to the Abidjan Convention share a state-centric approach but have core differences among them. Two political systems, presidential and parliamentary, are predominant on a continuum ranging from hierarchical and highly centralised to flexible and decentralised. The presidential system of Cameroon and Ivory Coast combines decentralisation with authoritarian traits into a political hybrid (Ottaway 2003) with hierarchical and highly centralised institutions after a typical French model (King 1976). The presidential system of Nigeria has decentralised and fragmented institutions (Ottaway 2003) and is typical of US’s ‘separated institutions sharing powers’ (Neustadt 1990). Serving as a contrast to the two different presidential systems is Ghana’s parliamentary system, which has decentralised and yet fused institutions with flexibility, in political integration (Ottaway 2003). Ghana’s system is similar to the British system (see Raustiala 1997).
The different institutional arrangements affect the coordination needed for implementing RCU’s measures. Cameroon for instance has the Ministry of Environment and Nature Protection (MinENP) as its national focal point. MinENP’s coordinating mechanisms across parallel and hierarchical institutions are ineffective. Formal responsibility for the national oil spill contingency plan is split between MinENP and the Ministry of Transport via its Merchant Shipping Department and the National Ports Authority. The plan remains in draft form (personal communication, Douala, 2010; Accra, 2011). In practise, however, oil installations have sub-national plans coordinated by the National Hydrocarbons Authority, which falls under the Prime Minister’s office. Ballast water is yet to be addressed by national regulation or inspection regime.
Ivory Coast has the Ministry of Environment, Water and Forests (MinEEF) as its national focal point. MinEEF together with its agency, the Ivorian Antipollution Centre have responsibility for oil spill and ballast water. There is no documented national or sub-national oil spill contingency plan, though the Ivorian Antipollution Centre and some private oil operators have some response equipment (personal communication, Accra/Abidjan, 2012/2015, respectively). Furthermore, there is no action yet on ballast water.
Nigeria has the National Environmental Standards Regulations and Enforcement Agency (NESREA) as its national focal point. However, responsibility for oil spill lies with multiple decentralised institutions. The Nigeria Maritime Administration and Safety Agency (NIMASA) has responsibility for spills beyond three nautical miles, while the National Oil Spill Detection and Response Agency (NOSDRA) takes charge for spills on land and inland waters. Despite functional overlaps, there is collaboration between NIMASA and NOSDRA. They hold periodic joint exercises to test response preparedness (personal communication, Lagos 2012). Ballast water is regulated by NIMASA and it was the first domestic institution among Parties to the Abidjan Convention to develop national ballast water regulation in 2011, in line with the regional ballast water plan and International Maritime Organisation’s ballast water convention, which had then not come into force.
Ghana’s Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is its national focal point. The Ghana Maritime Authority is the competent authority for shipping pollution but due to lack of capacity, the EPA mostly leads to co-ordination and collaboration. The EPA operates by a co-management approach that involves both state and non-state actors. It has oversight responsibility for national and sub-national contingency plans and organises periodic response preparedness exercises. In addition, a national ballast water regulatory framework implementing the regional ballast water action plan and International Maritime Organisation’s ballast water convention was adopted in 2013.
The differing political systems coupled with uncoordinated national institutions leave Parties to the Abidjan Convention with a shared difficulty in the implementation of negotiated measures. The centralised systems leave state actors pursuing their own interests and potentially marginalising the values and interests of sub-national and local actors who can contribute to implementation. The decentralised systems also do not share coordinated implementation mechanisms and leave disparities between approaches and motivations for on-the-ground implementation.
In sum, although Parties to the Abidjan Convention are collectively architects of the Convention, their heterogeneous political systems and varying domestic regulatory processes may constrain the receptivity and uptake of RCU’s measures for preventing shipping pollution.
4.2 Societal actors
A strong constituency for marine and coastal management among scientists and public officials in the Abidjan Convention region has long been asserted (Peart et al. 1999) but few actors engage in the field of shipping pollution. Potentially interested businesses and environmental non-governmental organisations have been relatively uninvolved and invisible. Port terminal operators are mostly pursuing environmental interests to obtain operational profits rather than for preventing shipping externalities. Similarly, civil society organisations mostly concern themselves with tourism, oil and gas, and fishing (see Mundus Maris 2013) and not shipping. Governments of Parties, including cases studied in this paper, are therefore barely lobbied by societal actors on the issue of preventing shipping pollution. Decentralisation is said to be enhancing policy participation in Africa (Crook 2003), but there is little to show in the field of shipping pollution. Incipient environmental mobilisations concerning shipping have been in the form of sporadic protests on toxic waste shipments to Koko port in Nigeria in 1988 (Ayobayo 2014) and Abidjan port in 2006 (Leigh 2009), and vessel dumping in Tema in 2000 and 2011 (personal communication, Tema 2012). These mobilisations have predominantly focused on pressing for compensation payment and livelihood security.
The low-level engagement of societal actors on shipping prevention implies that there is not much external pressure on the state and its politico-administrative mechanisms to implement the Abidjan Convention and engage with RCU’s efforts to increase the Convention’s implementation.
4.3 Political commitment
Parties studied, like many others in WCA, were beset with socio-economic decline during the 1980s, the period when the Convention was adopted. To reverse their declining situation, the Parties turned to the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank for structural adjustment programmes linked with conditionalities that constrained their policy-choices. The governments lost their policy-autonomy (see Ikpeze et al. 2004: 356) wilfully transferring domestic economic policy-making to donors (Akonor 2006). As observed by De Melo and Tsikata (2015), unequal resource endowment lowers the needed compromise for common policies towards externalities and leads to differential policy preferences. Parties studied are endowed with oil. While Nigeria is Africa’s largest producer oil producer, Ghana has quite substantial prospects (KPMG 2014). Both have developed national oil spill contingency plans with sub-plans for their ports, Lagos and Tema, respectively. Cameroon became a modest oil exporter in 1977 and has its production declining since 1985 due to maturing fields (Daly 2012). It has a draft national oil spill contingency plan, but has no sub-national plan for its Douala port. Ivory Coast also has modest oil endowments and known more as an oil refinery country than oil producer (Mbendi 2012). It has no documented national nor sub-national plan for its Abidjan port.
In managing ballast water, Ghana and Nigeria have adopted regulations. On the contrary, Cameroon and Ivory Coast are yet to show such commitment.
Apart from variation in adopted policies related to the implementation of the Abidjan Convention, Parties have not committed themselves to financial obligations to the trust fund for running activities of the Convention. This has been an underlying cause for the Convention’s slow and staggered performance (UNEP 2005a).
In sum, Parties have been apathetic towards Abidjan Convention’s implementation. They show no strong signs of political will. This is likely to constrain the ability of the RCU to influence the behaviour of Parties towards shipping polluting prevention.
5 Transnational governance
Next to national politics, this section uses the transnational governance part of the conceptual framework to analyse how the RCU interacts with non-state actors in its efforts for increasing the implementation of the Abidjan Convention in the area of shipping pollution. The emergence of agency beyond the state and the ensuing architecture are specifically explored.
5.1 Agency beyond the state
Beyond focusing its efforts through inter-governmental co-operation, the RCU has initiated direct dealings with non-state actors including port authorities of Parties and environmental non-governmental organisations. WCA ports are generally state-owned but most have undergone institutional reforms since the year 2000 towards public–private participation (Pálsson et al. 2007). The port authorities have thus gained more autonomy from the state with a new public–private governance character as public non-state actors. Port authorities have been working with the PENAf, an environmental non-governmental organisation that supports environmental capacity of African port authorities to co-operatively address their common environmental challenges. PENAf does not directly lobby governments but collaborates with the Port Management Association for West and Central Africa, the regional inter-governmental port organisation, in order to raise awareness and share information and to implement regionally agreed outcomes.
The RCU, using its facilitation, invited PENAf to make presentations on environmental challenges facing WCA ports at the stakeholder workshop segment of the Ninth and Tenth Conference of Parties meetings in 2011 in Accra and 2012 in Pointe Noire, respectively. Subsequently, parties in Decision CP.9/1(4) (UNEP 2011b) requested the RCU to include PENAf among its collaborative partners. The Tenth Conference of Parties meeting approved, with Decision CP.10/9, to operationalise the RCU-PENAf collaboration towards environmental capacity building for ports in the Convention region (UNEP 2012a). A Memorandum of Understanding (UNEP 2012b) was signed to that effect. National focal points interviewed at the Ninth and Tenth Conference of Parties meetings acknowledged there were gaps in the role for ports and the shipping sector in discussions and negotiations on shipping pollution. They revealed that actors from the ports sector have never been a part of Conference of Parties meetings. A review of participants list for Conference of Parties meetings confirmed this.
The RCU has operationalised its collaboration with PENAf through the organisation of the first meeting of panel of experts’ on SAPEIPP for the Abidjan Convention region in Abidjan in May 2015 (UNEP 2015). It was organised in collaboration with the Port Management Association for West and Central Africa and hosted by Abidjan port authority. The meeting was a benchmark for the engagement of ports in environmental governance in WCA, bringing together a dynamic mix of state and non-state actors led by an international (regional) bureaucracy. The participating port authorities, case study ports inclusive, shared their different environmental initiatives. Tema port had on its own volition adopted the regional ballast water action plan and initiated biological surveysFootnote 13 of its basin ahead of state regulations. The port authority did this in 2009 after participating in ballast water workshops in Accra and Abidjan. The green port concept and other forms of environmental knowledge and globalised practices were shared in the meeting by environmental professionals, academia, international organisations, from across Europe and Africa.
In sum, the port authorities and PENAf come up as emergent non-state actors with potential relevance for enhancing RCU’s effort towards shipping pollution prevention through non-state approaches outside state decisions.
5.2 Architecture
Differences in institutional arrangements and practices for implementing measures for multilateral environmental agreements, including those relating to shipping pollution got interlocked in a norm-setting and norm-implementation process at the SAPEIPP meeting in Abidjan 2015. Port authorities for the Parties studied have divergent environmental priorities, regulations and approaches contingent upon their respective national political systems. These straddle along a continuum of hierarchical top-down to co-management governance styles (see Sect. 4). However, they together prioritised four common environmental risks: ballast water, ship wastes, municipal waste and air pollution. An overarching action plan for addressing the risks was developed and adopted. The use of EcoPort tools and certificationFootnote 14 as a first-easy step towards ISO 14001 was adopted. Each port authority was tasked to nominate a contact person to work closely with national focal points for their respective countries. This was to link environmental co-operation among the ports with existing mechanisms of Abidjan Convention’s traditional inter-governmental negotiation. A declarationFootnote 15 called for commitment by the RCU in collaboration with PENAf, Port Management Association for West and Central Africa and the port authorities in a transnational arena mode (see Pattberg and Stripple 2008). It called for a steering mechanism for inter-port environmental co-operation across sub-national, national and supranational port levels to develop non-legally binding common procedures and norms, sharing of common database and harmonised policy guidelines. The declaration also called for the institutionalisation of the panel of experts and to be convened annually in an African Ports Environment Conference. Support from international organisations and development partners as International Maritime Organisation, UNEP, Africa Union, Africa Development Bank, among others was also emphasised. The declaration was approved at the Port Management Association for West and Central Africa’s Council Meeting in June 2015 in Abidjan.
In sum, the RCU is facilitating a hybrid transnational arrangement—inter-governmental, non-state actors and state actors—outside of different and non-synchronised inter-governmental co-operation. This offers potential for enabling RCU’s efforts toward shipping pollution prevention.
Altogether, transnational governance can be said to be potentially enabling for RCU’s influence towards shipping pollution prevention.
6 Discussion
The rational for this study was that, the influence of international bureaucracies could not be adequately understood through factors internal to their organisation alone. Empirical analysis of how the RCU engages in order to influence the behaviour of Parties of the Abidjan Convention towards ballast water and oil spill in preventing shipping pollution already provides some justifiable results. Table 2 presents a summary of the analysis using the framework for the study. Broadly, potential influence of the RCU as an international (regional) bureaucracy can be found to be characterised by two dynamics: existing state-centric inter-governmental co-operation and emergent transnational arena, that are nuanced with constraining and potentially enabling factors, respectively.
RCU’s existing state-centric inter-governmental co-operation gives an assumption of collective action with overriding emphasis on the role of the RCU as an international (regional) bureaucracy assisting Parties to the Abidjan Convention to realise common interests. Generating and disseminating knowledge and information by the RCU has set the agenda for framing shipping pollution prevention measures among Parties. It has shaped awareness and attention of Parties to oil spill and ballast water issues and led to the development of measures, the regional oil spill contingency plan and the regional strategic action plan for ballast water, to deal with them. In addition, the RCU initiating and facilitating a variety of discussions and negotiations in ways that makes it look like a service provider has shaped the processes for co-operation towards matters of common interest. This is particularly evident from how the RCU brought together Parties and non-Parties, regional economic communities and international actors to deliberate and decide on Abidjan Convention’s revitalisation as well as strengthening the RCU itself. These strong influences are, however, weakened by the RCU’s inability to provide adequate support for capacity building due to Parties’ lack of financial commitment. This makes the RCU’s efforts at influencing shipping pollution prevention through its internal resources and competencies rather inadequate. The lack of commitment by Parties already reveals that, next to efforts of international bureaucracies to influence Parties’ behaviour, much depends on how their efforts are received in the national politico-administrations of Parties. Ultimately, giving effect to RCU’s effort towards action on ballast water and oil spill is expressed in Parties’ receptivity and uptake of measures emanating from efforts of international (regional) bureaucracies. Therefore, understanding RCU’s influence becomes inclusive of both its internal organisational factors as well as external factors from Parties.
The receptivity and uptake of RCU’s measures by Parties is couched in heterogeneous domestic political systems. Moreover, here, presumption of equality among Parties and propensity for mutual benefit from inter-governmental co-operation becomes illusive. The uptake of RCU’s oil spill and ballast water measures varies among Parties, reflecting, e.g. lack of political will. Parties with hierarchical and highly centralised institutions as Cameroon and Ivory Coast have on one hand, to some degree, taken up oil spill measures at national and sub-national levels, but with no action on ballast water. On the other hand, Parties with decentralised institutions as Ghana and Nigeria have taken up and implemented both measures at national and sub-national levels. Evidently, Parties with modest oil endowment show less interest in Abidjan Convention’s implementation. Domestic politics therefore externally constrain the already inadequate potential influence of the RCU towards shipping pollution prevention using its internal organisational factors.
The RCU, however, knows how to exert its strongest pathway of influence, the normative pathway, through facilitating negotiations. It directs discussion processes and shapes outcomes letting it look like the idea of the Parties. This is visible in how it obtained approval of Parties at the Ninth and Tenth Conference of Parties meetings to collaborate with non-state actors connected with ports and the environment. In a countervailing effort that offsets domestic politics, the RCU ‘pushed’ Parties into giving it the mandate to move beyond traditional inter-governmental co-operation towards an emergent transnational arena with direct dealings among non-state actors across the Party-states. The new arrangement advances non-state actors’ interests and approaches that aim at independent port environmental governance responses rather than influencing the decisions of Parties. This is similar to transnational co-operation on climate change between sub-national governments, non-governmental organisations and state agencies (Andonova et al. 2009) and also, cities in climate governance (Betsil and Bulkeley 2004; Kern and Bulkeley 2009). The non-state actors are seeking to work together with core-state actors in finding practical solutions to common port environmental problems in a shift away from state-led approaches. They do not seem to be consciously set out to fill gaps in regulatory ambition of RCU’s shipping pollution measures. But the absence of established broader public–private arrangement for governing common and transboundary environmental problems faced by WCA ports creates a governance failure for which collaborative actions between and among the RCU and non-state actors across WCA states seem to construct a new political space. As asserted by Duffy (2013), ‘the complexity and transnationality of environmental issues leads to the call for a more and thorough engagement of non-state actors to develop effective frameworks of global governance’. The RCU, oriented towards traditional inter-governmental co-operation, can be seen to be pursuing transnational governance experiments (Bulkeley et al. 2012) with innovative ways in preventing shipping pollution beyond traditional inter-governmental co-operation. This transnational governance pursuit is potentially enabling for RCU’s efforts at influencing behavioural change of Parties.
Unlike private or private–public driven transnational governance arrangements established on the basis of market mechanisms (Bulkeley et al. 2012), the emergent transnational environmental governance for WCA ports is state-driven led by an international (regional) bureaucracy, but bypassing states at national level and dealing directly with non-state actors at sub- and supranational levels in a new space of political authority.
Overall, the discussion clearly underscores the relevance of a broadened analytical approach to understanding the influence of the RCU as a regional (international) bureaucracy towards the implementation of the obligations related to shipping pollution in the Abidjan Convention among Parties. Although influence cannot be directly measured, it seems clear that whereas the RCU’s influence through only its autonomy-centred efforts remain inadequate, traditional state-centric responsibility for implementation of negotiated measures through domestic regulatory-politics, that subsumes role for societal actors, obstructs its efforts and weakens its influence. A multi-centric analysis in which non-state actors alongside state actors engage in transnational steering largely independent of inter-governmental politics offers potential for harnessing RCU’s efforts and influence. It does suffice then to say that, with increasing role and relevance of non-state actors and the deepening institutionalisation of non-state actor approaches to global environmental governance beyond the state, particularly in climate change, the influence of international bureaucracies go beyond their internal organisation and also that of the states they work with, while transnational governance becomes an essential arena for additional focus.
7 Conclusions
This study has complemented perspectives of pathways of the influence of international bureaucracies with the potential role of domestic regulatory-politics and transnational governance to better understand the influence of international bureaucracies in the implementation of multilateral environmental agreements. The study expresses the linkage between internal organisational factors of international bureaucracies and external factors at the domestic level in determining the influence of international bureaucracies. Analysis from the study has particularly shown that a new conceptualisation of the influence of international bureaucracies is essential. First, it intertwines the influence of international bureaucracies to constraints of domestic politics and already exposes the inherent weaknesses of multilateral environmental agreements implementation. Second, it accounts for spheres of influence beyond the pre-eminent realm of states and the national level. It is interesting to note that this emergent regional (international) bureaucracy-led transnational arena of port environmental governance outside institutionalised governance arenas for WCA is unlike those mostly private-led ones, as in climate change, in the literature. In short, the study contributes to the literature on the influence of international bureaucracies and transnational approaches in international environmental governance. It remains to be seen how the emergent environmental governance approach can have influence. Nonetheless, change of perceptions, descriptions and normative understandings of port environmental problems are already evident among WCA ports. Besides, the approval of the SAPEIPP declaration by the Council of the Port Management Association for West and Central Africa indicates a trend towards the institutionalisation of regional port environmental governance beside state-led mechanisms for WCA.
Notes
Decisions CP.7/1; CP.7/2; CP.7/3.
Ports Environmental Network-Africa (PENAf) is a non-governmental organisation having interest in the environmental health of African ports.
Officially launched at COP10 of the Convention on Biological Diversity in Nagoya, Japan, in October 2010.
A joint programme between the GEF, UNPD and IMO to assist developing countries reduces transfer of harmful aquatic organisms in ships’ ballast water.
Partnership between IMO and IPIECA (the global oil and gas industry association for environmental and social issues).
The Ocean Data and Information Network for Africa project of the Inter-governmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO.
Decisions CP.7/1; CP.7/2; CP7/3.
Decision CP.8/8.
MOP.1/1/2008; MOP.1/2/2008; MOP.1/3/2008; MOP.1/4/2008.
Decision CP.9/6.
Decision CP.9/5.
Decision CP.9/4.
Considered vital for assessing existing levels and types of environmental and marine biological risks ports may be facing. It can be a useful tool for managing safety and environmental risks and gauging future impacts in ports.
The only environmental management standard especially designed for ports. The tools form a basic standardised port environmental management system as a first step for ports to organise environmental improvement.
Declaration, First Panel of Experts on the Strategic Assessment of Port Environmental Issues, Policies and Programmes in West, Central and Southern Africa, 5–7 May 2015, Abidjan, Ivory Coast.
Abbreviations
- EPA:
-
Environmental Protection Agency
- MinEFF:
-
Ministry of Environment, Water and Forests
- MinENP:
-
Ministry of Environment and Nature Protection
- NESREA:
-
National Environmental Standards, Regulations and Enforcement Agency
- NIMASA:
-
Nigeria Maritime Administration and Safety Agency
- NOSDRA:
-
National Oil Spill Detection and Response Agency
- OECD:
-
Organisation for Economic Development and Co-operation
- OSPAR:
-
Extension of the 1972 Oslo Convention against Dumping to cover Land-Based Sources of Marine Pollution and the Offshore Industry by the 1974 Paris Convention
- PENAf:
-
Ports Environmental Network-Africa
- PMAWCA:
-
Port Management Association for West and Central Africa
- RCU:
-
Regional Coordinating Unit
- SAPEIPP:
-
Strategic Assessment of Port Environmental Issues, Policies and Programmes
- UN:
-
United Nations
- UNEP:
-
United Nations Environment Programme
References
Abbott, K. W. (2012). The transnational regime complex for climate change. Environmental Planning C: Government and Policy, 30, 571–590.
Akonor, K. (2006). Africa and IMF conditionality: The unevenness of compliance, 1983–2000. London: Routledge.
Andonova, L., Betsill, M., & Bulkeley, H. (2009). Transnational climate governance. Global Environmental Politics, 9(2), 52–73.
Ayobayo, B. J. (2014). The Koko incident: Law of the sea and environmental protection. LL.M Dissertation, University of Lagos, Nigeria.
Barnett, M. N., & Finnemore, M. (1999). The politics, power, and pathologies of international organisations. International Organisation, 53(4), 699–732.
Bauer, S. (2009a). The Ozone Secretariat: The good shepherd of ozone politics. In F. Biermann & B. Siebenhüner (Eds.), Managers of global change (pp. 225–244). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Bauer, S. (2009b). The Desertification Secretariat: A castle made of sand. In F. Biermann & B. Siebenhüner (Eds.), Managers of global change (pp. 293–317). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Bauer, S., Anderson, S., & Biermann, F. (2012). International bureaucracies. In F. Biermann & P. Pattberg (Eds.), Global environmental governance reconsidered (pp. 27–44). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Bauer, S., Biermann, F., Dingwerth, K., & Siebenhüner, B. (2009). Understanding international bureaucracies: Taking stock. In F. Biermann & B. Siebenhüner (Eds.), Managers of global change (pp. 15–36). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Betsil, M., & Bulkeley, M. (2004). Transnational networks and global environmental governance: The cities for climate protection programme. International Quarterly Studies, 48(2), 471–493.
Biermann, F., & Pattberg, P. (2012). Global environmental governance revisited. In F. Biermann & P. Pattberg (Eds.), Global environmental governance reconsidered (pp. 1–23). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Biermann, F., & Siebenhüner, B. (2009). Managers of global change (pp. 1–14). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Biermann, F., & Siebenhüner, B. (2013). Problem solving by international bureaucracies: The influence of international secretariats on world politics. In B. Reinalda (Ed.), Routledge handbook of international organizations (pp. 149–161). London: Routledge.
Bulkeley, H., Hoffmann, M. J., VanDeveer, S. D., & Milledge, V. (2012). Transnational governance experiments. In F. Biermann & P. Pattberg (Eds.), Global environmental governance reconsidered (pp. 147–171). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Bulkeley, H., & Newell, P. (2010). Governing climate change. London: Routledge.
Chayes, A., & Chayes, A. H. (1993). On compliance. International Organisation, 47(2), 175–205.
Crook, R. C. (2003). Decentralisation and poverty reduction in Africa: The politics of local–central relations. Public Administration and Development, 23, 77–88.
Daly, J. (2012). Cameroon, West Africa’s latest oil battleground. www.oilprice.com Accessed October 18, 2016.
De Melo, J., & Tsikata, Y. (2015). Regional integration in Africa: Challenges and prospects. WIDER Working Paper, No. 2014/037.
Dellas, E., Pattberg, P., & Betsill, M. (2011). International Environmental Agreements, 11(1), 85–98.
Dessai, B. H. (2010). Multilateral environmental agreements: Legal status of the secretariats. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Duffy, R. (2013). Global environmental governance and north–south dynamics: The case of CITES. Environment and Planning C: Government and Policy, 31, 222–239.
Gray, K. R. (2003). Multilateral environmental agreements in Africa: Efforts and problems in implementation. International Environmental Agreements: Politics, Law and Economics, 3, 97–135.
Guinea Current Large Marine Ecosystem (GCLME). (2011). Report of third regional workshop and task force meeting on the ratification and implementation of the IMO convention on ballast water management. Lomé, Togo, 15–16 September 2011.
Hawkins, D. G., Lake, D. A., Nielson, D. L., & Tierney, M. J. (2006). Delegation under anarchy: States, international organisations, and principal-agent thoery. In D. G. Hawkins, D. A. Lake, D. L. Nielson, & M. J. Tierney (Eds.), Delegation and agency in international organisations (pp. 3–38). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Ibe, C., & Sherman, K. (2002). The Gulf of Guinea large marine ecosystem project: Turning challenges into achievements. In J. M. McGlade, P. Cury, K. A. Koranteng, & N. J. Hardman-Mountford (Eds.), The Gulf of Guinea large marine ecosystem (pp. 27–39). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science B.V.
Ikpeze, N. I., Soludo, C. C., & Elekwa, N. N. (2004). Nigeria: The political economy of policy process, policy choice and implementation. In C. C. Soludo, M. O. Ogbu, & H.-J. Chang (Eds.), The politics of trade and industrial policy in Africa: Forced consensus? (pp. 341–367). Trenton: Africa World Press.
Interim Guinea Current Commission (IGCC). (2009a). Regional Strategic Action Plan (SAP) to minimize transfer of harmful aquatic organisms and pathogens in ships’ ballast water and sediments. Abidjan, Ivory Coast: UNIDO/UNDP/UNEP/GEF/NOAA/NEPAD.
Interim Guinea Current Commission (IGCC). (2009b). Report of second regional workshop and task force meeting on the ratification and implementation of the IMO convention on ballast water management. Abidjan, Ivory Coast, 9–10 July 2009.
Kern, K., & Bulkeley, H. (2009). Cities, Europeanisation and multilevel governance: Governing climate change through transnational municipal networks. Journal of Common Market Studies, 47(2), 309–332.
King, A. (1976). Modes of executive-legislative relations: Great Britain, France, and Germany. Legislative Quarterly, 1(1), 21.
KPMG. (2014). Oil and gas in Africa: Reserves, potential and prospects of Africa. Amstelveen: KPMG Africa Limited.
Kuyper, J. W., & Bäckstrand, K. (2016). Accountability and representation: Non-state actors in UN climate diplomacy. Global Environmental Politics, 16(2), 61–81.
Leigh, D. (2009). Revealed: Trafigura–commissioned report into dumped toxic waste. London: The Guardian. https://theguardian.com/world/2009/oct/17/trafigura-minton-report-revealed. Accessed 15 May 2018.
Mundus Maris. (2013). Report of the regional coastal and marine forum (7th Edn.). Brussels, Belgium: Mundus Maris.
Mbendi. (2012). Oil and gas in Cote d’Ivoire: Overview. www.mbendi.com. Accessed October 25, 2016.
Miles, E. L., Underdal, Aril, Andresen, Steiner, Wetterstad, Jørgen, Skjærseth, J. B., & Carlin, E. M. (Eds.). (2001). Environmental regime effectiveness: Confronting theory with evidence. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Neustadt, R. (1990). Presidential power and the modern presidents. New York: Free Press.
Okereke, C., Bulkeley, H., & Schroeder, H. (2009). Conceptualizing climate governance beyond the international regime. Global Environmental Politics, 9(1), 58–78.
Ottaway, M. (2003). Democracy challenged: The rise of semi-authoritarianism. Washington D.C: Carnegie.
Pálsson, G., Harding, A., & Raballand, G. (2007). Port and maritime challenges in West and Central Africa. Sub-Saharan Africa Transport Policy Programme (SSATP) Working Paper No. 84.
Pattberg, P., Betsil, M., & Della, E. (Eds.) (2011). Agency in earth system governance. Special issue, International Environmental Agreements: Politics, Law and Economics, 11(1).
Pattberg, P., & Stripple, J. (2008). Beyond the public and private divide: remapping transnational climate governance in the 21st century. International Environmental Agreements: Politics, Law and Economics, 8, 367–388.
Peart, R., Rich, J., & Masia, M. (1999). Sub-Saharan Africa multilateral programmes for coastal management: How well have they performed? Ocean and Coastal Management, 42, 791–813.
Pollack, M. A. (1997). Delegation, agency, and agenda setting in the European community. International Organisation, 51(1), 99–134.
Raustiala, K. (1997). Domestic institutions and international cooperation: Comparative responses to the convention on biological diversity. World Politics, 49(4), 482–509.
Tatenhove, J., & Leroy, P. (2003). Environment and participation in a context of political modernisation. Environmental Values, 12, 155–174.
UNEP. (1981). Article of the convention for cooperation in the protection and development of the marine and coastal environment of the West and Central African region (Abidjan convention). New York: United Nations.
UNEP. (2005a). Report of a comprehensive review of the Abidjan convention. Nairobi: UNEP.
UNEP. (2005b). Report of seventh meeting of the contracting parties to the convention for the cooperation in the protection and development of the marine and coastal environment of West and Central Africa region. UNEP(DEC)/WAF/CP.7/8. Libreville, Gabon, 22–23 March 2005.
UNEP. (2008). Report of eight meeting of the contracting parties to the convention on co-operation for the protection and development of the marine environment and coastal areas of the Atlantic coast of the West, Central and Southern Africa region. UNEP(DEPI)/WAF/CP.8/10. Johannesburg, South Africa, 5–8 November 2007.
UNEP. (2009). Report of the first extraordinary meeting of the contracting parties to the Abidjan convention. UNEP(DEPI)/WAF/SS.1/2. Johannesburg, South Africa, 9–10 June 2008.
UNEP. (2011a). Regional oil spill contingency plan for West and Central Africa. Accra: UNEP.
UNEP. (2011b). Report of ninth meeting of the contracting parties to the convention for the cooperation in the protection and development of the marine and coastal environment of West and Central Africa region. UNEP(DEPI)/WACAF/COP.9/10. Accra, Ghana, 28 March–1 April 2011.
UNEP. (2012a). Report of tenth meeting of the contracting parties to the convention on co-operation for the protection and development of the marine environment and coastal areas of the Atlantic coast of the West, Central and Southern Africa region. UNEP[DEPI]/WACAF/COP.10/12. Pointe Noire, Republic of Congo, 12–16 November 2012.
UNEP. (2012b). Memorandum of understanding between Abidjan convention secretariat and PENAf. UNEP/MOU/DEPI/2012/FMEB-Abidjan Convention/003.
UNEP. (2015). Declaration of intent, first panel of experts meeting on strategic assessment of port environmental issues, policies and programmes (SAPEIPP) in West, Central and Southern Africa, 5–7 May 2015, Abidjan, Ivory Coast. Abidjan: UNEP.
Van Wingerde, K. (2015). The limits of environmental regulation in a globalised economy. In J. Van Erp, W. Huisman, & G. Vande Walle (Eds.), The routledge handbook of white-collar and corporate crime in Europe. London/New York: Routledge.
Widerberg, Oscar, & van Laerhoven, Frank. (2014). Measuring the autonomous influence of an international bureaucracy: The division for sustainable development. International Environmental Agreements, 14, 303–327.
Young, O. R. (1982). Resource regime rights: Natural resources and social institutions. Berkeley: University of California Press.
Young, O. R. (1994). International environmental governance. Protecting the environment in a stateless society. Ithaca: Cornell University Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Barnes-Dabban, H., Karlsson-Vinkhuyzen, S. The influence of the Regional Coordinating Unit of the Abidjan Convention: implementing multilateral environmental agreements to prevent shipping pollution in West and Central Africa. Int Environ Agreements 18, 469–489 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10784-018-9399-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10784-018-9399-8