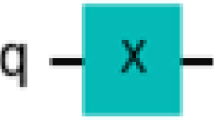
Abstract
Privacy-preserving geometric intersection (PGI) is an important issue in Secure multiparty computation (SMC). The existing quantum PGI protocols are mainly based on grid coding, which requires a lot of computational complexity. The phase-encoded query method which has been used in some Quantum SMC protocols is suitable to solve the decision problem, but it needs to apply high dimensional Oracle operators. In this paper, we use the principle of phase-encoded query to solve an important PGI problem, namely privacy-preserving two-party circle intersection. We study the implementation of Oracle operator in detail, and achieve polynomial computational complexity by decompsing it into quantum arithmetic operations. Performance analysis shows that our protocol is correct and efficient, and can protect the privacy of all participants against internal and external attacks.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availibility Statement
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Yao, A.C.: Protocols for secure computations. In: Proceeding of 23rd IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 160–164. IEEE, Piscataway (1982). https://doi.org/10.1109/SFCS.1982.38
Shi, R.H., Mu, Y., Zhong, H., Zhang, S.: Quantum oblivious set-member decision protocol. Physical Review A 92(2), 022309 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.92.022309
Ji, Z.X., Zhang, H.G., Wang, H.Z., Wu, F.S., Jia, J.W., Wu, W.Q.: Quantum protocols for secure multi-party summation. Quantum Information Processing 18(6), 168 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-2141-1
Liu, W.J., Li, C.T., Zheng, Y., Xu, Y., Xu, Y.S.: Quantum privacy-preserving price e-negotiation. International Journal of Theoretical Physics 58(10), 3259–3270 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04201-9
Shi, R.H., Liu, B., W., Z.M.: Secure two-party integer comparison protocol without any third party. Quantum Information Processing 20(12), 402 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03344-1
Liu, W.J., Li, W.B., Wang, H.B.: An improved quantum private set intersection protocol based on hadamard gates. International Journal of Theoretical Physics 61(3), 53 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-022-05048-3
Ye, T.Y., Xu, T.J., Geng, M.J., Chen, Y.: Two-party secure semiquantum summation against the collective-dephasing noise. Quantum Information Processing 21(3), 118 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03459-z
Atallah, M.J., Du, W.: Secure multi-party computational geometry. In: Dehne, F., Sack, J.-R., Tamassia, R. (eds.) Algorithms and Data Structures, pp. 165–179. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44634-6_16
Huang, H., Gong, T., Chen, P., Malekian, R., Chen, T.: Secure two-party distance computation protocol based on privacy homomorphism and scalar product in wireless sensor networks. Tsinghua Science and Technology 21(4), 385–396 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TST.2016.7536716
Chen, B.R., Yang, W., Huang, L.S.: Cryptanalysis and improvement of the novel quantum scheme for secure two-party distance computation. Quantum Information Processing 18(1), 35 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-2148-7
Liu, W.J., Xu, Y., Yang, J.C.N., Yu, W.B., Chi, L.H.: Privacy-preserving quantum two-party geometric intersection. Computers, Materials & Continua 60(3), 1237–1250 (2019). https://doi.org/10.32604/cmc.2019.03551
Shi, R.H., Mu, Y., Zhong, H., Cui, J., Zhang, S.: Privacy-preserving point-inclusion protocol for an arbitrary area based on phase-encoded quantum private query. Quantum Information Processing 16(1), 8 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-016-1476-8
Peng, Z.W., Shi, R.H., Zhong, H., Cui, J., Zhang, S.: A novel quantum scheme for secure two-party distance computation. Quantum Information Processing 16(12), 316 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1766-9
Peng, Z.W., Shi, R.H., Wang, P.H., Zhang, S.: A novel quantum solution to secure two-party distance computation. Quantum Information Processing 17(6), 145 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-018-1911-0
Cao, Y.H.: Quantum secure two-party euclidean distance computation based on mutually unbiased bases. Quantum Information Processing 21(7), 262 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03611-9
He, L.B., Huang, L.S., Yang, W., Xu, R.: A protocol for the secure two-party quantum scalar product. Physics Letters A 376(16), 1323–1327 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2012.02.048
Shi, R.H., Zhang, M.W.: Strong privacy-preserving two-party scalar product quantum protocol. International Journal of Theoretical Physics 58(12), 4249–4257 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04296-0
Li, S.D., Wu, C.Y., Wang, D.S., Dai, Y.Q.: Secure multiparty computation of solid geometric problems and their applications. Information Sciences 282, 401–413 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.04.004
Zhu, H., Wang, F., Lu, R., Liu, F., Fu, G., Li, H.: Efficient and privacy-preserving proximity detection schemes for social applications. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 5(4), 2947–2957 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2017.2766701
Olejnik, L.: Secure quantum private information retrieval using phase-encoded queries. Physical Review A 84(2), 022313 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.84.022313
Grover, L.K.: Quantum mechanics helps in serching for a needle in a haystack. Physical Review Letters 79(2), 325–328 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.79.325
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. Siam Journal on Computing 26(5), 1484–1509 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1137/S0097539795293172
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information: 10th Anniversary Edition. Cambridge University Press, New York (2010). https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511976667
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62071240), the Innovation Program for Quantum Science and Technology (2021ZD0302900), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This paper does not rely on clinical trials.
Human and animal participants
All researchs included in the submitted manuscript do not involve human participants and/or animal experimentation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, ZX., Yang, Q., Feng, B. et al. Quantum Privacy-preserving Two-party Circle Intersection Protocol Based on Phase-encoded Query. Int J Theor Phys 62, 138 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-023-05382-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-023-05382-0